
cell test review
... • Review your notes on the steps and be able to tell what is happening in each picture in order. ...
... • Review your notes on the steps and be able to tell what is happening in each picture in order. ...
Plant and Animal Cells Study Sheet
... CCGPSS5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, single-celled, multicelled). b. Identify parts of a plant cell (membrane, wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell (membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus) and determine the function of the parts. Studen ...
... CCGPSS5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, single-celled, multicelled). b. Identify parts of a plant cell (membrane, wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell (membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus) and determine the function of the parts. Studen ...
Cell Practice Activity File
... B tissues C organs D organ systems 18. Groups of cells that work together to do a specific job are called____. A cells B tissues C organs D organisms ...
... B tissues C organs D organ systems 18. Groups of cells that work together to do a specific job are called____. A cells B tissues C organs D organisms ...
Passive Transport (Chapter 7.4)
... Equilibrium when the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space. materials moving out of the cell equals the materials moving into the cell. Concentration Gradient a difference in the concentration of a substance across a space food coloring example ...
... Equilibrium when the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space. materials moving out of the cell equals the materials moving into the cell. Concentration Gradient a difference in the concentration of a substance across a space food coloring example ...
Membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus that contains DNA
... Fungi, and Protists (everything except bacteria) ...
... Fungi, and Protists (everything except bacteria) ...
Cells Jeopardy
... These balloonlike spaces within the cytoplasm store waste and food and other substances the cell cannot use right away. ...
... These balloonlike spaces within the cytoplasm store waste and food and other substances the cell cannot use right away. ...
H ions
... Substances that cells need can be taken up from their surrounding either by passive or by active transport Passive transport: Moving molecules across the cell membrane, does not need energy Types: 1-Simple diffusion: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low con ...
... Substances that cells need can be taken up from their surrounding either by passive or by active transport Passive transport: Moving molecules across the cell membrane, does not need energy Types: 1-Simple diffusion: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low con ...
OBJECTIVE MASTERY CHECKLIST – Science 8th Grade Third
... _____ 1. Identify different cell types (plant cell, animal cell, bacterial cell). _____ 2. Identify cell organelles : (nucleus, cytoplasm, cell wall, mitochondrion, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, chloroplasts, lysosomes). _____ 3. Explain fun ...
... _____ 1. Identify different cell types (plant cell, animal cell, bacterial cell). _____ 2. Identify cell organelles : (nucleus, cytoplasm, cell wall, mitochondrion, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, chloroplasts, lysosomes). _____ 3. Explain fun ...
Cell Mates
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
Overall macromolecular composition of an average E. coli
... 1) Read “Order-of-Magnitude Biology Toolkit” and suggest one value you would like to see added to the list. 2) Choose one vignette to read from Chapter 2 of “Cell Biology by the Numbers” textbook, related to your research or to your fields of interest, and write us the title of the vignette you read ...
... 1) Read “Order-of-Magnitude Biology Toolkit” and suggest one value you would like to see added to the list. 2) Choose one vignette to read from Chapter 2 of “Cell Biology by the Numbers” textbook, related to your research or to your fields of interest, and write us the title of the vignette you read ...
a. Cell membrane
... d. all of these. 5. All living things are made up of ________________. a. cellulose b. chlorophyll c. chloroplasts d. cells. ...
... d. all of these. 5. All living things are made up of ________________. a. cellulose b. chlorophyll c. chloroplasts d. cells. ...
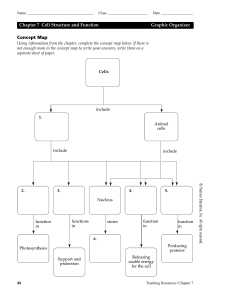
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
Notes Unit 2 Part 3 POWERPOINT
... can ______ • The cell membrane also plays a vital role in homeostasis by regulating what molecules can enter and ____ exit the cell ______ e.g. in = H2O, food out = waste, CO2 • selective permeability = the ability of the cell ___________ membrane to allow some materials to enter into a cell while k ...
... can ______ • The cell membrane also plays a vital role in homeostasis by regulating what molecules can enter and ____ exit the cell ______ e.g. in = H2O, food out = waste, CO2 • selective permeability = the ability of the cell ___________ membrane to allow some materials to enter into a cell while k ...
Cell Physiology [PPT]
... also known as plasma membrane or plasma lemma selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and ...
... also known as plasma membrane or plasma lemma selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and ...
The Living Cell
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
VOCAB Chapter 7
... passageway/tunnel across the cell membrane through which WATER molecules can diffuse PASSIVELY during osmosis ______ A small membrane bound sac in a eukaryotic cell used to transport substances around within a cell or contain them during exocytosis or endocytosis ...
... passageway/tunnel across the cell membrane through which WATER molecules can diffuse PASSIVELY during osmosis ______ A small membrane bound sac in a eukaryotic cell used to transport substances around within a cell or contain them during exocytosis or endocytosis ...
Review sheet – Chapter 5
... Understand that active transport allows cells or organelles to maintain concentrations of molecules that are different than their surroundings Know that pinocytosis and phagocytosis are two forms of endocytosis; a way to transport molecules against their concentration gradients involving an engulfin ...
... Understand that active transport allows cells or organelles to maintain concentrations of molecules that are different than their surroundings Know that pinocytosis and phagocytosis are two forms of endocytosis; a way to transport molecules against their concentration gradients involving an engulfin ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CELL ORGANELLE
... After packaging the vesicles bud off and immediately move towards the plasma membrane. Where they fuse and release the contents into the extracellular space in a process known as constitutive secretion. Antibodies release by activated plasma B cells. Secretory vesicles Vesicle contains pro ...
... After packaging the vesicles bud off and immediately move towards the plasma membrane. Where they fuse and release the contents into the extracellular space in a process known as constitutive secretion. Antibodies release by activated plasma B cells. Secretory vesicles Vesicle contains pro ...
Cell Structure and Functions
... (DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4) Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are ...
... (DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4) Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are ...
File
... 11. What is matter and what is it made of? 12. Draw and label the parts of an atom. Make sure to label the protons, neutrons, electrons, and put their charges. 13. Give a sample chemical equation and label its products and reactants. 14. Describe the structure and function of water. 15. Explain the ...
... 11. What is matter and what is it made of? 12. Draw and label the parts of an atom. Make sure to label the protons, neutrons, electrons, and put their charges. 13. Give a sample chemical equation and label its products and reactants. 14. Describe the structure and function of water. 15. Explain the ...
The Unit of Life — Cells - Singapore Asia Publishers
... • Both have cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus and vacuole(s). ...
... • Both have cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus and vacuole(s). ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.














![Cell Physiology [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000836372_1-f01c4ac0aa1884121950a80d4cb7cd49-300x300.png)







