Episode 21
... A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two molecules that have the same formula but have different structures. 8. How are organic compounds divided into categories? By functional groups. 9. How are esters used? Flavorings and scents. 10. What were the “in ...
... A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two molecules that have the same formula but have different structures. 8. How are organic compounds divided into categories? By functional groups. 9. How are esters used? Flavorings and scents. 10. What were the “in ...
Episode 21
... A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two molecules that have the same formula but have different structures. 8. How are organic compounds divided into categories? By functional groups. 9. How are esters used? Flavorings and scents. 10. What were the “in ...
... A compound formed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms. 7. What is meant by an isomer? Two molecules that have the same formula but have different structures. 8. How are organic compounds divided into categories? By functional groups. 9. How are esters used? Flavorings and scents. 10. What were the “in ...
aciee-2004-43-5442-palomo
... amino alcohol ligands[15] and macrocyclic thioaza ligands[16] have been described for the Henry reaction. Because the results are still poor, future developments in the area can be expected. In an important recent report, Evans et al.[17] have formulated that weakly Lewis acidic metal complexes bear ...
... amino alcohol ligands[15] and macrocyclic thioaza ligands[16] have been described for the Henry reaction. Because the results are still poor, future developments in the area can be expected. In an important recent report, Evans et al.[17] have formulated that weakly Lewis acidic metal complexes bear ...
Carbohydrates
... dependent on intermolecular forces, which are the same since enantiomers possess the same functional groups. – Enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents, but different solubility in a chiral solvent. – Reaction rates involving chiral reactants are the same when the second reactant is ...
... dependent on intermolecular forces, which are the same since enantiomers possess the same functional groups. – Enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents, but different solubility in a chiral solvent. – Reaction rates involving chiral reactants are the same when the second reactant is ...
Organic Chemistry –Syllabus- one Semester Sackler faculty of
... double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cyclohexane, Combustion of alk ...
... double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cyclohexane, Combustion of alk ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
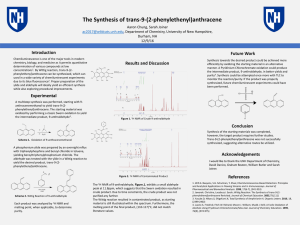
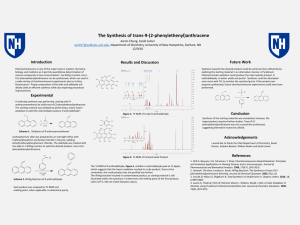
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
... [email protected], Department of Chemistry, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH ...
... [email protected], Department of Chemistry, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH ...
Chapter 17_CHEM 131
... • The enantiomer that rotates polarized light to the left is the levorotatory or (-) enantiomer. • The enantiomer that rotates it to the right is the dextrorotatory or (+) enantiomer. • The D and L designations do not represent dextrorotatory and levorotatory. • The property of rotating the plane of ...
... • The enantiomer that rotates polarized light to the left is the levorotatory or (-) enantiomer. • The enantiomer that rotates it to the right is the dextrorotatory or (+) enantiomer. • The D and L designations do not represent dextrorotatory and levorotatory. • The property of rotating the plane of ...
Scheme I a la 2a 3a d ~ ~`~ .~ff 3 4a 5a
... derivatives in CDCI3 .t2 (R)-(+)-a-methoxy-a-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetic acid adducts of racemic ctmethylamines, prepared under standard coupling conditions (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino)propylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole), display well-separated ct-methoxy proton absorbances. ...
... derivatives in CDCI3 .t2 (R)-(+)-a-methoxy-a-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetic acid adducts of racemic ctmethylamines, prepared under standard coupling conditions (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino)propylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole), display well-separated ct-methoxy proton absorbances. ...
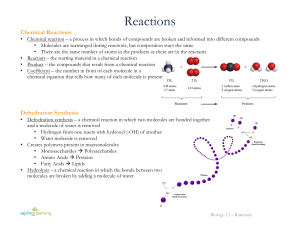
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
... In these reactions, two different molecules or atoms combine to form a single substance. ...
Final Exam from 2006 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... amine group in compound A was neutralized with HCl to produce structure B, an ammonium ...
