Krebs cycle - biology.org.uk
... follows, Krebs cycle, also takes place here. Krebs cycle consists of a number of reactions which (in one turn of the cycle): produces two molecules of carbon dioxide produces one molecule of ATP reduces three molecules of NAD to NADH2 and reduces one molecule of FAD to FADH2 The chain of react ...
... follows, Krebs cycle, also takes place here. Krebs cycle consists of a number of reactions which (in one turn of the cycle): produces two molecules of carbon dioxide produces one molecule of ATP reduces three molecules of NAD to NADH2 and reduces one molecule of FAD to FADH2 The chain of react ...
Lipid metabolism
... producing acetyl CoA, NADH and FADH2 Site: in the mitochondria of all tissues particularly in the liver. So there is no fatty acid oxidation in RBCs which have no mitochondria Activation of fatty acids: Before its oxidation, fatty acid must be firstly activated. Long chain fatty acid (more than 12 c ...
... producing acetyl CoA, NADH and FADH2 Site: in the mitochondria of all tissues particularly in the liver. So there is no fatty acid oxidation in RBCs which have no mitochondria Activation of fatty acids: Before its oxidation, fatty acid must be firstly activated. Long chain fatty acid (more than 12 c ...
Document
... 1. Stem loop structure 2-3 does not result in transcriptional termination whole operon mRNA made. 2. What happens to the stalled ribosome? (i) Since the genes in the operon have their own start sites other ribosomes can come and translate those proteins (ii) Stalled ribosome can eventually either ...
... 1. Stem loop structure 2-3 does not result in transcriptional termination whole operon mRNA made. 2. What happens to the stalled ribosome? (i) Since the genes in the operon have their own start sites other ribosomes can come and translate those proteins (ii) Stalled ribosome can eventually either ...
VEN 124 Section IV
... Other Compounds The Lactic Acid Bacteria are capable of producing numerous other aroma compounds, especially from the degradation of amino acids. It is likely that some of these compounds are also being produced during growth in wine. ...
... Other Compounds The Lactic Acid Bacteria are capable of producing numerous other aroma compounds, especially from the degradation of amino acids. It is likely that some of these compounds are also being produced during growth in wine. ...
Theramine™ Product Information
... to satisfy metabolic demand. When needs are altered as in some types of pain syndromes, the usual rate of synthesis is no longer sufficient and these amino acids become conditionally essential, requiring that a supplemental amount be consumed. Histidine has also been considered nonessential for adul ...
... to satisfy metabolic demand. When needs are altered as in some types of pain syndromes, the usual rate of synthesis is no longer sufficient and these amino acids become conditionally essential, requiring that a supplemental amount be consumed. Histidine has also been considered nonessential for adul ...
DISCLAIMER: This lecture outline is intended to help you take notes
... - amino acids for protein synthesis - conversion to other metabolic intermediates - energy production - amino acid catabolism - removal of amino groups - transamination - one reaction - all parts of cell - ΔGo' ≈ 0 (reversible) - aminotransferases (or transaminases) - specific for α-ketoglutarate - ...
... - amino acids for protein synthesis - conversion to other metabolic intermediates - energy production - amino acid catabolism - removal of amino groups - transamination - one reaction - all parts of cell - ΔGo' ≈ 0 (reversible) - aminotransferases (or transaminases) - specific for α-ketoglutarate - ...
Powerpoint
... Damage to other targets induced by reactive intermediates of protein oxidation • Protein peroxides can induce damage to other proteins by: – Non-radical reactions (oxidation of Cys and Met residues) – Radical-mediated reactions ...
... Damage to other targets induced by reactive intermediates of protein oxidation • Protein peroxides can induce damage to other proteins by: – Non-radical reactions (oxidation of Cys and Met residues) – Radical-mediated reactions ...
Project Manual Bio3055 Metabolic Disease: Hypoxanthine
... Metabolic disease is a broad term that is generally used to describe diseases that result from enzyme deficiencies in either catabolic or biosynthesis pathways. When these enzyme deficiencies occur, there is not only a decrease in the products of the pathway, but the intermediates in the pathway als ...
... Metabolic disease is a broad term that is generally used to describe diseases that result from enzyme deficiencies in either catabolic or biosynthesis pathways. When these enzyme deficiencies occur, there is not only a decrease in the products of the pathway, but the intermediates in the pathway als ...
Histidine and tyrosine phosphorylation in pea mitochondria
... transduction pathways tyrosine phosphoproteins are typically found in the beginning of the signal pathway as membrane receptor kinases. Since the tyrosine phosphoproteins detected in this study were found to be membrane associated, it is possible that they represent mitochondrial receptor tyrosine k ...
... transduction pathways tyrosine phosphoproteins are typically found in the beginning of the signal pathway as membrane receptor kinases. Since the tyrosine phosphoproteins detected in this study were found to be membrane associated, it is possible that they represent mitochondrial receptor tyrosine k ...
Unit 04 Lecture Notes - Roderick Anatomy and Physiology
... • I can explain the process of Translation. (Where, what molecules are involved and why it’s important) ...
... • I can explain the process of Translation. (Where, what molecules are involved and why it’s important) ...
Chapter 21
... derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
... derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
Guideline for the investigation of hyperammonaemia
... • Inherited Defects of the Urea Cycle (Table 1) • Other Inherited Metabolic Disorders (Table 1) • Acquired (Table 2) The most common cause of raised plasma ammonia is artefactual due to poor sample collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sa ...
