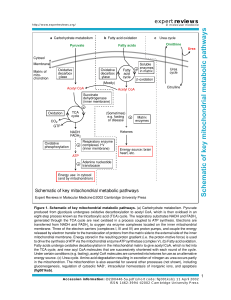
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
... generated through the TCA cycle are next oxidised in a process coupled to ATP synthesis. Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via enzyme complexes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Three of the electron carriers (complexes I, III and IV) are proton pumps, and couple the ...
DNA to Protein Synthesis Internet Quest
... Purpose: To give you a better understanding of how the message found on a molecule of DNA is used to build a protein. Site 1 – DNA and RNA Comparison ...
... Purpose: To give you a better understanding of how the message found on a molecule of DNA is used to build a protein. Site 1 – DNA and RNA Comparison ...
Macromolecules of the Cell
... Globular proteins: they are involved in cellular structure. They are folded into compact form. The formation of a-helix or B-sheets depends on the type of amino acids present in the polypeptide. Leucine, methionine, and glutamate are strong a-helix formers, whereas isoleucine, valine, and phenylalan ...
... Globular proteins: they are involved in cellular structure. They are folded into compact form. The formation of a-helix or B-sheets depends on the type of amino acids present in the polypeptide. Leucine, methionine, and glutamate are strong a-helix formers, whereas isoleucine, valine, and phenylalan ...
Protein Structure
... planar with the C=O sticking out one side, and the H on the nitrogen sticking out the other side. These groups are both polar and easily form hydrogen bonds. The other two bonds in the polypeptide backbone are called psi (ψ), between the acid carbon and the alpha carbon, and phi (φ), between the ami ...
... planar with the C=O sticking out one side, and the H on the nitrogen sticking out the other side. These groups are both polar and easily form hydrogen bonds. The other two bonds in the polypeptide backbone are called psi (ψ), between the acid carbon and the alpha carbon, and phi (φ), between the ami ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor). • At a certain pH known as the isoelectric point, a zwitterion forms. This contains the –NH3+ group and the –COO– group in the same molecule. • Amino acids polymerise to form proteins while proteins can undergo hydrolysis to form a-amino acids. ...
... (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor). • At a certain pH known as the isoelectric point, a zwitterion forms. This contains the –NH3+ group and the –COO– group in the same molecule. • Amino acids polymerise to form proteins while proteins can undergo hydrolysis to form a-amino acids. ...
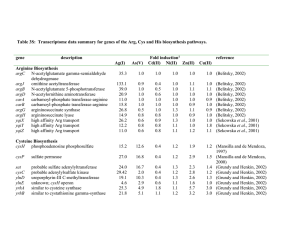
Table 3S
... enzymes for the synthesis of Cys from sulfate and O-acetylserine and the yrhAB genes encode the cystathionine -synthase and lyase for conversion of homocysteine to Cys (Grundy and Henkin, 2002). The yrrT gene is located upstream of the yrhAB genes, appears to be regulated by a Met-specific antiter ...
... enzymes for the synthesis of Cys from sulfate and O-acetylserine and the yrhAB genes encode the cystathionine -synthase and lyase for conversion of homocysteine to Cys (Grundy and Henkin, 2002). The yrrT gene is located upstream of the yrhAB genes, appears to be regulated by a Met-specific antiter ...
Lecture 2 Slides
... carboxyl group of another to form a peptide bond (=amide linkage) with the elimination of a water molecule. • The polarity of the molecule is retained. The monomers are all joined together in the same orientation. The polypeptide chain has polarity. • The polypeptide contains a free amino group at o ...
... carboxyl group of another to form a peptide bond (=amide linkage) with the elimination of a water molecule. • The polarity of the molecule is retained. The monomers are all joined together in the same orientation. The polypeptide chain has polarity. • The polypeptide contains a free amino group at o ...
Amino Acids
... • The AA sequence of a protein's polypeptide chain is called its primary structure. • Different regions of sequence form local regular secondary structures, (a-helices or -strands). • Tertiary structure is formed by packing structural elements into one or several compact globular units called domai ...
... • The AA sequence of a protein's polypeptide chain is called its primary structure. • Different regions of sequence form local regular secondary structures, (a-helices or -strands). • Tertiary structure is formed by packing structural elements into one or several compact globular units called domai ...
Application Note
... Alanine (Ala), arginine (Arg), aspartic acid (Asp), cystine (Cys)2, glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), histidine (His), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), lysine (Lys), methionine (Met), phenylalanine (Phe), proline (Pro), serine (Ser), taurin, threonine (Thr), tryptophan (Trp),tyrosine (Tyr), valine ...
... Alanine (Ala), arginine (Arg), aspartic acid (Asp), cystine (Cys)2, glutamic acid (Glu), glycine (Gly), histidine (His), isoleucine (Ile), leucine (Leu), lysine (Lys), methionine (Met), phenylalanine (Phe), proline (Pro), serine (Ser), taurin, threonine (Thr), tryptophan (Trp),tyrosine (Tyr), valine ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet
... groups of amino acids are joined together, a protein is formed. 23. What are some of the functions of proteins? __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the monomer of proteins? ___________________________ ...
