Cell Structure and Function Dr. Ehan Abdulhadi PhD in Microbology
... Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell Channels usually are transport proteins (aquaporins facilitate the movement of water) No energy is used ...
... Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell Channels usually are transport proteins (aquaporins facilitate the movement of water) No energy is used ...
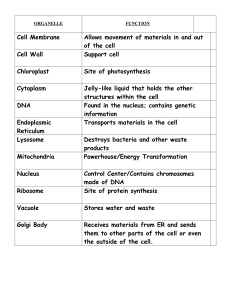
Cell Organelles - Bartlett High School
... rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
... rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
The Cell In Its Environment Slide Show Notes
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
Cell Membranes: Chapt. 6
... Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells contain an extensive intracellular membrane system. Membranes fence off the cell's interior from its surroundings. Membranes let in water, certain ions and substrates and they excrete waste substances. They act to protect the cell. ...
... Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells contain an extensive intracellular membrane system. Membranes fence off the cell's interior from its surroundings. Membranes let in water, certain ions and substrates and they excrete waste substances. They act to protect the cell. ...
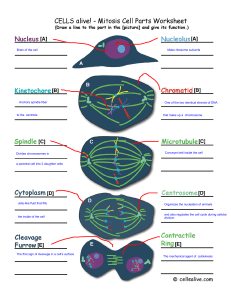
Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
Week 18 - Crossroads Academy
... • Prokaryotic cells lack true nuclei and other bodies bound by membranes. • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of flattene ...
... • Prokaryotic cells lack true nuclei and other bodies bound by membranes. • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of flattene ...
Lecture, Cell Membrane Structure and Function
... • A characteristic of cell membranes that allows it to regulate the passage of molecules • Selective permeability depends on the structure of the membrane • Not to be confused with semi-permeability – Dialysis tubing is semi-permeable. What characteristic allows molecules to travel through the membr ...
... • A characteristic of cell membranes that allows it to regulate the passage of molecules • Selective permeability depends on the structure of the membrane • Not to be confused with semi-permeability – Dialysis tubing is semi-permeable. What characteristic allows molecules to travel through the membr ...
Cell Transport Review Worksheet
... ________ Particle movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration _______ Process by which a cell expels wastes from a vacuole ________ A form of passive transport that uses proteins ________ Particle movement from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher c ...
... ________ Particle movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration _______ Process by which a cell expels wastes from a vacuole ________ A form of passive transport that uses proteins ________ Particle movement from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher c ...
Cellular Organization
... Consists of cells known as neurons Various parts to the cell such as the axon and the ...
... Consists of cells known as neurons Various parts to the cell such as the axon and the ...
Cell Parts Notes
... • Prokaryote = 1 celled organisms that lack a nucleus or other structures bound by a membrane. • They have been on Earth the Longest. ...
... • Prokaryote = 1 celled organisms that lack a nucleus or other structures bound by a membrane. • They have been on Earth the Longest. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... 2. As the amount of toxin increases around the outside of the three cubed shaped cells above, which size of “cell” would be the first to have an enriched concentration of toxin in its center (core) region? Explain your answer using the surface area to volume ratio. ...
... 2. As the amount of toxin increases around the outside of the three cubed shaped cells above, which size of “cell” would be the first to have an enriched concentration of toxin in its center (core) region? Explain your answer using the surface area to volume ratio. ...
Unit 4 Study Guide: Cell Membrane and Homeostasis Answer Key
... materials can travel through the lipid bilayer. Neither process requires energy. 5. Structure of the cell membrane is - lipid bilayer (flexible) - hydrophilic heads (outside membrane) attract water (water-loving) - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins m ...
... materials can travel through the lipid bilayer. Neither process requires energy. 5. Structure of the cell membrane is - lipid bilayer (flexible) - hydrophilic heads (outside membrane) attract water (water-loving) - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins m ...
Cell Membrane - Ms. Peterschick`s Classroom
... A few molecules, such as glucose, seem to pass through a cell membrane much more quickly than they should. How does this happen? ◦ Protein channels act as carriers, making it easy for certain molecules to pass. ◦ Red blood cells have membrane proteins with carrier channels that allow glucose to pass ...
... A few molecules, such as glucose, seem to pass through a cell membrane much more quickly than they should. How does this happen? ◦ Protein channels act as carriers, making it easy for certain molecules to pass. ◦ Red blood cells have membrane proteins with carrier channels that allow glucose to pass ...
Question Report
... evidence suggests two cell parts have evolved from early prokaryote ancestors. Name these 2 organelles and give an example of the evidence for this theory. ...
... evidence suggests two cell parts have evolved from early prokaryote ancestors. Name these 2 organelles and give an example of the evidence for this theory. ...
Concepts IV Cell Structure and Function
... 4. Describe the functions of the organelles: pages 175 – 181 Prentice Hall Biology or page 74 in HMH Biology Use notebook flashcards to do this. Include notebook page numbers here. 5. Identify the main roles of the cytoskeleton. 6. Identify the main functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall. ...
... 4. Describe the functions of the organelles: pages 175 – 181 Prentice Hall Biology or page 74 in HMH Biology Use notebook flashcards to do this. Include notebook page numbers here. 5. Identify the main roles of the cytoskeleton. 6. Identify the main functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall. ...
cell theory - Brookings School District
... Made mainly of _______________________ and _____________________ HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID ________________ with POLAR heads facing _______ and NON-POLAR tails facing ________ Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)= _____________ Proteins stuck ...
... Made mainly of _______________________ and _____________________ HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID ________________ with POLAR heads facing _______ and NON-POLAR tails facing ________ Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)= _____________ Proteins stuck ...
Chapter 5
... Passive Processes of Membrane Transport • Biological membranes are selectively permeable: allow some substances to pass, while others are restricted. • Some substances can move by Simple Diffusion: movement from high concentration to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion: passive movement of s ...
... Passive Processes of Membrane Transport • Biological membranes are selectively permeable: allow some substances to pass, while others are restricted. • Some substances can move by Simple Diffusion: movement from high concentration to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion: passive movement of s ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.