Ms. Robyn Klemptner
... Bind PRR at cell membrane. Signal transduction. WRKYs. MAMP/PAMP-triggered immunity (M/PTI). Effectors Against specific host. Suppress M/PTI. Effector-triggered immunity (ETI). Recognized by intracellular receptors. ROS, HR, SAR. ...
... Bind PRR at cell membrane. Signal transduction. WRKYs. MAMP/PAMP-triggered immunity (M/PTI). Effectors Against specific host. Suppress M/PTI. Effector-triggered immunity (ETI). Recognized by intracellular receptors. ROS, HR, SAR. ...
CHAPTER 3 ESSENTIALS OF METABOLISM
... • As electrons move from one molecule to another in the chain, energy is released via a process called chemiosmosis. • As electrons are transferred along the electron transport chain, protons are pumped out of the cell. • This causes the proton concentration outside the cell to be higher than inside ...
... • As electrons move from one molecule to another in the chain, energy is released via a process called chemiosmosis. • As electrons are transferred along the electron transport chain, protons are pumped out of the cell. • This causes the proton concentration outside the cell to be higher than inside ...
Evolution
... b. OUT Oxygen as a result of water splitting Where does the dark reaction (Calvin cycle) occur? a. In the stroma of the thylakoid (open space) What goes into dark reactions? What comes out? a. IN CO2 b. OUT glucose Which pigment is directly involved with photosynthesis? (The primary pigment) a ...
... b. OUT Oxygen as a result of water splitting Where does the dark reaction (Calvin cycle) occur? a. In the stroma of the thylakoid (open space) What goes into dark reactions? What comes out? a. IN CO2 b. OUT glucose Which pigment is directly involved with photosynthesis? (The primary pigment) a ...
Pentose phosphate pathway = PPP Pentose phosphate cycle
... ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP are energy donating compound in coupled reaction, they have regulatory role in enzyme reaction, transporters cAMP, cGMP are second messengers during signal transduction of neurotransmitters, hormons, paracrin hormons nucleic acids: RNA, DNA are synthesized from them for the synthe ...
... ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP are energy donating compound in coupled reaction, they have regulatory role in enzyme reaction, transporters cAMP, cGMP are second messengers during signal transduction of neurotransmitters, hormons, paracrin hormons nucleic acids: RNA, DNA are synthesized from them for the synthe ...
1.3.7 Metabolic Role of Biomolecules
... Respiration – energy is released when glucose is broken down to form carbon dioxide and water – catabolism Photosynthesis – glucose molecules are made from carbon dioxide and water using the sun’s energy – anabolism ...
... Respiration – energy is released when glucose is broken down to form carbon dioxide and water – catabolism Photosynthesis – glucose molecules are made from carbon dioxide and water using the sun’s energy – anabolism ...
Cell Biology
... Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions (2 points each) 1. You attempt to study a particular cell-signaling pathway of C. elegans. However, though the signal continues to be transducted, a response fails to take place. Which of the following amino acids is the most likely to have been affected? A. Ty ...
... Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions (2 points each) 1. You attempt to study a particular cell-signaling pathway of C. elegans. However, though the signal continues to be transducted, a response fails to take place. Which of the following amino acids is the most likely to have been affected? A. Ty ...
Non-Living Inclusions
... hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, with formula R—CH (NH2)—COOH, where R is a variable grouping of atoms, an amino group always being attached to the carbon atom next to the carboxyl group. 3. Fats and Fatty Oils: y The fats and fatty oils in plants are composed of glycerine and organic acids. They occ ...
... hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, with formula R—CH (NH2)—COOH, where R is a variable grouping of atoms, an amino group always being attached to the carbon atom next to the carboxyl group. 3. Fats and Fatty Oils: y The fats and fatty oils in plants are composed of glycerine and organic acids. They occ ...
Where in the cell is your protein most likely found?
... Markov Models (TMHMM) • A Hidden Markov Model is a probabilistic model developed from observed sequences of proteins of a known function. • TMHMM is a tool used to predict the presence of transmembrane helices in proteins. The results will indicate the segments of the protein that lie inside, outs ...
... Markov Models (TMHMM) • A Hidden Markov Model is a probabilistic model developed from observed sequences of proteins of a known function. • TMHMM is a tool used to predict the presence of transmembrane helices in proteins. The results will indicate the segments of the protein that lie inside, outs ...
Immunoglobulln E Plus Antigen Challenge Induces
... our gene seems to be narrow. This is in contrast to most other members of this chemokine superfamily which are broadly expressed after a variety of stimuli. Even if it seems very unlikely that a cell line in the process of its establishment has gained a function in terms of a novel signal transducti ...
... our gene seems to be narrow. This is in contrast to most other members of this chemokine superfamily which are broadly expressed after a variety of stimuli. Even if it seems very unlikely that a cell line in the process of its establishment has gained a function in terms of a novel signal transducti ...
Biogenenet: Learning Biological Gene and Protein Networks from
... Gene regulatory network: two genes are connected if the expression of one gene modulates expression of another one by either activation or inhibition Protein interaction network: proteins that are connected in physical interactions or metabolic and signaling pathways of the cell; Metabolic net ...
