Irreversible Inhibitors of Serine, Cysteine, and Threonine Proteases
... β-proteins, there are clearly major distinct families within this group. With serine proteases of the SerHis type, there appear to be at least five distinct protein folds. These are the chymotrypsin/trypsin fold, the subtilisin fold (R,β-protein), the R/β-hydrolase fold, the Pro oligopeptidase fold, ...
... β-proteins, there are clearly major distinct families within this group. With serine proteases of the SerHis type, there appear to be at least five distinct protein folds. These are the chymotrypsin/trypsin fold, the subtilisin fold (R,β-protein), the R/β-hydrolase fold, the Pro oligopeptidase fold, ...
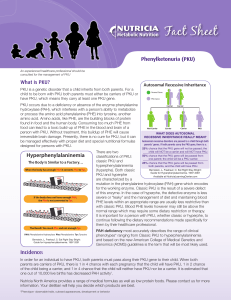
PKU - Nutricia Learning Center
... Since all foods with protein contain PHE, a person with PKU must restrict the amount and types of food containing protein. For this reason, PKU is managed with a low PHE diet consisting of foods low in protein and a PHE-free metabolic formula. The main sources of foods with protein allowed in the lo ...
... Since all foods with protein contain PHE, a person with PKU must restrict the amount and types of food containing protein. For this reason, PKU is managed with a low PHE diet consisting of foods low in protein and a PHE-free metabolic formula. The main sources of foods with protein allowed in the lo ...
The Genera Staphylococcus and Macrococcus
... record counts separately. When plates at the lowest dilution plated contain < 20 colonies, they may be used. If plates containing > 200 colonies have colonies with the typical appearance of S. aureus and typical colonies do not appear on plates at higher dilutions, use these plates for enumeration o ...
... record counts separately. When plates at the lowest dilution plated contain < 20 colonies, they may be used. If plates containing > 200 colonies have colonies with the typical appearance of S. aureus and typical colonies do not appear on plates at higher dilutions, use these plates for enumeration o ...
Acute hibernation decreases myocardial pyruvate carboxylation and
... Received 3 April 2001; accepted in final form 25 May 2001 ...
... Received 3 April 2001; accepted in final form 25 May 2001 ...
Saccharomyces species in the Production of Beer
... brewing will be discussed in Section 8. Yeast is cultured in an acidic aqueous sugary solution called wort prepared from barley malt and other cereals such as corn (maize), wheat, rice, sorghum, and also cane and beet sugar. The cells absorb dissolved sugars, simple nitrogenous matter (amino acids, ...
... brewing will be discussed in Section 8. Yeast is cultured in an acidic aqueous sugary solution called wort prepared from barley malt and other cereals such as corn (maize), wheat, rice, sorghum, and also cane and beet sugar. The cells absorb dissolved sugars, simple nitrogenous matter (amino acids, ...
Title of Document: HIGH-THROUGHPUT TIME-SERIES
... response of systematically perturbed Arabidopsis thaliana liquid culture system to study regulation of its primary metabolism. The biological system was studied under conditions of elevated CO2 stress, salt (NaCl) stress, sugar (trehalose) signal, and hormone (ethylene) signal, applied individually; ...
... response of systematically perturbed Arabidopsis thaliana liquid culture system to study regulation of its primary metabolism. The biological system was studied under conditions of elevated CO2 stress, salt (NaCl) stress, sugar (trehalose) signal, and hormone (ethylene) signal, applied individually; ...
Characterization of the Two-Component, FAD-Dependent Monooxygenase SgcC That Requires Carrier Protein-Tethered
... similarities.17–19 The first class, or one-component monooxygenases, are single polypeptides that utilize FAD or FMN as a cofactor and require NADH or NADPH to initiate oxidation of substrates; thus, these monooxygenases have both flavin reductase and monooxygnease activity. The second class, or two ...
... similarities.17–19 The first class, or one-component monooxygenases, are single polypeptides that utilize FAD or FMN as a cofactor and require NADH or NADPH to initiate oxidation of substrates; thus, these monooxygenases have both flavin reductase and monooxygnease activity. The second class, or two ...
Single-Amino Acid Substitutions Alter the Specificity and Affinity of
... nNOS (Figure 1C, R70A). However, R70A failed to bind Kv1.4. Thus, a single-amino acid substitution (Arg to Ala) confers nNOS binding on PDZ1 of PSD-95, but disrupts C-terminal peptide binding. These results suggest that an Arg or Lys residue in the carboxylate-binding loop of PDZ domains is required ...
... nNOS (Figure 1C, R70A). However, R70A failed to bind Kv1.4. Thus, a single-amino acid substitution (Arg to Ala) confers nNOS binding on PDZ1 of PSD-95, but disrupts C-terminal peptide binding. These results suggest that an Arg or Lys residue in the carboxylate-binding loop of PDZ domains is required ...
Carbamate Transport in Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase: A Theoretical and Experimental Investigation
... of the catalytic activity for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate relative to the wild type CPS, respectively. ...
... of the catalytic activity for the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate relative to the wild type CPS, respectively. ...
Production of acylated homoserine lactone by a novel marine strain
... Five supplementary figures are available with the online version of this paper. ...
... Five supplementary figures are available with the online version of this paper. ...
Anaerobic and aerobic pathways for salvage of proximal tubules
... explanation is that, during reoxygenation, succinate, which is a product of both pathways A and B (Fig. 1), donates electrons to complex III via complex II (succinate dehydrogenase), bypassing the limitation of metabolism of complex I substrates (pathway C in Fig. 1). In this fashion, succinate-depe ...
