ppt
... [protein] molecule are its complexity and its lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein structure.’ – John Kendrick, 1958 ...
... [protein] molecule are its complexity and its lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein structure.’ – John Kendrick, 1958 ...
Protein: A polymer of amino acids Amino Acid Structure
... Tertiary Structure: Further bending and folding of proteins into globular or fibrous shapes ...
... Tertiary Structure: Further bending and folding of proteins into globular or fibrous shapes ...
DN: Protein
... • proteins. True proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids, each protein distinguishable by its unique sequence of the 20 different amino acids as illustrated on the left. In the feed lab, protein is distinguishable from carbohydrate and lipid due to its content of nitrogen (N) feed protei ...
... • proteins. True proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids, each protein distinguishable by its unique sequence of the 20 different amino acids as illustrated on the left. In the feed lab, protein is distinguishable from carbohydrate and lipid due to its content of nitrogen (N) feed protei ...
The Living World
... Used for long-term energy storage Also termed triglycerides or triacylglycerol Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to glycerol ...
... Used for long-term energy storage Also termed triglycerides or triacylglycerol Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to glycerol ...
Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can
... winter. These workers burn the wood that was supposed to be used to build the house in order to stay warm.. They succeed in staying warm, but have no wood to build the house. What does this story have to do with diets and protein? ...
... winter. These workers burn the wood that was supposed to be used to build the house in order to stay warm.. They succeed in staying warm, but have no wood to build the house. What does this story have to do with diets and protein? ...
Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with
... Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with two or more peptides using MaxQuant (version 1.2.2.5) from experiments using anti-acetyl-lysine immunoprecipitation and SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture) analysis of MOLM-13 cells treated with nutlin-3 ...
... Supplementary Table 1: A complete list of proteins identified with two or more peptides using MaxQuant (version 1.2.2.5) from experiments using anti-acetyl-lysine immunoprecipitation and SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture) analysis of MOLM-13 cells treated with nutlin-3 ...
Notes
... – arranged in specific sequence – linked by PEPTIDE BONDS – range in length from a few to 1000+ ...
... – arranged in specific sequence – linked by PEPTIDE BONDS – range in length from a few to 1000+ ...
Importance of Proteins PowerPoint
... incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles of the chemistry of protein to cooking eggs, milk, and meat products and in creating egg foams and ...
... incomplete proteins. Explain what happens during the denaturation of protein and how the process occurs. Explain coagulation and apply basic principles of the chemistry of protein to cooking eggs, milk, and meat products and in creating egg foams and ...
Standard B-2
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
Proteins
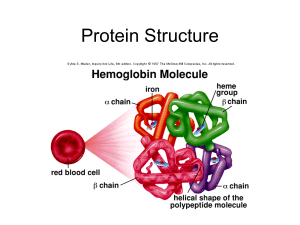
... Levels of Protein Structure • Like describing a knot by starting with the strands of the rope – Primary: The amino acid sequence – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
... Levels of Protein Structure • Like describing a knot by starting with the strands of the rope – Primary: The amino acid sequence – Secondary: Coiling or folding – Tertiary: folding, kinking, twisting entire structure – Quaternary: Two or more chains together ...
Estimation of the protein secondary structure in aqueous solutions
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
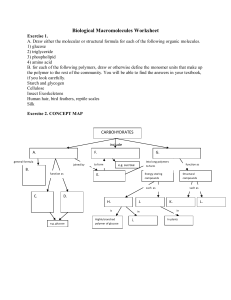
Biological Macromolecules Worksheet
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
... Exercise 3. 1. A triglyceride contains ______ and _______. 2. A fatty acid is unsaturated if it contains ____________. 3. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in ___________. 4. Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer membrane. Exercise 4. Define what a protein is and/or of wha ...
Chem 464 Biochemistry
... 12. (10 points) In class we talked about three types of fibrous proteins. Name these three protein types and tell how the structures observed in these proteins are similar to, or different than, structures observed in globular proteins. á- Keratin - observed in hair-wool, nails, claws, quill horn, h ...
... 12. (10 points) In class we talked about three types of fibrous proteins. Name these three protein types and tell how the structures observed in these proteins are similar to, or different than, structures observed in globular proteins. á- Keratin - observed in hair-wool, nails, claws, quill horn, h ...
Intro to Biochem - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... Can form single, double, or triple bonds with other atoms to form compounds Can form long chains or rings Carbon is very common! ...
... Can form single, double, or triple bonds with other atoms to form compounds Can form long chains or rings Carbon is very common! ...
CH 2.3-Carbon Compounds
... - It can bond with many other elements to make complex structures - It is a component of the four types of molecules all living things use: ...
... - It can bond with many other elements to make complex structures - It is a component of the four types of molecules all living things use: ...
Protein Structure 2 - Interactions - Hydrolysis
... Tend to form α-helix sections: Ala, Cys, Leu Met, Glu, Gln, His, Lys Tend to form β-sheet sections: Val, Ser, Asp, Asn, Pro, Arg Triple Helix – 3 strands. Collagen has this structure. (Collagen is the most abundant protein. Found in skin, connective tissue, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments, cartila ...
... Tend to form α-helix sections: Ala, Cys, Leu Met, Glu, Gln, His, Lys Tend to form β-sheet sections: Val, Ser, Asp, Asn, Pro, Arg Triple Helix – 3 strands. Collagen has this structure. (Collagen is the most abundant protein. Found in skin, connective tissue, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments, cartila ...
Importance of Proteins Test
... 10. When a protein is agitated, this disrupts the protein structures and causes them to form new positions with other molecules. 11. When chemicals, such as acids, are added to a proteins, it causes curdling. 12. It is important to remember that denaturation can be over done (over coagulation), whic ...
... 10. When a protein is agitated, this disrupts the protein structures and causes them to form new positions with other molecules. 11. When chemicals, such as acids, are added to a proteins, it causes curdling. 12. It is important to remember that denaturation can be over done (over coagulation), whic ...
2. Intro to Proteins
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
Cyclol

The cyclol hypothesis is the first structural model of a folded, globular protein. It was developed by Dorothy Wrinch in the late 1930s, and was based on three assumptions. Firstly, the hypothesis assumes that two peptide groups can be crosslinked by a cyclol reaction (Figure 1); these crosslinks are covalent analogs of non-covalent hydrogen bonds between peptide groups. These reactions have been observed in the ergopeptides and other compounds. Secondly, it assumes that, under some conditions, amino acids will naturally make the maximum possible number of cyclol crosslinks, resulting in cyclol molecules (Figure 2) and cyclol fabrics (Figure 3). These cyclol molecules and fabrics have never been observed. Finally, the hypothesis assumes that globular proteins have a tertiary structure corresponding to Platonic solids and semiregular polyhedra formed of cyclol fabrics with no free edges. Such ""closed cyclol"" molecules have not been observed either.Although later data demonstrated that this original model for the structure of globular proteins needed to be amended, several elements of the cyclol model were verified, such as the cyclol reaction itself and the hypothesis that hydrophobic interactions are chiefly responsible for protein folding. The cyclol hypothesis stimulated many scientists to research questions in protein structure and chemistry, and was a precursor of the more accurate models hypothesized for the DNA double helix and protein secondary structure. The proposal and testing of the cyclol model also provides an excellent illustration of empirical falsifiability acting as part of the scientific method.