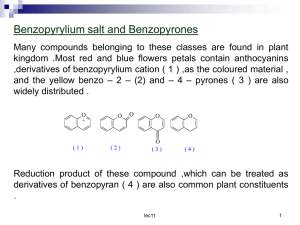
Lactobacillus sanfrancisco a key sourdough lactic acid bacterium: a
... source and fructose as an additional electron acceptor, thereby obtaining an optimal growth rate (Axelsson 1993). The action of fructose as electron acceptor occurs via its reduction to mannitol accompanied by a decrease in the level of ethanol, which is normally produced from the degradation of mal ...
... source and fructose as an additional electron acceptor, thereby obtaining an optimal growth rate (Axelsson 1993). The action of fructose as electron acceptor occurs via its reduction to mannitol accompanied by a decrease in the level of ethanol, which is normally produced from the degradation of mal ...
A New Species of Actinomycete, Amycolata alni
... strains received by us as Amycolata autotrophica have been studied and described in detail previously (1, 14, 18, 19, 29). In particular, the strains isolated from alder associations were characterized by their ability to divide swollen hyphal fragments in transverse and longitudinal planes (1, 18, ...
... strains received by us as Amycolata autotrophica have been studied and described in detail previously (1, 14, 18, 19, 29). In particular, the strains isolated from alder associations were characterized by their ability to divide swollen hyphal fragments in transverse and longitudinal planes (1, 18, ...
Photorespiration in C4 grasses remains slow under drought
... the leaves may decrease because of decreased stomatal conductance and should cause photorespiration to increase. Mechanistic modelling of C4 photosynthesis is not used as frequently as that of C3 photosynthesis, mostly because of the additional complexity resulting from the structural and biochemica ...
... the leaves may decrease because of decreased stomatal conductance and should cause photorespiration to increase. Mechanistic modelling of C4 photosynthesis is not used as frequently as that of C3 photosynthesis, mostly because of the additional complexity resulting from the structural and biochemica ...
Mechanistic studies on the diazo transfer reaction
... roles in a variety of chemical transformations which include the celebrated copper catalyzed ‘click’ reaction.1,2 An azide plays the role of a protecting group for amines as it can be readily reduced to regenerate the amine3, or converted to an amide4 or a carbamate5,6 using the Staudinger reaction. ...
... roles in a variety of chemical transformations which include the celebrated copper catalyzed ‘click’ reaction.1,2 An azide plays the role of a protecting group for amines as it can be readily reduced to regenerate the amine3, or converted to an amide4 or a carbamate5,6 using the Staudinger reaction. ...
Lecture 1 - "Hudel" Luecke
... Proteins are very complicated moleucules. With 20 different amino acids that can be arranged in any order to make a polypeptide of up to thousands of amino acids long, their potential for variety is extraordinary. This variety allows proteins to function as exquisitely specific enzymes that compose ...
... Proteins are very complicated moleucules. With 20 different amino acids that can be arranged in any order to make a polypeptide of up to thousands of amino acids long, their potential for variety is extraordinary. This variety allows proteins to function as exquisitely specific enzymes that compose ...
Maillard Browning in Ethanolic Solution
... solvent. Studies in nonaqueous systems are rare. In aqueous systems, the key chemical components that directly influence the progress of the Maillard reaction are sugars and amino acids. Del Pilar Buera and others (1987) compared the activities of various monosaccharides and disaccharides below pH 6 ...
... solvent. Studies in nonaqueous systems are rare. In aqueous systems, the key chemical components that directly influence the progress of the Maillard reaction are sugars and amino acids. Del Pilar Buera and others (1987) compared the activities of various monosaccharides and disaccharides below pH 6 ...
Structure, mechanism and regulation of pyruvate carboxylase
... catalyses the HCO3 − - and MgATP-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate. This is a very important anaplerotic reaction, replenishing oxaloacetate withdrawn from the tricarboxylic acid cycle for various pivotal biochemical pathways. PC is therefore considered as an enzyme that is cr ...
