2.3 Cellular Transport
... work on the diffusion problems. • First try to do this by yourself, then verify your answers with a partner. Try to help each other. If you are confused, raise your hand and I will come help you!! • If you finish early, try to answer the “Think about it” questions on my desk! If you don’t ...
... work on the diffusion problems. • First try to do this by yourself, then verify your answers with a partner. Try to help each other. If you are confused, raise your hand and I will come help you!! • If you finish early, try to answer the “Think about it” questions on my desk! If you don’t ...
VOCAB Chapter 7
... Process that REQUIRES ENERGY to move molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient (moves molecules from lower concentration → higher concentration) PASSIVE TRANSPORT: Process that moves molecules across a cell membrane WITHOUT USING ENERGY DIFFUSION: Process by which molecules t ...
... Process that REQUIRES ENERGY to move molecules across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient (moves molecules from lower concentration → higher concentration) PASSIVE TRANSPORT: Process that moves molecules across a cell membrane WITHOUT USING ENERGY DIFFUSION: Process by which molecules t ...
Organelles of the Plant Cell - University of Central Oklahoma
... Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
... Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
Cell Structure and Function - Crossword
... Assignment 1 PBG311 Cell Structure and Function - Crossword ...
... Assignment 1 PBG311 Cell Structure and Function - Crossword ...
AP Biology
... 11) Define and contrast the following terms: membrane potential, electrochemical gradient, electrogenic pump and proton pump. membrane potential: electrochemical gradient: electrogenic pump: proton pump: ...
... 11) Define and contrast the following terms: membrane potential, electrochemical gradient, electrogenic pump and proton pump. membrane potential: electrochemical gradient: electrogenic pump: proton pump: ...
Centriole organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division
... Used for movement/moving substances around outside of the cell ...
... Used for movement/moving substances around outside of the cell ...
Eukaryotic cells .................................... and
... Sugar produced by photosynthesis is then used by ………………………………….. to make ……………… ...
... Sugar produced by photosynthesis is then used by ………………………………….. to make ……………… ...
Cells Study Guide - Little Miami Schools
... The structure of cell membrane. What factors determine if a molecule move through the membrane or must move through a transport protein. --semi-permeable (also known as selectively permeable). Solutions—solute, solvent, concentration, concentration gradient Diffusion--depends on random particle move ...
... The structure of cell membrane. What factors determine if a molecule move through the membrane or must move through a transport protein. --semi-permeable (also known as selectively permeable). Solutions—solute, solvent, concentration, concentration gradient Diffusion--depends on random particle move ...
4-2: Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell
... Prominent in cells that export large amounts of proteins from the cell or use in cell ...
... Prominent in cells that export large amounts of proteins from the cell or use in cell ...
Chapter 3 Vocabulary
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
Name: Period: Cell Membrane Review 1. The cell membrane needs
... C. What would happen to the cell if there was no cell membrane? (Do not say, “it would die”). A) Balanced internal condition of cells. B) Regulates materials inside and outside the cell. C) Things would be able to move freely in and out the cell, including organelles, toxins, etc. ...
... C. What would happen to the cell if there was no cell membrane? (Do not say, “it would die”). A) Balanced internal condition of cells. B) Regulates materials inside and outside the cell. C) Things would be able to move freely in and out the cell, including organelles, toxins, etc. ...
MEMBRANA BACTERIAS ARQUEAS
... means that for many Archaea, the membrane is not a fluid mosaic, but a more solid gel mosaic. ...
... means that for many Archaea, the membrane is not a fluid mosaic, but a more solid gel mosaic. ...
Chapter 2 Review 1. What is the difference between the cell
... membrane 19. Jelly-like substance that contains all organelles. E - cytoplasm 20. Working part of the cell. C - organelle 21. Breaks down food in cell and makes energy; powerhouse of the cell H mitochondria 22. Found in nucleus, contains genes L - DNA 23. Command center of the cell B - nucleus 24. T ...
... membrane 19. Jelly-like substance that contains all organelles. E - cytoplasm 20. Working part of the cell. C - organelle 21. Breaks down food in cell and makes energy; powerhouse of the cell H mitochondria 22. Found in nucleus, contains genes L - DNA 23. Command center of the cell B - nucleus 24. T ...
Nervous System Review
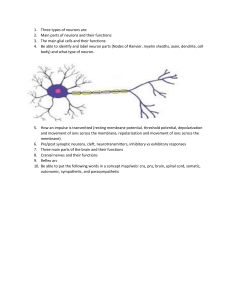
... Three types of neurons are: Main parts of neurons and their functions: The main glial cells and their functions: Be able to identify and label neuron parts (Nodes of Ranvier, myelin sheaths, axon, dendrite, cell body) and what type of neuron. ...
