A1987K192000001
... six-week fast. Furthermore, in prolonged starvation, plasma alanine levels fell to a greater extent than all other amino acids, and the hypoalaninemia, rather than a change in splanchnic fractional extraction of alanine, accounted for the marked reduction in splanchnic alanine uptake observed during ...
... six-week fast. Furthermore, in prolonged starvation, plasma alanine levels fell to a greater extent than all other amino acids, and the hypoalaninemia, rather than a change in splanchnic fractional extraction of alanine, accounted for the marked reduction in splanchnic alanine uptake observed during ...
Ch. 2 - The Chemistry of Life
... Include cholesterol, bile salts, vitamin D, and some hormones Cholesterol is the basis for all steroids made in the body High levels of cholesterol can lead to heart disease Excess saturated fats are converted to cholesterol in the body ...
... Include cholesterol, bile salts, vitamin D, and some hormones Cholesterol is the basis for all steroids made in the body High levels of cholesterol can lead to heart disease Excess saturated fats are converted to cholesterol in the body ...
Samples Ch 10 to 12.tst
... 1) An enzyme will increase the rate of certain reactions with certain substances. This characteristic is called: A) inhibition B) specificity C) regulation D) selectivity ...
... 1) An enzyme will increase the rate of certain reactions with certain substances. This characteristic is called: A) inhibition B) specificity C) regulation D) selectivity ...
(key)
... Longer Chain lengths of the fatty acid components Less unsaturation of the fatty acid components Cross linking of fatty acid components ...
... Longer Chain lengths of the fatty acid components Less unsaturation of the fatty acid components Cross linking of fatty acid components ...
Amino acids and proteins
... When unfolded, all polar/hydrophillic sidechains can interact via Hbonds with water. When the protein folds, they must H-bond to each other and exclude much of the water. All groups capable of forming a hydrogen bond MUST, hence Hbonding in the backbone (C=O to N-H) by way of helices and sheets is a ...
... When unfolded, all polar/hydrophillic sidechains can interact via Hbonds with water. When the protein folds, they must H-bond to each other and exclude much of the water. All groups capable of forming a hydrogen bond MUST, hence Hbonding in the backbone (C=O to N-H) by way of helices and sheets is a ...
Chapter 5
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
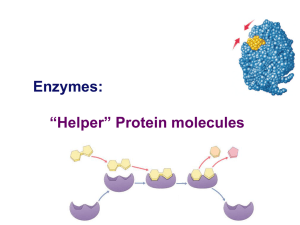
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... sucrase breaks down sucrose Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
... sucrase breaks down sucrose Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different rati ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different rati ...
Biological Molecules
... There is usually a small (usually charged or polar) molecule attached to the phosphate group ...
... There is usually a small (usually charged or polar) molecule attached to the phosphate group ...
1. The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is an
... An effector may either inhibit or activate an enzyme. Binding of the effector changes the conformation of the enzyme molecule. Heterotropic allosteric effectors compete with substrate for binding sites. ...
... An effector may either inhibit or activate an enzyme. Binding of the effector changes the conformation of the enzyme molecule. Heterotropic allosteric effectors compete with substrate for binding sites. ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 6. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
... 6. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
Buffers - Philadelphia University
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
... • (H,C,N,O,P,S,Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca). – Chemical makeup appears to be determined partly by the availability of raw materials and the specific roles of of molecules in life processes. – Do not reflect the composition of the biosphere – Examples on per atom basis, H in organisms = 49% ...
organic molecules
... VI. Proteins A. Proteins: composed of N, C, H, O B. Polymers called amino acids 1. Amine (NH2) on one end, carboxyl (COOH) on the other end, and H and R groups a. portion that differs: R-group 2. More than 20 different amino acids in nature 3. Sequence of amino acids determines the protein C. 2 ami ...
... VI. Proteins A. Proteins: composed of N, C, H, O B. Polymers called amino acids 1. Amine (NH2) on one end, carboxyl (COOH) on the other end, and H and R groups a. portion that differs: R-group 2. More than 20 different amino acids in nature 3. Sequence of amino acids determines the protein C. 2 ami ...
