absorbing X-ray photons
... pass through most stuff. X-rays also pass through most things, but for the opposite reason: They have too much energy. They can, however, knock an electron away from an atom altogether. Some of the energy from the X-ray photon works to separate the electron from the atom, and the rest sends the el ...
... pass through most stuff. X-rays also pass through most things, but for the opposite reason: They have too much energy. They can, however, knock an electron away from an atom altogether. Some of the energy from the X-ray photon works to separate the electron from the atom, and the rest sends the el ...
CT Imaging
... • It is also the time constant for the first component of exponential decay of that output after the input is turned off. Clinical Significance: • Primary speed is critical to maintaining high resolution during sub-second scanning. It must be fast enough to prevent blurring especially at the perimet ...
... • It is also the time constant for the first component of exponential decay of that output after the input is turned off. Clinical Significance: • Primary speed is critical to maintaining high resolution during sub-second scanning. It must be fast enough to prevent blurring especially at the perimet ...
03 Fluoroscopy Dosimetry KAP CM
... • Upper GI series, Barium Swallow • Lower GI series Barium Enema ...
... • Upper GI series, Barium Swallow • Lower GI series Barium Enema ...
03 Fluoroscopy Dosimetry KAP CM
... • Upper GI series, Barium Swallow • Lower GI series Barium Enema ...
... • Upper GI series, Barium Swallow • Lower GI series Barium Enema ...
Motor unit and Electromyogram (EMG )
... images of the structures inside a body. This technology has led to a detailed study of the function and problems pertaining to the human body. In CT, an x-ray source and x-ray detectors, enclosed in a doughnut-shaped assembly, move in a circular path. In general, multidetectors are used as they allo ...
... images of the structures inside a body. This technology has led to a detailed study of the function and problems pertaining to the human body. In CT, an x-ray source and x-ray detectors, enclosed in a doughnut-shaped assembly, move in a circular path. In general, multidetectors are used as they allo ...
Siemens AXIOM Vertix Solitaire M The AXIOM Vertix Solitaire M is a
... wheelchair, and bedside exposures. Siemens Flat Detector delivers superb detail resolution and is conveniently stored next to the tube housing for easy access. The Flat Detector is flexible, so it can be placed anywhere without having to reposition the patient. This allows all around access to patie ...
... wheelchair, and bedside exposures. Siemens Flat Detector delivers superb detail resolution and is conveniently stored next to the tube housing for easy access. The Flat Detector is flexible, so it can be placed anywhere without having to reposition the patient. This allows all around access to patie ...
COURSE SYLLABUS Instructor Information
... Students will be allowed to make up tests; however, 10 points will be deducted for each class day a student fails to schedule and complete the examination. It is the student’s responsibility to schedule the retake with regards to the instructor’s schedule. Expectations for Engagement – Face to Face ...
... Students will be allowed to make up tests; however, 10 points will be deducted for each class day a student fails to schedule and complete the examination. It is the student’s responsibility to schedule the retake with regards to the instructor’s schedule. Expectations for Engagement – Face to Face ...
Chapter 11
... vacancy and soon pulls another electron into the orbit to fill it. Each time an electron falls into an orbit, energy is lost and is emitted in the form of electromagnetic radiation (characteristic radiation) and it does not make it out of the patient to expose the film. ...
... vacancy and soon pulls another electron into the orbit to fill it. Each time an electron falls into an orbit, energy is lost and is emitted in the form of electromagnetic radiation (characteristic radiation) and it does not make it out of the patient to expose the film. ...
Energy selective computed tomography: a potential revolution for
... precisely which regions should receive large doses and to locate the radiosensitive tissues that would be damaged by too large a dose. However the delivery of radiotherapy depends in an even more critical way on CT imaging, since the preparation of treatment plans relies entirely on certain physical ...
... precisely which regions should receive large doses and to locate the radiosensitive tissues that would be damaged by too large a dose. However the delivery of radiotherapy depends in an even more critical way on CT imaging, since the preparation of treatment plans relies entirely on certain physical ...
