Enzymes Detection
... much more sensitive than the currently available fluorimetric assay for this enzyme activity. This method eliminates the interference that occurs in some biological samples and can be readily used to detect lysyl oxidase activity in cell culture experiments. ...
... much more sensitive than the currently available fluorimetric assay for this enzyme activity. This method eliminates the interference that occurs in some biological samples and can be readily used to detect lysyl oxidase activity in cell culture experiments. ...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System, 3e
... monomers, which can then be used in synthesis reactions to build new macromolecules for use by the cell, whereas synthesis reactions utilize component monomers to build larger molecules. Bloom's Rank: Application Section: Chemical Reactions 2) Discuss the importance of hydrogen bonds in the chemistr ...
... monomers, which can then be used in synthesis reactions to build new macromolecules for use by the cell, whereas synthesis reactions utilize component monomers to build larger molecules. Bloom's Rank: Application Section: Chemical Reactions 2) Discuss the importance of hydrogen bonds in the chemistr ...
Cholesterol Synthesis
... Reactions catalyzed by different P450 enzymes include hydroxylation, epoxidation, dealkylation, peroxidation, deamination, desulfuration, dehalogenation, etc. P450 substrates include steroids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, eicosanoids, retinoids, & various non-polar xenobiotics (drugs & other fo ...
... Reactions catalyzed by different P450 enzymes include hydroxylation, epoxidation, dealkylation, peroxidation, deamination, desulfuration, dehalogenation, etc. P450 substrates include steroids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, eicosanoids, retinoids, & various non-polar xenobiotics (drugs & other fo ...
Effect of Aminoguanidine (Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor
... nutritional and hormonal states. Thus, the regulation of PDC is critical in glucose and fatty acids metabolism. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC): structure and function PDC is located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, where it oxidatively decarboxylates pyruvate to acetyl CoA and CO2 coupled ...
... nutritional and hormonal states. Thus, the regulation of PDC is critical in glucose and fatty acids metabolism. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC): structure and function PDC is located on the mitochondrial inner membrane, where it oxidatively decarboxylates pyruvate to acetyl CoA and CO2 coupled ...
Glutathione Peroxidase Activity
... Glutathione, a tripeptide consisting of glutamic acid - cysteine – glycine, is the substrate for glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx), which protects cytosolic organelles from the damaging effects of the hydroperoxides formed by normal aerobic metabolism. GSHPx catalyses the reduction of hydrogen peroxide ...
... Glutathione, a tripeptide consisting of glutamic acid - cysteine – glycine, is the substrate for glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx), which protects cytosolic organelles from the damaging effects of the hydroperoxides formed by normal aerobic metabolism. GSHPx catalyses the reduction of hydrogen peroxide ...
UNIT 9. COMMON CATABOLIC PATHWAY. TRICARBOXYLIC ACID
... Study the main mechanisms of the TCA cycle regulation. l. Look at fig 19.16 (p.303) and remember the major regulatory reactions in the TCA cycle. Memorize: the TCA cycle is controlled by regulation of several enzyme activities. The most important of these enzymes are citrate synthase, isocitrate deh ...
... Study the main mechanisms of the TCA cycle regulation. l. Look at fig 19.16 (p.303) and remember the major regulatory reactions in the TCA cycle. Memorize: the TCA cycle is controlled by regulation of several enzyme activities. The most important of these enzymes are citrate synthase, isocitrate deh ...
Plant growth-promoting endophytic bacteria versus
... promoted and rescued plant growth by modulating defense hormones and regulating amino acids. This suggests that bacterial endophytes could be used for possible control of F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici in an eco-friendly way. Subjects Agricultural Science, Biotechnology, Plant Science Keywords Grow ...
... promoted and rescued plant growth by modulating defense hormones and regulating amino acids. This suggests that bacterial endophytes could be used for possible control of F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici in an eco-friendly way. Subjects Agricultural Science, Biotechnology, Plant Science Keywords Grow ...
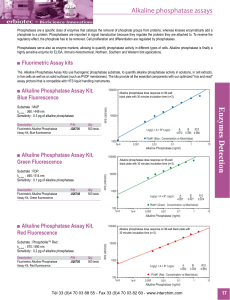
Enzymes at work
... lyze, a diverse supply of enzymes must be present in cells to carry out all the different chemical transformations required. Most ...
... lyze, a diverse supply of enzymes must be present in cells to carry out all the different chemical transformations required. Most ...
Plant purple acid phosphatases — genes, structures and biological
... 1999b). In one sweet potato PAP form a Fe-Mn binuclear metal center was found (Schenk et al., 2001), in the other — a Fe-Zn center, identical with the kbAP metal center (Durmus et al., 1999a). In the Arabidopsis thaliana genome twenty nine potential PAP genes have been identified (Li et al., 2002). ...
... 1999b). In one sweet potato PAP form a Fe-Mn binuclear metal center was found (Schenk et al., 2001), in the other — a Fe-Zn center, identical with the kbAP metal center (Durmus et al., 1999a). In the Arabidopsis thaliana genome twenty nine potential PAP genes have been identified (Li et al., 2002). ...
Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate
... (iBMK-parental cells)13, without enforcing any constraints on NADPH production routes. The model, assessed via flux balance analysis with an objective of minimizing total enzyme expression requirements and hence flux14 (see Methods), predicted that both the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and ma ...
... (iBMK-parental cells)13, without enforcing any constraints on NADPH production routes. The model, assessed via flux balance analysis with an objective of minimizing total enzyme expression requirements and hence flux14 (see Methods), predicted that both the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and ma ...
Protonation States and pKa
... Since amino acids are (at least) diprotic their titration curves appear a little different from a simple acid -each proton will have a pKa value and thus there are two or more stages in the titration curve Depending on where in the titration you are looking (i.e. at which pH) a different form of the ...
... Since amino acids are (at least) diprotic their titration curves appear a little different from a simple acid -each proton will have a pKa value and thus there are two or more stages in the titration curve Depending on where in the titration you are looking (i.e. at which pH) a different form of the ...
Molecular characteristics of sucrose synthase
... profiles of genes associated with carbon metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem 2008; 46:34-45. 19. Zabalza A, Gálvez L, Marino D, Royuela M, Arrese-Igor C, González EM. The application of ascorbate or its immediate precursor, galactono-1,4-lactone, does not affect the response of nitrogen-fixing pea ...
... profiles of genes associated with carbon metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem 2008; 46:34-45. 19. Zabalza A, Gálvez L, Marino D, Royuela M, Arrese-Igor C, González EM. The application of ascorbate or its immediate precursor, galactono-1,4-lactone, does not affect the response of nitrogen-fixing pea ...
Lactic Acid : Brief History
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
... dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine trip hosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it wa ...
... 16. (12 pts) Please do one of the following questions. Choice A: Pretend it’s next Sunday and you just finished the Pittsburgh marathon. As a consequence, your glycogen levels and ATP levels in the liver are quite low. Discuss the process, with the major focus on regulation in your answer, by which ...
CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2
... •24 NADH = 72 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •8 FADH2 = 16 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •8 GTP = 8 ATP •7 NADH generated by beta oxidation itself = 21 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •7 FADH2 generated by beta oxidation itself = 14 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) Total number of ATP ...
... •24 NADH = 72 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •8 FADH2 = 16 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •8 GTP = 8 ATP •7 NADH generated by beta oxidation itself = 21 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) •7 FADH2 generated by beta oxidation itself = 14 ATP (by oxidative phosphorylation) Total number of ATP ...
26/2/2010 Branched Chain Amino Acids as Adjunctive Therapy to Ketogenic Diet
... Their circulating concentrations can influence the brain uptake of precursor amino acids for neurotransmitter synthesis, and they can regulate protein synthesis in a variety of tissues. ...
... Their circulating concentrations can influence the brain uptake of precursor amino acids for neurotransmitter synthesis, and they can regulate protein synthesis in a variety of tissues. ...
16 Gluconeogenesis
... Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are coordinated so that, within a cell, one pathway is relatively inactive while the other is highly active. If both sets of reactions were highly active at the same time, the net result would be the hydrolysis of four nucleoside triphosphates (two ATP molecules plus t ...
... Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are coordinated so that, within a cell, one pathway is relatively inactive while the other is highly active. If both sets of reactions were highly active at the same time, the net result would be the hydrolysis of four nucleoside triphosphates (two ATP molecules plus t ...
Mittenthal, J.E., Clarke, B., Waddell, T., and Fawcett, G.
... carbon atoms in the reacting metabolites. Each of these metabolites is only speci"ed by the number of carbon atoms it contains. Conversion of a Cto an R-paranet proceeds through the following stages, here as in our work on the pentose phosphate pathway (Mittenthal et al., 1998). (a) For each metabol ...
... carbon atoms in the reacting metabolites. Each of these metabolites is only speci"ed by the number of carbon atoms it contains. Conversion of a Cto an R-paranet proceeds through the following stages, here as in our work on the pentose phosphate pathway (Mittenthal et al., 1998). (a) For each metabol ...
1/22
... • BSC: Reaction reversed….CO2 + pyruvate (3 C) • CO2 to Calvin Cycle • Pyruvate to mesophyll, converted to PEP Calvin Cycle (Rubisco) ...
... • BSC: Reaction reversed….CO2 + pyruvate (3 C) • CO2 to Calvin Cycle • Pyruvate to mesophyll, converted to PEP Calvin Cycle (Rubisco) ...
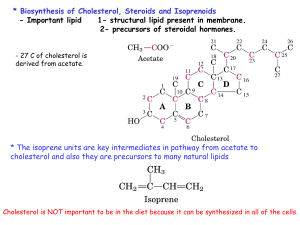
S17 Cholesterol And Steroids Biosynthesis
... * Metabolism of Chylomicrons - The largest in size and least density of lipoproteins. - Synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum of epithelial cells that line the small intestine, then they are packaged in secretory vesicles by Golgi and exported to lymphatic system then enter the blood stream. * T ...
... * Metabolism of Chylomicrons - The largest in size and least density of lipoproteins. - Synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum of epithelial cells that line the small intestine, then they are packaged in secretory vesicles by Golgi and exported to lymphatic system then enter the blood stream. * T ...