NIH Public Access - The Scripps Research Institute
... (PCPs), which are ~75 amino acid long domains (predicted bioinformatically) or ~80–95 amino acid long proteins that are posttranslationally modified with a 4′-phosphopantetheinyl (ppant) group from coenzyme A by phosphopantetheinyl transferases (PPTase), also known as holo-ACP or holo-PCP synthases. ...
... (PCPs), which are ~75 amino acid long domains (predicted bioinformatically) or ~80–95 amino acid long proteins that are posttranslationally modified with a 4′-phosphopantetheinyl (ppant) group from coenzyme A by phosphopantetheinyl transferases (PPTase), also known as holo-ACP or holo-PCP synthases. ...
Role of the ubiquitinselective CDC48UFD1/NPL4 chaperone
... grown in YPGal to an OD600 of 0.5 at 23°C and shifted for another 2 h to 37°C. The experiment was started by adding glucose and cycloheximide to the medium. At each time point indicated, the cellular level of both epitope-tagged OLE1 variants was analyzed by anti-myc immunoblots (upper panel). As a ...
... grown in YPGal to an OD600 of 0.5 at 23°C and shifted for another 2 h to 37°C. The experiment was started by adding glucose and cycloheximide to the medium. At each time point indicated, the cellular level of both epitope-tagged OLE1 variants was analyzed by anti-myc immunoblots (upper panel). As a ...
BIOCHEMISTRY I (CHMI 2227 E) PROBLEMS and
... chromatography on DEAE-cellulose must have a pH greater than 6 but less than 9 in order to ensure the enzyme is efficiently bound to the column. 3.4. Protein Purification. Would the enzyme, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase bind to a CM-cellulose resin if the same conditions as the previous problem w ...
... chromatography on DEAE-cellulose must have a pH greater than 6 but less than 9 in order to ensure the enzyme is efficiently bound to the column. 3.4. Protein Purification. Would the enzyme, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase bind to a CM-cellulose resin if the same conditions as the previous problem w ...
Longins and their longin domains: regulated SNAREs and
... Sec22 and Ykt6 The proteome of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains five R-SNAREs: its two ‘brevins’ [7,8] (Snc1 and Snc2) function in trafficking to the cell surface, both within the endosomal system and between endosomes and the Golgi [50]; Nyv1 is the largest of the five R-SNAREs and the least ...
... Sec22 and Ykt6 The proteome of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains five R-SNAREs: its two ‘brevins’ [7,8] (Snc1 and Snc2) function in trafficking to the cell surface, both within the endosomal system and between endosomes and the Golgi [50]; Nyv1 is the largest of the five R-SNAREs and the least ...
Although the administration of testosterone clearly causes marked
... 0° C (12), a 100-fold excess of nonradioactive amino acid was added in order to prevent further incorporation of Cl'amino acid. ...
... 0° C (12), a 100-fold excess of nonradioactive amino acid was added in order to prevent further incorporation of Cl'amino acid. ...
How will Hemoglobin Affect the Winner of this Year`s Super Bowl
... acid has a certain chemical character in relation to water molecules. Some amino acids love being around water (Hydrophilic), some hate water and hide from it (Hydrophobic), and for some, it doesn’t matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional ...
... acid has a certain chemical character in relation to water molecules. Some amino acids love being around water (Hydrophilic), some hate water and hide from it (Hydrophobic), and for some, it doesn’t matter as much. Proteins do not exist as a string of amino acids, but must fold into a 3 dimensional ...
medical management: portosystemic vascular anomalies (psva)
... creatinine (reflecting muscle mass) and ammonium biurate crystalluria. Initial assessments are done at 7 to 10 day intervals. If all goes well (HE controlled, maintained weight, no ammonium biurates) additional protein supplements may be explored. This is done using 0.3 gm/protein/kg BWt additional ...
... creatinine (reflecting muscle mass) and ammonium biurate crystalluria. Initial assessments are done at 7 to 10 day intervals. If all goes well (HE controlled, maintained weight, no ammonium biurates) additional protein supplements may be explored. This is done using 0.3 gm/protein/kg BWt additional ...