CT-Generations
... • Later versions: procedures = series of scans – procedure time reduced some what by using two detectors so that two parallel sections were acquired in one scan • Contrast resolution of internal structures was ...
... • Later versions: procedures = series of scans – procedure time reduced some what by using two detectors so that two parallel sections were acquired in one scan • Contrast resolution of internal structures was ...
Presentation Here
... There’s no way to tell exactly what questions you’ll be asked, but if you have a good working knowledge of radiographic equipment, you can FIGURE OUT 90% of the questions they ask. ...
... There’s no way to tell exactly what questions you’ll be asked, but if you have a good working knowledge of radiographic equipment, you can FIGURE OUT 90% of the questions they ask. ...
MEGN 536 * Computational Biomechanics
... 1975-1977: Richard Ernst and Peter Mansfifield develop MR imaging An object is exposed to a spatially varying magnetic field, causing certain atomic nuclei to spin at their resonant frequencies An electromagnetic signal is generated and varies with spatial position and tissue type Hydrogen i ...
... 1975-1977: Richard Ernst and Peter Mansfifield develop MR imaging An object is exposed to a spatially varying magnetic field, causing certain atomic nuclei to spin at their resonant frequencies An electromagnetic signal is generated and varies with spatial position and tissue type Hydrogen i ...
scientific opportunities with an ultrabright
... X-ray-L: proximity lithography @ hν~ 1.2 keV EUV-L: projection lithography @ hν~ 90 eV EPL: Electron Projection Lithography @ e--beam IONS-L: projection lithography @ ions-beam ...
... X-ray-L: proximity lithography @ hν~ 1.2 keV EUV-L: projection lithography @ hν~ 90 eV EPL: Electron Projection Lithography @ e--beam IONS-L: projection lithography @ ions-beam ...
CARESTREAM OnSight 3D Extremity System
... "MRI VS CT SCAN." Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and American College of Radiology (ACR). "Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams." Patient Safety. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Curvebm. "Weight Bearing CT Archives - CurveBeam." CurveBeam. N.p., n.d. W ...
... "MRI VS CT SCAN." Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and American College of Radiology (ACR). "Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams." Patient Safety. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Curvebm. "Weight Bearing CT Archives - CurveBeam." CurveBeam. N.p., n.d. W ...
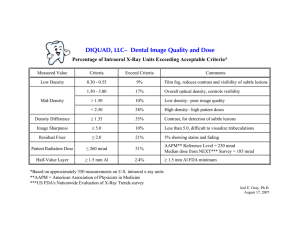
DIQUAD, LLC– Dental Image Quality and Dose
... • Patient Radiation Dose is critical especially considering the amount of information in the lay press about high radiation doses from x-ray examinations. One must know what radiation doses are being used to know if you are doing a good job! • If the median Patient Radiation Dose is 185 mrad, why sh ...
... • Patient Radiation Dose is critical especially considering the amount of information in the lay press about high radiation doses from x-ray examinations. One must know what radiation doses are being used to know if you are doing a good job! • If the median Patient Radiation Dose is 185 mrad, why sh ...
X-ray fluoroscopy imaging in the invasive cardiac laboratory
... X-ray fluoroscopy imaging in the invasive cardiac laboratory: Medical physics support of a contemporary practice 1. Introduction to the invasive cardiac invasive laboratory a. Procedure types b. Imaging equipment c. X-ray imaging tasks 2. Interventional x-ray systems a. Hardware components b. System ...
... X-ray fluoroscopy imaging in the invasive cardiac laboratory: Medical physics support of a contemporary practice 1. Introduction to the invasive cardiac invasive laboratory a. Procedure types b. Imaging equipment c. X-ray imaging tasks 2. Interventional x-ray systems a. Hardware components b. System ...