... Gene regulatory network: two genes are connected if the expression of one gene modulates expression of another one by either activation or inhibition Protein interaction network: proteins that are connected in physical interactions or metabolic and signaling pathways of the cell; Metabolic net ...
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
... • The INK4 locus at 9p21, gives rise to multiple proteins after differential splicing. • These proteins are involved cell cycle control through Rb and P53 growth suppressors. ...
... • The INK4 locus at 9p21, gives rise to multiple proteins after differential splicing. • These proteins are involved cell cycle control through Rb and P53 growth suppressors. ...
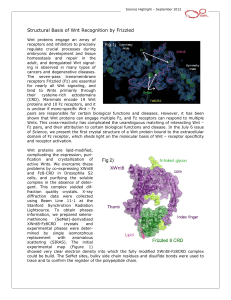
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
Poster
... Signal transduction is an essential process in cells. One critical signaling molecule, protein kinase A (PKA), phosphorylates target proteins, thereby changing their conformations and modifying their functions. PKA is a component of multiple signaling pathways that regulate a variety of proteins. Si ...
... Signal transduction is an essential process in cells. One critical signaling molecule, protein kinase A (PKA), phosphorylates target proteins, thereby changing their conformations and modifying their functions. PKA is a component of multiple signaling pathways that regulate a variety of proteins. Si ...
Slide 1
... Because water soluble molecules, and especially the charged ones such as the electrolytes, have a very hard time crossing the lipid bi-layer, membranes allow the environment outside of a cell to be very different from the inside and many different specific trans-membrane transport proteins need to ...
... Because water soluble molecules, and especially the charged ones such as the electrolytes, have a very hard time crossing the lipid bi-layer, membranes allow the environment outside of a cell to be very different from the inside and many different specific trans-membrane transport proteins need to ...
A Quantitative Cell-Based High
... Involved in the regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells. Many different stimuli, including growth factors, cytokines, virus infection, ligands for heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide– binding protein (G protein)–coupled receptors, transforming agents, and carc ...
... Involved in the regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells. Many different stimuli, including growth factors, cytokines, virus infection, ligands for heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide– binding protein (G protein)–coupled receptors, transforming agents, and carc ...
Supporting information
... cell samples in the 4 different nutrient conditions. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle (G1, S or G2) was calculated for control and treated samples in 4 different media conditions: A) 5 mM glucose, B) 1 mM glucose, C) 1 mM glucose without glutamine and D) 1mM glucose without gl ...
... cell samples in the 4 different nutrient conditions. The percentage of cells in each phase of the cell cycle (G1, S or G2) was calculated for control and treated samples in 4 different media conditions: A) 5 mM glucose, B) 1 mM glucose, C) 1 mM glucose without glutamine and D) 1mM glucose without gl ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Lectures For UG-5
... (from carbon 1 of glucose), and a second molecule of NADPH (Figure 13.2). ...
... (from carbon 1 of glucose), and a second molecule of NADPH (Figure 13.2). ...
2005 Images SC 1 to 4 - Cancer Insights at ASU
... Mitochondria in Health & Disease • Mitochondria have about 1600 imported gene • products ppppppp - about half have specialized functions and are organ-specific - functions include lipid metabolism, signal transduction • Clinical expression of mitochondrial disease requires a high level of mutations ...
... Mitochondria in Health & Disease • Mitochondria have about 1600 imported gene • products ppppppp - about half have specialized functions and are organ-specific - functions include lipid metabolism, signal transduction • Clinical expression of mitochondrial disease requires a high level of mutations ...
The 14-3-3 proteins in regulation of cellular metabolism - BORA
... and appears to be the most specialized of the mammalian isoforms, which may explain why it preferentially forms homodimers. This brings up a second unresolved issue of 14-3-3 function – homodimers versus heterodimers, and the severe effects of 14-3-3 disruption might be related to its ability to fo ...
... and appears to be the most specialized of the mammalian isoforms, which may explain why it preferentially forms homodimers. This brings up a second unresolved issue of 14-3-3 function – homodimers versus heterodimers, and the severe effects of 14-3-3 disruption might be related to its ability to fo ...
Stem Cells and cell division
... normal cells – called contact inhibition. • Normal cells receive signals form the external environment and do not divide unless they get a signal to send them from G0 into the G1 phase – such molecules are called growth factors. • The 1st messenger are cytokines – bind to specific receptors ...
... normal cells – called contact inhibition. • Normal cells receive signals form the external environment and do not divide unless they get a signal to send them from G0 into the G1 phase – such molecules are called growth factors. • The 1st messenger are cytokines – bind to specific receptors ...
CELL
... d) An organism as a whole can be understood through the collective activities & interactions of its cells. ...
... d) An organism as a whole can be understood through the collective activities & interactions of its cells. ...
Protein Targeting
... the protein into the lipid bilayer • For secretory/water-soluble proteins, targeting leads to translocation of the entire protein across the membrane into the aqueous interior of the organelle. • Protein destined for cytosol simply remain where they are synthesized • Mitochondrial and chloroplast pr ...
... the protein into the lipid bilayer • For secretory/water-soluble proteins, targeting leads to translocation of the entire protein across the membrane into the aqueous interior of the organelle. • Protein destined for cytosol simply remain where they are synthesized • Mitochondrial and chloroplast pr ...