... catalyses the HCO3 − - and MgATP-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate. This is a very important anaplerotic reaction, replenishing oxaloacetate withdrawn from the tricarboxylic acid cycle for various pivotal biochemical pathways. PC is therefore considered as an enzyme that is cr ...
... h. Plasma glutamine concentrations increased by 40% (p< 0.01) after 12 h of fasting and declined thereafter, although values remained higher than baseline after 24 and 48 of fasting. Tyrosine and phenylalanine, which are viewed as markers of muscle catabolism, increased significantly with fasting, w ...
Time course of differential mitochondrial energy metabolism
... In the heart, mitochondria provide, through oxidative phosphorylation, more than 95% of the energy supply in the form of ATP. In the course of oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred through the respiratory enzymatic complexes of the mitochondrial inner membrane, thus releasing energy u ...
... In the heart, mitochondria provide, through oxidative phosphorylation, more than 95% of the energy supply in the form of ATP. In the course of oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred through the respiratory enzymatic complexes of the mitochondrial inner membrane, thus releasing energy u ...
Assessment of the mosaic structure in the
... highly abundant amplicons, present in the initial amplification derived from H. pylori HJM18MDA-DNA, were detectable by CGE. Numerous PCR amplification assays have been described for the identification of the CagA EPIYA/T phosphorylation motif, including multiple PCR amplification steps and ethidium ...
... highly abundant amplicons, present in the initial amplification derived from H. pylori HJM18MDA-DNA, were detectable by CGE. Numerous PCR amplification assays have been described for the identification of the CagA EPIYA/T phosphorylation motif, including multiple PCR amplification steps and ethidium ...
Chondroitinase ABC I from Proteus vulgaris: cloning, recombinant
... matrix) and at the cell surface as constituents of proteoglycans. These sugars, apart from having important structural roles in the ECM, are also fundamental modulators of many biological processes, such as development, cell proliferation, signalling and inflammation [1–3]. The great chemical hetero ...
... matrix) and at the cell surface as constituents of proteoglycans. These sugars, apart from having important structural roles in the ECM, are also fundamental modulators of many biological processes, such as development, cell proliferation, signalling and inflammation [1–3]. The great chemical hetero ...
Biosynthesis of Glucosyl Glycerol, a Compatible Solute, Using
... that the suh gene from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines, a causative agent of bacterial pustule disease in soybeans, showed a very strong deduced amino acid homology with various ASases [17]. However, it only displayed sucrose hydrolysis activity without any glucosyltransferase or isomerization a ...
... that the suh gene from Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines, a causative agent of bacterial pustule disease in soybeans, showed a very strong deduced amino acid homology with various ASases [17]. However, it only displayed sucrose hydrolysis activity without any glucosyltransferase or isomerization a ...
Vitamin - definition
... while lacto-ovo vegetarians usually get enough B12 through consuming diary products, vegan will lack B12 ...
... while lacto-ovo vegetarians usually get enough B12 through consuming diary products, vegan will lack B12 ...
Glycogen Mobilization: Glycogenolysis
... The liver releases glucose to the blood to be taken up by brain and active muscle. The liver regulates blood glucose levels. The muscle retains glucose 6-phosphate to be use for energy. Phosphorylated glucose is not transported out of muscle cells. ...
... The liver releases glucose to the blood to be taken up by brain and active muscle. The liver regulates blood glucose levels. The muscle retains glucose 6-phosphate to be use for energy. Phosphorylated glucose is not transported out of muscle cells. ...
disturbances of metabolic homeostasis in liver disease
... The main gluconeogenic precursors are lactate, pyruvate, glucogenic aminoacids (primarily alanine, glutamine, glutamate and glycine) and glycerol. Lactate and pyru vate provide approximately half of the precursor requirernent. Some of this lactate, about half, is derived from giucose (the Cori cycle ...