... • Inherited Defects of the Urea Cycle (Table 1) • Other Inherited Metabolic Disorders (Table 1) • Acquired (Table 2) The most common cause of raised plasma ammonia is artefactual due to poor sample collection or a delay in analysis. Plasma ammonia levels should be taken from a free flowing venous sa ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl
... derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
... derivatives have an acyl carbon bonded to a group Y that can leave A tetrahedral intermediate is formed and the leaving group is expelled to generate a new carbonyl compound, leading to substitution ...
Antioxidant Activity Associated with Lipid and Phenolic Mobilization
... related to the four tocopherols associated with vitamin E, but tocotrienols are less widely distributed in nature. Tocopherols naturally present in foods have been strongly correlated with the polyunsaturated fatty acid because it counteracts the potential oxidative deterioration caused by fats in t ...
... related to the four tocopherols associated with vitamin E, but tocotrienols are less widely distributed in nature. Tocopherols naturally present in foods have been strongly correlated with the polyunsaturated fatty acid because it counteracts the potential oxidative deterioration caused by fats in t ...
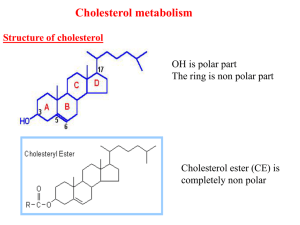
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... 1- Feed back inhibition by cholesterol: Cholesterol (the end product of the pathway) acts as feed back inhibitor of the pre-existing HMG –CoA reductase as well as inducing rapid degradation of the enzyme.. ...
... 1- Feed back inhibition by cholesterol: Cholesterol (the end product of the pathway) acts as feed back inhibitor of the pre-existing HMG –CoA reductase as well as inducing rapid degradation of the enzyme.. ...
Full Text - Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health
... acid; Gly, glycine; His, histidine; Ile, isoleucine; Leu, leucine; Lys, lysine Orn, ornithine; Phe, phenylalanine; Ser, serine; Thr, threonine; Tyr, tyrosine; Val, valine. ...
... acid; Gly, glycine; His, histidine; Ile, isoleucine; Leu, leucine; Lys, lysine Orn, ornithine; Phe, phenylalanine; Ser, serine; Thr, threonine; Tyr, tyrosine; Val, valine. ...
review nitrogen excretion: three end products
... acid in the liver. In animals that are very sensitive to ammonia, such as mammals, ammonia is transported in the blood as glutamine, before it is converted to urea for excretion. In addition to amino acid catabolism, nitrogenous end products may also result from purine, methylamine and creatine meta ...
... acid in the liver. In animals that are very sensitive to ammonia, such as mammals, ammonia is transported in the blood as glutamine, before it is converted to urea for excretion. In addition to amino acid catabolism, nitrogenous end products may also result from purine, methylamine and creatine meta ...
ppt
... Regulation matches function (tissue-specific differences) Often at rate-limiting step, slowest step Often first committed step of pathway, or branchpoint Regulatory enzymes often catalyze physiological irreversible reactions (differ in catabolic, biosynthetic paths) • Often feedback regulation by en ...
... Regulation matches function (tissue-specific differences) Often at rate-limiting step, slowest step Often first committed step of pathway, or branchpoint Regulatory enzymes often catalyze physiological irreversible reactions (differ in catabolic, biosynthetic paths) • Often feedback regulation by en ...
Acidaminococcus fermentans type strain (VR4T)
... of Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at http://www.jgi.doe.gov/. 454 Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler version 2.0.0-PostRelease11/04/2008 (Roche). Large Newbler contigs were broken into 2,561 ov ...
... of Sanger and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at http://www.jgi.doe.gov/. 454 Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler version 2.0.0-PostRelease11/04/2008 (Roche). Large Newbler contigs were broken into 2,561 ov ...
Structure-Based Prediction of DNA Target Sites by Regulatory Proteins
... whereas possible acceptors are A N7 and N3, T O4 and O2, G N7, N3 and O6, C O2, protein backbone oxygen atoms and Asp OD1, Asp OD2, Cys SG, Glu OE1, Glu OE2, Gln OE2, His ND1, Met SD, Asn OD1, Gln OE1, Ser OG, Thr OG1, and Tyr OH. We have also examined radial distributions of hydrophobic amino-acid ...
... whereas possible acceptors are A N7 and N3, T O4 and O2, G N7, N3 and O6, C O2, protein backbone oxygen atoms and Asp OD1, Asp OD2, Cys SG, Glu OE1, Glu OE2, Gln OE2, His ND1, Met SD, Asn OD1, Gln OE1, Ser OG, Thr OG1, and Tyr OH. We have also examined radial distributions of hydrophobic amino-acid ...
Source
... The use of industrial alcohol in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and fragrances product are permissible (National Islamic Fatwa Council of Malaysia,1984) However there are some of the cosmetic products use the alcohol from intoxicating beverage as the ingredient ▫ Eg. Alcohol from sake, pitera (yeast) fr ...
... The use of industrial alcohol in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and fragrances product are permissible (National Islamic Fatwa Council of Malaysia,1984) However there are some of the cosmetic products use the alcohol from intoxicating beverage as the ingredient ▫ Eg. Alcohol from sake, pitera (yeast) fr ...
alignment-2005
... • The count matrix is used to estimate a mutation matrix at 1 PAM (evolutionary unit) • From the mutation matrix, a Dayhoff scoring matrix is constructed • This Dayhoff matrix along with a model of indel events is then used to score new alignments which can then be used in an iterative process to ...
... • The count matrix is used to estimate a mutation matrix at 1 PAM (evolutionary unit) • From the mutation matrix, a Dayhoff scoring matrix is constructed • This Dayhoff matrix along with a model of indel events is then used to score new alignments which can then be used in an iterative process to ...