1. Introduction to Multi Slice Computed Tomography (MSCT)
... transverse cross sections of the body. The technique in particular offered improved low contrast resolution for better visualization of soft tissue, but with relatively high absorbed radiation doses. The initial potential of the imaging modality has been realised by rapid technological developments, ...
... transverse cross sections of the body. The technique in particular offered improved low contrast resolution for better visualization of soft tissue, but with relatively high absorbed radiation doses. The initial potential of the imaging modality has been realised by rapid technological developments, ...
RT 255 C Cross Sectional Anatomy
... used to do • Flat board used instead of curved couch • Dose to normal tissue is minimized ...
... used to do • Flat board used instead of curved couch • Dose to normal tissue is minimized ...
Clinical Waste for Treatment Yellow Lidded Sharps Unit
... Orange Bag - Hazardous/Infectious Clinical Waste: Chest drains, suction canisters, items that have been in contact with blood and bodily fluids from an infected source. NO medicinal waste (including used IV bags and giving sets). ...
... Orange Bag - Hazardous/Infectious Clinical Waste: Chest drains, suction canisters, items that have been in contact with blood and bodily fluids from an infected source. NO medicinal waste (including used IV bags and giving sets). ...
Image Processing Project Tomographic Image Reconstruction
... We are constantly exposed to naturally occurring radiation (radon, cosmic rays) ...
... We are constantly exposed to naturally occurring radiation (radon, cosmic rays) ...
computed tomography
... c. The center CT number is called the window level. d. The range of CT numbers above and below the window level is called the window width. 2. A bone window would have a window level of about +200. 3. A soft tissue window would be between +20 to +40. 4. The window width may be set at any level with ...
... c. The center CT number is called the window level. d. The range of CT numbers above and below the window level is called the window width. 2. A bone window would have a window level of about +200. 3. A soft tissue window would be between +20 to +40. 4. The window width may be set at any level with ...
X-ray
X-radiation (composed of X-rays) is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3×1016 Hz to 3×1019 Hz) and energies in the range 100 eV to 100 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to with terms meaning Röntgen radiation, after Wilhelm Röntgen, who is usually credited as its discoverer, and who had named it X-radiation to signify an unknown type of radiation. Spelling of X-ray(s) in the English language includes the variants x-ray(s), xray(s) and X ray(s).X-rays with photon energies above 5–10 keV (below 0.2–0.1 nm wavelength) are called hard X-rays, while those with lower energy are called soft X-rays. Due to their penetrating ability, hard X-rays are widely used to image the inside of objects, e.g., in medical radiography and airport security. As a result, the term X-ray is metonymically used to refer to a radiographic image produced using this method, in addition to the method itself. Since the wavelengths of hard X-rays are similar to the size of atoms they are also useful for determining crystal structures by X-ray crystallography. By contrast, soft X-rays are easily absorbed in air and the attenuation length of 600 eV (~2 nm) X-rays in water is less than 1 micrometer.There is no universal consensus for a definition distinguishing between X-rays and gamma rays. One common practice is to distinguish between the two types of radiation based on their source: X-rays are emitted by electrons, while gamma rays are emitted by the atomic nucleus. This definition has several problems; other processes also can generate these high energy photons, or sometimes the method of generation is not known. One common alternative is to distinguish X- and gamma radiation on the basis of wavelength (or equivalently, frequency or photon energy), with radiation shorter than some arbitrary wavelength, such as 10−11 m (0.1 Å), defined as gamma radiation.This criterion assigns a photon to an unambiguous category, but is only possible if wavelength is known. (Some measurement techniques do not distinguish between detected wavelengths.) However, these two definitions often coincide since the electromagnetic radiation emitted by X-ray tubes generally has a longer wavelength and lower photon energy than the radiation emitted by radioactive nuclei.Occasionally, one term or the other is used in specific contexts due to historical precedent, based on measurement (detection) technique, or based on their intended use rather than their wavelength or source.Thus, gamma-rays generated for medical and industrial uses, for example radiotherapy, in the ranges of 6–20 MeV, can in this context also be referred to as X-rays.