... groups of amino acids are joined together, a protein is formed. 23. What are some of the functions of proteins? __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the monomer of proteins? ___________________________ ...
Regulation of metabolism by PPARs and Angiopoietin like proteins
... fasting-induced adipose factor) leads to a rapid reduction in adipose tissue LPL activity during fasting. The collective data point to a scenario where ANGPTL4 is the central component of a feedback mechanism that regulates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis and subsequent tissue fatty acid uptake in re ...
... fasting-induced adipose factor) leads to a rapid reduction in adipose tissue LPL activity during fasting. The collective data point to a scenario where ANGPTL4 is the central component of a feedback mechanism that regulates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis and subsequent tissue fatty acid uptake in re ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... How does synthesis provide important organic macromolecules using six essential elements? B. ...
... How does synthesis provide important organic macromolecules using six essential elements? B. ...
Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates
... Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an en ...
... Chemistry of Fats and Carbohydrates All living things are composed of many different kinds of chemical molecules. Two very important chemical molecules are fats and proteins. Both make up parts of living cells. Fats are a part of all cellular membranes. They also may be stored within a cell as an en ...
Gene Ontology (GO)
... Gene Ontology Gene Ontology (GO) is a collection of controlled vocabularies describing the biology of a gene product in any organism There are 3 independent sets of vocabularies, or ontologies: • Molecular Function (MF) – e.g. ”DNA binding” and ”catalytic activity” ...
... Gene Ontology Gene Ontology (GO) is a collection of controlled vocabularies describing the biology of a gene product in any organism There are 3 independent sets of vocabularies, or ontologies: • Molecular Function (MF) – e.g. ”DNA binding” and ”catalytic activity” ...
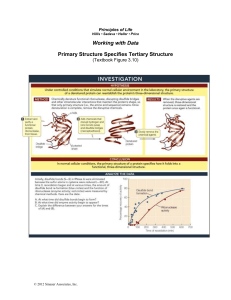
Principles of Life
... question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available from pancreases at slaughterhouses. Because it works in the highly acidic environment of ...
... question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available from pancreases at slaughterhouses. Because it works in the highly acidic environment of ...
METABOLISM
... Lipolysis = triglycerides are split into fatty acids and glycerol. As a part of normal fatty acid catabolism, ketone bodies are formed. An excess of ketone bodies (ketosis), may cause acidosis or abnormally low blood pH. ...
... Lipolysis = triglycerides are split into fatty acids and glycerol. As a part of normal fatty acid catabolism, ketone bodies are formed. An excess of ketone bodies (ketosis), may cause acidosis or abnormally low blood pH. ...
Ch18.doc
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
... 5. Both alanine and lactate have to be converted to pyruvate. From lactate, it is the lactate dehydrogenase reaction (1 NADH), then pyruvate gets oxidized by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2 ...
Chemistry of Life 3a Puzzle Paragraph
... Enzymes are globular proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to ____________ them, many chemical processes happen at a very slow rate in living organisms. By making some enzymes and not others, cells can control what chemical reactions happen in their cytoplasm. Denatu ...
... Enzymes are globular proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions. Without enzymes to ____________ them, many chemical processes happen at a very slow rate in living organisms. By making some enzymes and not others, cells can control what chemical reactions happen in their cytoplasm. Denatu ...
1 Molecular Evolution I: Protein Evolution 1. Protein Evolution We
... sequences are more complex than DNA (20 amino acids versus 4 nucleotides), proteins are generally more conserved throughout evolution and easier to align and compare between distantly related species. As we will see later, DNA is also more complicated because it may be coding or non-coding, and even ...
... sequences are more complex than DNA (20 amino acids versus 4 nucleotides), proteins are generally more conserved throughout evolution and easier to align and compare between distantly related species. As we will see later, DNA is also more complicated because it may be coding or non-coding, and even ...
Hand Outs B 1 - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... emphasis is on some responsibility at this stage in your child’s life. The Know to Grow program has separate teaching sessions for three other age groups of children with PKU ages 5 to 18. We are excited to be partners with you in teaching and enabling your child to ultimately manage the PKU treatme ...
... emphasis is on some responsibility at this stage in your child’s life. The Know to Grow program has separate teaching sessions for three other age groups of children with PKU ages 5 to 18. We are excited to be partners with you in teaching and enabling your child to ultimately manage the PKU treatme ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... 16) a) True b) False: The same transcription factors are expressed at the same level in all eukaryotic cells. 17) Addition of ubiquitin to nascent _________causes its half life to be _____________. a) RNA, decreased b) RNA, increased c) protein, decreased d) protein, increased 18) a) True b) False: ...
... 16) a) True b) False: The same transcription factors are expressed at the same level in all eukaryotic cells. 17) Addition of ubiquitin to nascent _________causes its half life to be _____________. a) RNA, decreased b) RNA, increased c) protein, decreased d) protein, increased 18) a) True b) False: ...
proteins
... (b) Functional molecules - three-dimensional conformation of proteins (1) and their binding sites (1) and essential for these functions. ...
... (b) Functional molecules - three-dimensional conformation of proteins (1) and their binding sites (1) and essential for these functions. ...