... Three types of neurons are: Main parts of neurons and their functions: The main glial cells and their functions: Be able to identify and label neuron parts (Nodes of Ranvier, myelin sheaths, axon, dendrite, cell body) and what type of neuron. ...
Kingdom Monera - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... pressure), chromatin, cytoplasm, capsule (protects the cell from our immune system/viruses), and flagellas. No other structures (ER, vacuoles, etc.) are present. The only organelle is the ribosome. Cellular respiration takes place along the inside surface of the cell membrane. Bacterial nutrition Tw ...
... pressure), chromatin, cytoplasm, capsule (protects the cell from our immune system/viruses), and flagellas. No other structures (ER, vacuoles, etc.) are present. The only organelle is the ribosome. Cellular respiration takes place along the inside surface of the cell membrane. Bacterial nutrition Tw ...
Chapter 5 Cell Membrane
... nonpolar hydrophobic tail • Hydrogen bonds form between the phospholipid "heads" and the watery environment inside and outside of the cell Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded i ...
... nonpolar hydrophobic tail • Hydrogen bonds form between the phospholipid "heads" and the watery environment inside and outside of the cell Hydrophobic interactions force the "tails" to face inward Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid • Cholesterol embedded i ...
Chapt03 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... It is a ____________ bilayer. It is embedded with proteins that move in space. It contains ____________ for support. It contains carbohydrates on proteins and lipids. It is _____________________. ...
... It is a ____________ bilayer. It is embedded with proteins that move in space. It contains ____________ for support. It contains carbohydrates on proteins and lipids. It is _____________________. ...
Organelles and Transport
... 7. The direction of water movement across the cell membrane depends on the concentration of free water[ molecules / solutions ]. 8. A solution that causes a cell to swell is called a [ hypertonic / hypotonic] solution. 9. The process of taking material into the cell by infolding the cell membrane is ...
... 7. The direction of water movement across the cell membrane depends on the concentration of free water[ molecules / solutions ]. 8. A solution that causes a cell to swell is called a [ hypertonic / hypotonic] solution. 9. The process of taking material into the cell by infolding the cell membrane is ...
Body Cells
... Cell Membrane • aka: plasma membrane • Membrane separates the cell from its external environment and other cells • Regulates the passage or transport of certain molecules into and out of the cell. ...
... Cell Membrane • aka: plasma membrane • Membrane separates the cell from its external environment and other cells • Regulates the passage or transport of certain molecules into and out of the cell. ...
Course Outline
... Telophase. The separated daughter chromosomes uncoil. Segments of the nuclear envelope reform. Constriction of the cytoplasm occurs, which gives way to pull the daughter cells apart. III. Cellular exchange. Passage of substances through the plasma membrane. A. Passive movement - no expenditures of c ...
... Telophase. The separated daughter chromosomes uncoil. Segments of the nuclear envelope reform. Constriction of the cytoplasm occurs, which gives way to pull the daughter cells apart. III. Cellular exchange. Passage of substances through the plasma membrane. A. Passive movement - no expenditures of c ...
RG Transport Review 0910
... 8. Critical Thinking – The cell membrane regulate what enters and exits the cell. Most materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules water ...
... 8. Critical Thinking – The cell membrane regulate what enters and exits the cell. Most materials can pass through by diffusion, without a problem. The graph below shows the size of some molecules that need to move across the lipid bilayer. Size of Molecules water ...
MICROSCOPE - Use the cards to help identify the parts of the
... CELL TRANSPORT – Fill in. There are two types of cell transport: active and passive. Passive transport does not require energy. This type of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the ...
... CELL TRANSPORT – Fill in. There are two types of cell transport: active and passive. Passive transport does not require energy. This type of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the ...
BioCellsCh7through p. 180
... Cell Size is Limited In most cases, a living thing grows because it produces MORE cells An adult simply has more cells than an infant, not simply larger cells. WHY more cells, not larger cells? Remember—Membrane Function… How fast exchange occurs depends upon the SURFACE AREA of the cell BUT, how q ...
... Cell Size is Limited In most cases, a living thing grows because it produces MORE cells An adult simply has more cells than an infant, not simply larger cells. WHY more cells, not larger cells? Remember—Membrane Function… How fast exchange occurs depends upon the SURFACE AREA of the cell BUT, how q ...
AQA B2 ESQ - Bacterial vs Plant Cell ANS
... The DNA of the bacterial cell is labelled. Name the structure where DNA is found in the plant cell. Nucleus [1 mark] ...
... The DNA of the bacterial cell is labelled. Name the structure where DNA is found in the plant cell. Nucleus [1 mark] ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.