... amine group in compound A was neutralized with HCl to produce structure B, an ammonium ...
asymmetric alkyne addition to aldehydes
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
... Chiral propargylic alcohols are important compounds, as this structural motif is often found in pharmaceutical compounds as well as natural products and can also serve as versatile synthetic intermediates.1 Although there are many methods available for the preparation of these compounds (e.g. asymme ...
Chapter 1 Chirality in clinical analysis 1.1. Introduction
... Three primary sources are reported as sources for chiral compounds [12]: 1. isolation of naturally occurring molecules through extraction from plant materials; 2. fermentation of inexpensive available feed stocks using de novo techniques; ...
... Three primary sources are reported as sources for chiral compounds [12]: 1. isolation of naturally occurring molecules through extraction from plant materials; 2. fermentation of inexpensive available feed stocks using de novo techniques; ...
Additional file 1
... BPR1P034): Hydrazide 5 (0.5 g, 1.2 mmol) and o-nitrophenyl carbaxaldehyde (0.19 g, 1.3 ...
... BPR1P034): Hydrazide 5 (0.5 g, 1.2 mmol) and o-nitrophenyl carbaxaldehyde (0.19 g, 1.3 ...
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Practice
... 1. The JOINING of two monomers causes a water molecule to be lost. This joining to make a polymer is called _______________________. 2. The SPLITTING apart of two organic molecules in a polymer and ...
... 1. The JOINING of two monomers causes a water molecule to be lost. This joining to make a polymer is called _______________________. 2. The SPLITTING apart of two organic molecules in a polymer and ...
Programma Inglese XXXII Scuola Corbella
... Non-heme iron oxidation catalysis: from bioinspiration to practical application ...
... Non-heme iron oxidation catalysis: from bioinspiration to practical application ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Constitution, configuration and conformation Specifying stereochemistry - CIP notation, Fischer convention Chirality as a property of matter Enantiomeric relationships Enantiomeric excess (ee), optical activity - how to determine it Origin of chirality - asymmetric carbon atom, asymmetric heteroatom ...
... Constitution, configuration and conformation Specifying stereochemistry - CIP notation, Fischer convention Chirality as a property of matter Enantiomeric relationships Enantiomeric excess (ee), optical activity - how to determine it Origin of chirality - asymmetric carbon atom, asymmetric heteroatom ...
Carbohydrate Structure
... 70-80% human energy needs (US~50%) >90% dry matter of plants Monomers and polymers Functional properties – Sweetness – Chemical reactivity – Polymer functionality ...
... 70-80% human energy needs (US~50%) >90% dry matter of plants Monomers and polymers Functional properties – Sweetness – Chemical reactivity – Polymer functionality ...
Chapter 17 – Stereoisomerism
... is in molecules possessing tetrahedral carbons with 4 different groups attached. Remember that any carbon with four different groups attached is chiral. This property of optically active molecules was discovered in 1815 by Jean-Baptiste Biot, but remained an unexplained curiosity until a very famous ...
... is in molecules possessing tetrahedral carbons with 4 different groups attached. Remember that any carbon with four different groups attached is chiral. This property of optically active molecules was discovered in 1815 by Jean-Baptiste Biot, but remained an unexplained curiosity until a very famous ...
Carbohydrate Structure
... 70-80% human energy needs (US~50%) >90% dry matter of plants Monomers and polymers Functional properties – Sweetness – Chemical reactivity – Polymer functionality ...
... 70-80% human energy needs (US~50%) >90% dry matter of plants Monomers and polymers Functional properties – Sweetness – Chemical reactivity – Polymer functionality ...
File
... • A protein with a D amino acid instead of L will have its R group sticking out in the wrong direction. • Many other kinds of organic molecules exist as enantiomers. Usually only one form is active in biological systems. For example, if one form binds to a receptor protein on the surface of a cell, ...
... • A protein with a D amino acid instead of L will have its R group sticking out in the wrong direction. • Many other kinds of organic molecules exist as enantiomers. Usually only one form is active in biological systems. For example, if one form binds to a receptor protein on the surface of a cell, ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.