... The main gluconeogenic precursors are lactate, pyruvate, glucogenic aminoacids (primarily alanine, glutamine, glutamate and glycine) and glycerol. Lactate and pyru vate provide approximately half of the precursor requirernent. Some of this lactate, about half, is derived from giucose (the Cori cycle ...
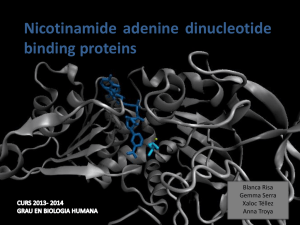
NAD - SBI
... • NAD-binding proteins show small sequence identity. • The overall topologies of the NAD-binding domain show variations. Not all the 6 strands are essential to NAD- binding. • There is a minimum structure conserved in most proteins: first motif (βαβαβ) and β4. β1 and β4 are located in the center of ...
... • NAD-binding proteins show small sequence identity. • The overall topologies of the NAD-binding domain show variations. Not all the 6 strands are essential to NAD- binding. • There is a minimum structure conserved in most proteins: first motif (βαβαβ) and β4. β1 and β4 are located in the center of ...
Different packing of external residues can explain differences in the
... Results: A unique database of 373 structurally well-aligned protein pairs from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms is constructed. Comparison of proteins from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms has shown that the external, water-accessible residues of the first group are more closely packed tha ...
... Results: A unique database of 373 structurally well-aligned protein pairs from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms is constructed. Comparison of proteins from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms has shown that the external, water-accessible residues of the first group are more closely packed tha ...
Mechanism of the Inhibitory Action of Linoleic Acid on
... measured by monitoring the incorporation of [2-14C]thymidine, [5-SH]uracil, [2-3H]glycine, L - [ U - ~ ~ C ] phenylalanine and [2-3H]glycerol,respectively, into material precipitated by ice-cold 5 % (w/v) trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Since glycine is incorporated into both cell wall and protein, but ...
... measured by monitoring the incorporation of [2-14C]thymidine, [5-SH]uracil, [2-3H]glycine, L - [ U - ~ ~ C ] phenylalanine and [2-3H]glycerol,respectively, into material precipitated by ice-cold 5 % (w/v) trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Since glycine is incorporated into both cell wall and protein, but ...
Guide Kjeldahl
... (1849–1900) has been an internationally accepted standard. The method was introduced in 1883 at a meeting of the Danish Chemical Society by Johan Kjeldahl as a means to determine nitrogen in barley and yeast [1]. The method named after its inventor has since found wide-spread application in life sci ...
... (1849–1900) has been an internationally accepted standard. The method was introduced in 1883 at a meeting of the Danish Chemical Society by Johan Kjeldahl as a means to determine nitrogen in barley and yeast [1]. The method named after its inventor has since found wide-spread application in life sci ...
Transport and Utilization of Lipids in Insect Flight
... efficient exchange of DAG-depleted and DAG-enriched lipophorin species is an essential element of the lipophorin shuttle mechanism. Through ligand blotting techniques, a number of flight muscle membrane proteins were shown to bind to HDLp or LDLp, most prominently a 30-kDa protein. At present, it is ...
... efficient exchange of DAG-depleted and DAG-enriched lipophorin species is an essential element of the lipophorin shuttle mechanism. Through ligand blotting techniques, a number of flight muscle membrane proteins were shown to bind to HDLp or LDLp, most prominently a 30-kDa protein. At present, it is ...
DNA sequencing revealed a definitive
... Leu Phe Asn Met Tyr Leu Thr Arg Asp Arg Arg Hox 3.2 --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Hox 1.7 --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --XlHbox 6 --- --- --- --- -- --- --- --- --- --- --iab-7 --Ala --- Val Ser Lys Gin Lys --- ...
... Leu Phe Asn Met Tyr Leu Thr Arg Asp Arg Arg Hox 3.2 --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --Hox 1.7 --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --XlHbox 6 --- --- --- --- -- --- --- --- --- --- --iab-7 --Ala --- Val Ser Lys Gin Lys --- ...