Bioinformatics of proteins: Sequence, structure and the `symbiosis
... There are two components to Pfam: • Pfam-A entries are high quality, manually curated families. these Pfam-A entries cover a large proportion of the sequences in the sequence database. • Pfam-B- automatically generated entries. Although of lower quality, Pfam-B families can be useful for identifying ...
... There are two components to Pfam: • Pfam-A entries are high quality, manually curated families. these Pfam-A entries cover a large proportion of the sequences in the sequence database. • Pfam-B- automatically generated entries. Although of lower quality, Pfam-B families can be useful for identifying ...
Intrinsically Disordered Domains of the B Cell Receptor
... A long-standing belief has been that the functional properties of proteins depend upon their three-dimensional structure, the so-called structurefunction paradigm [9]. The primary origin for this paradigm was the "lockand-key" model (Emil Fischer 1894), which suggested a strict geometric complementa ...
... A long-standing belief has been that the functional properties of proteins depend upon their three-dimensional structure, the so-called structurefunction paradigm [9]. The primary origin for this paradigm was the "lockand-key" model (Emil Fischer 1894), which suggested a strict geometric complementa ...
Gel-based proteomics • Electrophoresis • One dimensional
... • Native molecular weight • Post-translational modification ...
... • Native molecular weight • Post-translational modification ...
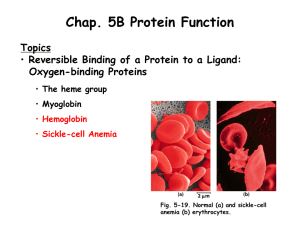
Chapter 5B Lecture
... Although much is known about the structures of the T and R states of Hb, the mechanism by which this structural transition occurs on sequential ligand binding still is unsolved. Two principle models for cooperative binding of O2 to Hb (and ligand binding to any allosteric protein) are widely used to ...
... Although much is known about the structures of the T and R states of Hb, the mechanism by which this structural transition occurs on sequential ligand binding still is unsolved. Two principle models for cooperative binding of O2 to Hb (and ligand binding to any allosteric protein) are widely used to ...
Health relevance of intestinal protein fermentation in young
... formation likely reducing accessibility of susceptible sites to proteases (Carbonaro et al., 1993, 1997). On the other hand, the presence of random coil or unordered secondary structures in animal food proteins has been related to the increment in digestibility. Differences in protein digestibility ...
... formation likely reducing accessibility of susceptible sites to proteases (Carbonaro et al., 1993, 1997). On the other hand, the presence of random coil or unordered secondary structures in animal food proteins has been related to the increment in digestibility. Differences in protein digestibility ...
Introduction
... Detection and Quantification • Models for prediction and interpretation • often not well justified ...
... Detection and Quantification • Models for prediction and interpretation • often not well justified ...
Conservation and relative importance of residues across protein
... rim or the rest of the protein surface. With the division into core and rim residues one can ask the question of whether as two groups these residues have different contributions to binding energy, and consequently have different evolutionary pressure for their conservation. The degree of conservati ...
... rim or the rest of the protein surface. With the division into core and rim residues one can ask the question of whether as two groups these residues have different contributions to binding energy, and consequently have different evolutionary pressure for their conservation. The degree of conservati ...
Divalent Metal Ions in Plant Mitochondria and Their Role in
... 40% decrease in Cu content (Table II). This loss of Cu could be traced to both the soluble and integral membrane protein fractions (Table II), which implies damage to mitochondrial soluble cuproproteins and also to cuprocomponents of the membrane-bound ETC. A 40% to 50% reduction of Fe and Mn conten ...
... 40% decrease in Cu content (Table II). This loss of Cu could be traced to both the soluble and integral membrane protein fractions (Table II), which implies damage to mitochondrial soluble cuproproteins and also to cuprocomponents of the membrane-bound ETC. A 40% to 50% reduction of Fe and Mn conten ...
Protein
... amino acids. The body needs 20 different amino acids to choose from when building these sequences. Nine of these amino acids are called essential amino acids because your body cannot make them and must get them in the diet. Your body can manufacture the remaining 11, called nonessential amino acids, ...
... amino acids. The body needs 20 different amino acids to choose from when building these sequences. Nine of these amino acids are called essential amino acids because your body cannot make them and must get them in the diet. Your body can manufacture the remaining 11, called nonessential amino acids, ...
