Influence of free linoleic acid on the fatty acids profile of fermentation
... was investigated (sugars, amino acids, metal ions, salts, enzyme cofactors and enzyme inhibitors) added to the reaction mixture. These compounds reduced CLA2 production, thus increasing the apparent selectivity for CLA1. Additions of L-serine or AgNO3 were effective for selective production of CLA1. ...
... was investigated (sugars, amino acids, metal ions, salts, enzyme cofactors and enzyme inhibitors) added to the reaction mixture. These compounds reduced CLA2 production, thus increasing the apparent selectivity for CLA1. Additions of L-serine or AgNO3 were effective for selective production of CLA1. ...
herbicides with novel modes of action?
... HTS methods, permit the screening of such targets with tenshundreds of thousands of molecules, however even if potent inhibitors are identified, they may not have in vivo herbicidal activity due to limited bioavailability. For many years, natural phytotoxins that reduce or prevent plant growth have ...
... HTS methods, permit the screening of such targets with tenshundreds of thousands of molecules, however even if potent inhibitors are identified, they may not have in vivo herbicidal activity due to limited bioavailability. For many years, natural phytotoxins that reduce or prevent plant growth have ...
lipoprotein metabolism
... Where is VLDL formed? What are the lipids Carried by VLDL? Which lipid is delivered by VLDL? What is the mechanism of FFA release from VLDL? What is the fate of Remnant VLDL? What are the lipids present in excess when VLDL becomes VLDLR? ...
... Where is VLDL formed? What are the lipids Carried by VLDL? Which lipid is delivered by VLDL? What is the mechanism of FFA release from VLDL? What is the fate of Remnant VLDL? What are the lipids present in excess when VLDL becomes VLDLR? ...
Allosteric pathways in imidazole glycerol phosphate synthase
... the glutamine amidotransferase family that catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine (Gln) to produce ammonia. The ammonia travels to the other monomer, HisF, passing through the ðβ∕αÞ8 barrel and reacting with the effector PRFAR; i.e., N′-[(5′-phosphoribulosyl)formimino]-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ...
... the glutamine amidotransferase family that catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine (Gln) to produce ammonia. The ammonia travels to the other monomer, HisF, passing through the ðβ∕αÞ8 barrel and reacting with the effector PRFAR; i.e., N′-[(5′-phosphoribulosyl)formimino]-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ...
SPECIFIC PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN CELLULAR
... laterally so as to form voluminous channels for yolk transport (King and Aggarwal, 1965) . In addition, the cells synthesize and secrete into the channels a macromolecule, probably a glycoprotein, which finds its way into the yolk spheres of the oocyte (Anderson and Telfer, 1969) . From experiments ...
... laterally so as to form voluminous channels for yolk transport (King and Aggarwal, 1965) . In addition, the cells synthesize and secrete into the channels a macromolecule, probably a glycoprotein, which finds its way into the yolk spheres of the oocyte (Anderson and Telfer, 1969) . From experiments ...
Effect of salinity on growth of green alga Botryococcus braunii and
... strains are also known to produce exopolysaccharides up to 250 g m¡3, whereas L race produce up to 1 kg m¡3 (Banerjee et al., 2002). However, the amount of exopolysaccharides production varies with the strains and the culture conditions. Algae diVer in their adaptability to salinity and based on the ...
... strains are also known to produce exopolysaccharides up to 250 g m¡3, whereas L race produce up to 1 kg m¡3 (Banerjee et al., 2002). However, the amount of exopolysaccharides production varies with the strains and the culture conditions. Algae diVer in their adaptability to salinity and based on the ...
Regulation of Arabidopsis 14-3
... Since 14-3-3 proteins regulate several aspects N metabolism in plants, we were interested to determine whether the 14-3-3s themselves might be subject to regulation by N metabolites. We therefore examined the expression of all members of the 14-3-3 gene family in Arabidopsis seedlings grown with dif ...
... Since 14-3-3 proteins regulate several aspects N metabolism in plants, we were interested to determine whether the 14-3-3s themselves might be subject to regulation by N metabolites. We therefore examined the expression of all members of the 14-3-3 gene family in Arabidopsis seedlings grown with dif ...
What is a Multiple Alignment?
... by pairs of unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests an α-helix with one face packed in the protein core. Similarly, an i, i+3, i+4, i+7 pattern of conserved residues.” ...
... by pairs of unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests an α-helix with one face packed in the protein core. Similarly, an i, i+3, i+4, i+7 pattern of conserved residues.” ...
H +
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
Document
... quantities (micrograms or at best milligrams). These are vitamins, minerals and trace elements. Dr S Nayak ...
... quantities (micrograms or at best milligrams). These are vitamins, minerals and trace elements. Dr S Nayak ...
Soil Biology and Biochemistry
... method (Dubois et al., 1956). For starch determination, the resulting pellet was treated with perchloric acid and then aliquots of the supernatant were utilized (McCready et al., 1950). The extraction and determination of leghemoglobin in the cowpea nodules was performed using Drabkin’s reagent foll ...