... explanation is that, during reoxygenation, succinate, which is a product of both pathways A and B (Fig. 1), donates electrons to complex III via complex II (succinate dehydrogenase), bypassing the limitation of metabolism of complex I substrates (pathway C in Fig. 1). In this fashion, succinate-depe ...
Reprint
... II (MPO-Fe4+-OH) and can oxidize AH by one-electron transfer with formation of A•-radicals (reaction 3, Fig. 1) [12, 16, 19]. Compound II is catalytically inactive in hypohalous acid formation, but, like Compound I, it can cause one-electron oxidation of substrate (AH) with regeneration of the nativ ...
... II (MPO-Fe4+-OH) and can oxidize AH by one-electron transfer with formation of A•-radicals (reaction 3, Fig. 1) [12, 16, 19]. Compound II is catalytically inactive in hypohalous acid formation, but, like Compound I, it can cause one-electron oxidation of substrate (AH) with regeneration of the nativ ...
- Free Documents
... The largest group oI kinases are those that phsophorylate either serines or threonines and as such are termed serine/threonine kinases. The ratio oI phosphorylation oI the three diIIerent amino acids is approximately // Ior serine/threonine/tyrosine. ...
... The largest group oI kinases are those that phsophorylate either serines or threonines and as such are termed serine/threonine kinases. The ratio oI phosphorylation oI the three diIIerent amino acids is approximately // Ior serine/threonine/tyrosine. ...
CYP-450
... (谷光苷肽) or amino acids (e.g. glycine (甘氨酸), taurine ( 牛 磺 酸 ), glutamine( 谷 氨 酰 胺 ), all of which increase the water solubility of the ...
... (谷光苷肽) or amino acids (e.g. glycine (甘氨酸), taurine ( 牛 磺 酸 ), glutamine( 谷 氨 酰 胺 ), all of which increase the water solubility of the ...
Osmo- and thermo-adaptation in hyperthermophilic Archaea
... salinities above 4.5% NaCl, reaching a value of 3.34 μmol/mg protein at 6.0% NaCl. In response to salt stress, A. fulgidus VC-16S accumulated mainly diglycerol phosphate, an osmolyte thus far confined to the Archaeoglobales. Furthermore, the level of diglycerol phosphate increased approximately 28-f ...
... salinities above 4.5% NaCl, reaching a value of 3.34 μmol/mg protein at 6.0% NaCl. In response to salt stress, A. fulgidus VC-16S accumulated mainly diglycerol phosphate, an osmolyte thus far confined to the Archaeoglobales. Furthermore, the level of diglycerol phosphate increased approximately 28-f ...
Serotonin and dopamine differentially affect
... 1983; Colwill and Rescorla 1988), but more recently was also demonstrated in humans (Paredes-Olay et al. 2002; Hogarth et al. 2007; Allman et al. 2010; Huys et al. 2011; Nadler et al. 2011). Structures such as the amygdala, the striatum, and the prefrontal cortex have been implicated as the neural l ...
... 1983; Colwill and Rescorla 1988), but more recently was also demonstrated in humans (Paredes-Olay et al. 2002; Hogarth et al. 2007; Allman et al. 2010; Huys et al. 2011; Nadler et al. 2011). Structures such as the amygdala, the striatum, and the prefrontal cortex have been implicated as the neural l ...
Technical Brief
... regarding the origin of the disease. 6 It noted simply that it is frequently associated with a monotonous maize-based diet and concludes with the following statement: “Breast milk is probably deficient in some factors, which are at present uncertain. As maize is the only source of supplementary food ...
... regarding the origin of the disease. 6 It noted simply that it is frequently associated with a monotonous maize-based diet and concludes with the following statement: “Breast milk is probably deficient in some factors, which are at present uncertain. As maize is the only source of supplementary food ...
Chapter 25 Slides
... • 1) Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent kinases inactivates the reductase • 2) Degradation of HMG-CoA reductase half-life is 3 hrs and depends on cholesterol level • 3) Gene expression (mRNA production) is controlled by cholesterol levels Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
... • 1) Phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent kinases inactivates the reductase • 2) Degradation of HMG-CoA reductase half-life is 3 hrs and depends on cholesterol level • 3) Gene expression (mRNA production) is controlled by cholesterol levels Copyright © 1999 by Harcourt Brace & Company ...
Mechanistic Role of an NS4A Peptide Cofactor with the Truncated
... treatment available for the progression of chronic hepatitis. The catalytic activity of a viral serine protease located in the N-terminal one-third of nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) is required for polyprotein processing at four site-specific junctions. The three-dimensional crystal structure of the ...
... treatment available for the progression of chronic hepatitis. The catalytic activity of a viral serine protease located in the N-terminal one-third of nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) is required for polyprotein processing at four site-specific junctions. The three-dimensional crystal structure of the ...
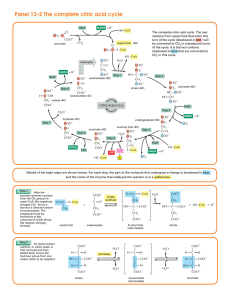
Panel 13–2 The complete citric acid cycle
... converted to a carbonyl group. The immediate product is unstable, losing CO2 while still bound to the enzyme. ...
... converted to a carbonyl group. The immediate product is unstable, losing CO2 while still bound to the enzyme. ...
novel aspects of carnitine function and metabolism
... membrane (OMM) is still far from being elucidated. It has been suggested that carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) forms oligomeric complexes in the OMM. This would result in the formation of a hexameric structure that could function as a pore, facilitating the transport of acylcarnitines across ...
... membrane (OMM) is still far from being elucidated. It has been suggested that carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) forms oligomeric complexes in the OMM. This would result in the formation of a hexameric structure that could function as a pore, facilitating the transport of acylcarnitines across ...