The ACT Domain: A Small Molecule Binding Domain
... domains. As will be seen later in this review, recently determined structures demonstrate that the ACT domain shows an increasing diversity in tertiary and quaternary architecture as well as ligand binding interactions. A novel type of ACT domain-containing protein family whose members contain ACT d ...
... domains. As will be seen later in this review, recently determined structures demonstrate that the ACT domain shows an increasing diversity in tertiary and quaternary architecture as well as ligand binding interactions. A novel type of ACT domain-containing protein family whose members contain ACT d ...
Pharmacophore screening of the Protein Data Bank for specific
... required residue types, but also the relative geometry. The number of unique sites selected using various radius (Qm/n) and direction (Qv) b-factors is shown in Fig. 3 (results from the individual pharmacophore queries were merged and redundant hits were clustered). Ultimately, the objective is not ...
... required residue types, but also the relative geometry. The number of unique sites selected using various radius (Qm/n) and direction (Qv) b-factors is shown in Fig. 3 (results from the individual pharmacophore queries were merged and redundant hits were clustered). Ultimately, the objective is not ...
Relationship between Protein Synthesis and Secretion in Liver Cells
... Sodium pyruvate, phosphoenolpyruvate (potassium salt), IX-oxoglutaric acid, ADP (disodium salt), AMP (disodium salt), P-NADH (disodium salt), P-NADP (disodium salt), hexokinase from yeast (EC 2.7.1.1), myokinase from rabbit muscle (EC 2.7.4.3), pyruvate kinase from rabbit muscle (EC 2.7.1.40), gluco ...
... Sodium pyruvate, phosphoenolpyruvate (potassium salt), IX-oxoglutaric acid, ADP (disodium salt), AMP (disodium salt), P-NADH (disodium salt), P-NADP (disodium salt), hexokinase from yeast (EC 2.7.1.1), myokinase from rabbit muscle (EC 2.7.4.3), pyruvate kinase from rabbit muscle (EC 2.7.1.40), gluco ...
ADVANTAGES OF PORCINE BLOOD PLASMA AS A COMPONENT
... and photographed using a TCP-20M UV transilluminator (VilberLourmat, the United States) at a wavelength of 312 nm. A gel documenting system (Vitran-Photo) was used to save and process the data. An automatic amino acid analyzer Aracus PMA GmbH conforming to the EU Directives 98/64 and 2000/45 was use ...
... and photographed using a TCP-20M UV transilluminator (VilberLourmat, the United States) at a wavelength of 312 nm. A gel documenting system (Vitran-Photo) was used to save and process the data. An automatic amino acid analyzer Aracus PMA GmbH conforming to the EU Directives 98/64 and 2000/45 was use ...
Folie 1 - FLI
... Structural genomics consists in the determination of the three dimensional structure of all proteins of a given organism, by experimental methods such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy or computational approaches such as homology modelling. As opposed to traditional structural biology, the ...
... Structural genomics consists in the determination of the three dimensional structure of all proteins of a given organism, by experimental methods such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy or computational approaches such as homology modelling. As opposed to traditional structural biology, the ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... retarded while the larger proteins do not enter the pores and thus are eluted faster. ...
... retarded while the larger proteins do not enter the pores and thus are eluted faster. ...
The mapping of linear B-cell epitope regions in desmoglein 1 and 3
... proteins can be an alternative way to identify epitope regions because of the sufficient similarity to the native antigen which allows the binding of antibodies. This is a rapid, practical, and cost-effective method for linear epitope region identification [20, 21]. B-cell epitope mapping using a se ...
... proteins can be an alternative way to identify epitope regions because of the sufficient similarity to the native antigen which allows the binding of antibodies. This is a rapid, practical, and cost-effective method for linear epitope region identification [20, 21]. B-cell epitope mapping using a se ...
Protein purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the characterization of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.The methods used in protein purification can roughly be divided into analytical and preparative methods. The distinction is not exact, but the deciding factor is the amount of protein that can practically be purified with that method. Analytical methods aim to detect and identify a protein in a mixture, whereas preparative methods aim to produce large quantities of the protein for other purposes, such as structural biology or industrial use. In general, the preparative methods can be used in analytical applications, but not the other way around.