What amino acids really look like
... Amino acid Structure The central carbon (Cα-atom) is a chiral center Encoded proteins have the L-configuration at this chiral center Configuration can be remembered as the CORN law Looking along the H-Cα bond with H atom closest to you Reading clockwise, the groups attached to the Cα spell CORN ...
... Amino acid Structure The central carbon (Cα-atom) is a chiral center Encoded proteins have the L-configuration at this chiral center Configuration can be remembered as the CORN law Looking along the H-Cα bond with H atom closest to you Reading clockwise, the groups attached to the Cα spell CORN ...
16N-containing Substances
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole ...
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole ...
UNIT-1 Carbohydrates
... structural support Characteristics: H – C – OH ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms is 2:1 Monomer is the monosaccharide ...
... structural support Characteristics: H – C – OH ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms is 2:1 Monomer is the monosaccharide ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Purpose The unit aims to provide fundamental concepts with a focus on description, organization, and functions of metabolic pathways of primary metabolites in microorganisms, plants and mammalian systems. Course Objectives 1. To deliver a concise knowledge and understanding of primary basic metaboli ...
... Purpose The unit aims to provide fundamental concepts with a focus on description, organization, and functions of metabolic pathways of primary metabolites in microorganisms, plants and mammalian systems. Course Objectives 1. To deliver a concise knowledge and understanding of primary basic metaboli ...
Application Note
... Alanine (Ala), arginine (Arg), aspartic acid (Asp), cysteine (Cys), glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), histidine (His), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), lysine (Lys), methionine (Met), phenylalanine (Phe), proline (Pro), serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), tyrosine (Tyr), valine (Val) VBS0001N, 09/09, u ...
... Alanine (Ala), arginine (Arg), aspartic acid (Asp), cysteine (Cys), glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), histidine (His), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), lysine (Lys), methionine (Met), phenylalanine (Phe), proline (Pro), serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), tyrosine (Tyr), valine (Val) VBS0001N, 09/09, u ...
3. What are macromolecules?
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
... The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper functioning of all living things are known as polymers or macromolecules. All of these compounds are built primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but in different ratio ...
Whittier Union High School District
... 14. What is an enzyme? An enzyme is a type of protein that works like a catalyst. It speeds up reaction by lowering activation energy. 15. What factors can reduce the activity of an enzyme? Temperature, pH level, Ionic conditions or overuse. All of these would make the enzyme not work as efficiently ...
... 14. What is an enzyme? An enzyme is a type of protein that works like a catalyst. It speeds up reaction by lowering activation energy. 15. What factors can reduce the activity of an enzyme? Temperature, pH level, Ionic conditions or overuse. All of these would make the enzyme not work as efficiently ...
Biomolecule Test Review 2015
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
Exam 1
... A. ____________ The conversion of an alkene into an alcohol is an example of an oxidation reaction. B. ____________The first pKa of NaH2PO4 is about 7. C. ____________ DNA double helices with high G-C content have higher melting points than those with lower G-C content. D. ____________ In blue/white ...
... A. ____________ The conversion of an alkene into an alcohol is an example of an oxidation reaction. B. ____________The first pKa of NaH2PO4 is about 7. C. ____________ DNA double helices with high G-C content have higher melting points than those with lower G-C content. D. ____________ In blue/white ...
Biomolecules Test Review -KEY
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
Review Questions
... The next level is called the tertiary level. Tertiary means “third”. The polypeptide continues to bond to itself but this time the individual amino acids join to each other by bonds between their R groups. Remember, the 20 kinds of amino acids differ because of their R groups. These R groups also h ...
... The next level is called the tertiary level. Tertiary means “third”. The polypeptide continues to bond to itself but this time the individual amino acids join to each other by bonds between their R groups. Remember, the 20 kinds of amino acids differ because of their R groups. These R groups also h ...