... method (Dubois et al., 1956). For starch determination, the resulting pellet was treated with perchloric acid and then aliquots of the supernatant were utilized (McCready et al., 1950). The extraction and determination of leghemoglobin in the cowpea nodules was performed using Drabkin’s reagent foll ...
Once this was accomplished we were able to study
... Once this was accomplished we were able to study the quantitative distribution of other enzymes for which less information was available. In this paper the results of assay of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) activity on renal tissues from healthy humans and laboratory animals are reported. LDH was chosen ...
... Once this was accomplished we were able to study the quantitative distribution of other enzymes for which less information was available. In this paper the results of assay of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) activity on renal tissues from healthy humans and laboratory animals are reported. LDH was chosen ...
10 Translocation in the Phloem Chapter
... coiled. They generally disperse into tubular or fibrillar forms during cell maturation. P-proteins have been characterized at the molecular level. For example, P-proteins from the genus Cucurbita consist of two major proteins: PP1, the phloem filament protein, and PP2, the phloem lectin. The gene th ...
... coiled. They generally disperse into tubular or fibrillar forms during cell maturation. P-proteins have been characterized at the molecular level. For example, P-proteins from the genus Cucurbita consist of two major proteins: PP1, the phloem filament protein, and PP2, the phloem lectin. The gene th ...
Biopathways Representation and Simulation on Hybrid Functional
... and cases that the amounts can be counted as integers. HFPN inherits all the aspects of the original Petri net. 2. Hybrid Petri net allows continuous feature of amounts in addition to the original ability of Petri net. Thus ODEs can be realized very intuitively and easily. But dynamic changes of the ...
... and cases that the amounts can be counted as integers. HFPN inherits all the aspects of the original Petri net. 2. Hybrid Petri net allows continuous feature of amounts in addition to the original ability of Petri net. Thus ODEs can be realized very intuitively and easily. But dynamic changes of the ...
Analysis of structural robustness of metabolic
... mutants of micro-organisms are still able to grow, some with almost the same growth rate as the wild type. This has been shown, for example, by a systematic study on single knockout mutants of virtually all genes in baker’s yeast [1, 2]. In many cells, there are parallel and thus redundant metabolic ...
... mutants of micro-organisms are still able to grow, some with almost the same growth rate as the wild type. This has been shown, for example, by a systematic study on single knockout mutants of virtually all genes in baker’s yeast [1, 2]. In many cells, there are parallel and thus redundant metabolic ...
NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase. From a model enzyme to
... Several high resolution structures of PseFDH are available to date: the apo-enzyme (resolution 1.80 Å) [17], the ternary complex of enzyme with NAD+ and azide mimicking putative transition state (2.05 Å) [17], and a complex with ADPR (1.50 Å) [23]. Several other binary complexes of PseFDH (PseFDH-fo ...
... Several high resolution structures of PseFDH are available to date: the apo-enzyme (resolution 1.80 Å) [17], the ternary complex of enzyme with NAD+ and azide mimicking putative transition state (2.05 Å) [17], and a complex with ADPR (1.50 Å) [23]. Several other binary complexes of PseFDH (PseFDH-fo ...
Final published version
... Manipulation of NADH-dependent steps, and particularly disruption of the las-located lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene in Lactococcus lactis, is common to engineering strategies envisaging the accumulation of reduced end products other than lactate. Reverse transcription-PCR experiments revealed that ...
... Manipulation of NADH-dependent steps, and particularly disruption of the las-located lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene in Lactococcus lactis, is common to engineering strategies envisaging the accumulation of reduced end products other than lactate. Reverse transcription-PCR experiments revealed that ...
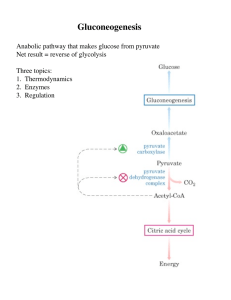
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
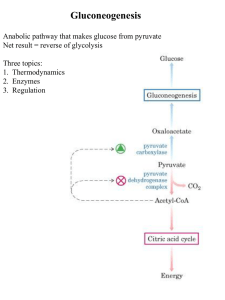
No Slide Title
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
Document
... A two-component system bacteria common / well-characterized key mechanism protein phosphorylation ...
... A two-component system bacteria common / well-characterized key mechanism protein phosphorylation ...
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
... Biochemistry and molecular biology AMPA receptors are pentameric assemblies of the four subunits GluR1–GluR4. Each subunit comprises approximately 900 amino acid residues and has a molecular weight of about 100 kDa. Sequence identity between the four subunits is around 70%. Alternative splicing of a ...
... Biochemistry and molecular biology AMPA receptors are pentameric assemblies of the four subunits GluR1–GluR4. Each subunit comprises approximately 900 amino acid residues and has a molecular weight of about 100 kDa. Sequence identity between the four subunits is around 70%. Alternative splicing of a ...