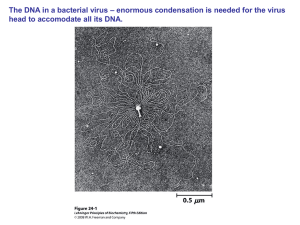
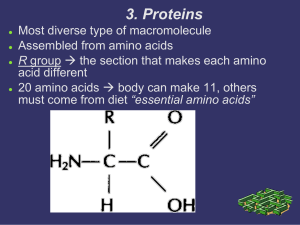
Examples and Nonexamples
... 3. Changes in a species occur through mutations in DNA that happen in a sperm or egg cell. 4. All mutations in DNA that occur in sperm or egg cells result in a change in the phenotype of the offspring. 5. An example of natural selection would be if an organism had a mutation in its DNA that occurred ...
... 3. Changes in a species occur through mutations in DNA that happen in a sperm or egg cell. 4. All mutations in DNA that occur in sperm or egg cells result in a change in the phenotype of the offspring. 5. An example of natural selection would be if an organism had a mutation in its DNA that occurred ...
Factor VIII Inhibitor
... Colchicine is not as effective Responsive to corticosteroids and intermittent use of NSAIDS. These do not address risk and complications from amyloid TNF blockers are now being evaluated with promising results in reduction of amyloid ...
... Colchicine is not as effective Responsive to corticosteroids and intermittent use of NSAIDS. These do not address risk and complications from amyloid TNF blockers are now being evaluated with promising results in reduction of amyloid ...
Genetic Disorders
... disc-shaped, become crescent shaped. As a result, they function abnormally and cause small blood clots. These clots give rise to recurrent painful episodes called "sickle cell pain crises". ...
... disc-shaped, become crescent shaped. As a result, they function abnormally and cause small blood clots. These clots give rise to recurrent painful episodes called "sickle cell pain crises". ...
Document
... them into surrogate mothers. The offspring are identical to each other, but NOT to either parent. Extinction When all members of a species die out, which may be due to changes in environment, new predators, new diseases or new competitors. Fossil Impression of dead animal or plant left behind in roc ...
... them into surrogate mothers. The offspring are identical to each other, but NOT to either parent. Extinction When all members of a species die out, which may be due to changes in environment, new predators, new diseases or new competitors. Fossil Impression of dead animal or plant left behind in roc ...
Practice Exam- KEY - mvhs
... 6. a) No. Protein will not be translated (at least not starting there) because there would no longer be a start codon. b) No. A frameshift will occur. This will change all the amino acids after K. There will no longer be the signal sequence, so the Stfn4 protein will not be secreted. c) Yes. GUG sta ...
... 6. a) No. Protein will not be translated (at least not starting there) because there would no longer be a start codon. b) No. A frameshift will occur. This will change all the amino acids after K. There will no longer be the signal sequence, so the Stfn4 protein will not be secreted. c) Yes. GUG sta ...
DNA Control (Protein Synthesis)
... 2. How do you get different types of cells? 3. In the song, what does “each cell recipe” really refer to? ...
... 2. How do you get different types of cells? 3. In the song, what does “each cell recipe” really refer to? ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... WINK SHEET— DNA Structure and Replication Theme: Each chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule. Each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of DNA. The chemical structure of DNA provides a mechanism that ensures that information is preserved and transferred to subsequent generations. ...
... WINK SHEET— DNA Structure and Replication Theme: Each chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule. Each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of DNA. The chemical structure of DNA provides a mechanism that ensures that information is preserved and transferred to subsequent generations. ...
What to know for First Semester Final
... What to know for First Semester Final (this is not exhaustive) ...
... What to know for First Semester Final (this is not exhaustive) ...
Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures
... Have to visualize gene (locus)/alleles/chromosomes/metaphase/chromatids segregating/gamete formation 1. Stretch of DNA that codes for a protein; in the middle of a bunch of bases that are not encoding 2. The location of that gene (sequence) relative to the chromosome it exists on 3. The specific cop ...
... Have to visualize gene (locus)/alleles/chromosomes/metaphase/chromatids segregating/gamete formation 1. Stretch of DNA that codes for a protein; in the middle of a bunch of bases that are not encoding 2. The location of that gene (sequence) relative to the chromosome it exists on 3. The specific cop ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... which amino acid to use • There are 64 codons that make up the information in the genetic code • Start @ start codon. End @ stop codon 1 start codon, 3 stop codons ...
... which amino acid to use • There are 64 codons that make up the information in the genetic code • Start @ start codon. End @ stop codon 1 start codon, 3 stop codons ...
Phenotypic variability of osteogenesis imperfecta is not accounted
... histories of more than 10 fractures before age 13 years, but three other members experienced no fracture. One son (II-1) had hearing loss from age 10 years and hip joint deformities due to repeated femoral fractures. We identified a dominant missense mutation, c.3235G>A in COL1A1 exon 45, in four pa ...
... histories of more than 10 fractures before age 13 years, but three other members experienced no fracture. One son (II-1) had hearing loss from age 10 years and hip joint deformities due to repeated femoral fractures. We identified a dominant missense mutation, c.3235G>A in COL1A1 exon 45, in four pa ...
30. genetic disorders 31. pedigree 32. Punnett Square
... detect birth defects such as Down syndrome, chromosome abnormalities, genetic diseases and other conditions, such as spina bifida, Tay Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, and cystic fibrosis. Screening can also determine the gender of the fetus. 3 types of fetal testing: 1. amniotic fluid sample (amn ...
... detect birth defects such as Down syndrome, chromosome abnormalities, genetic diseases and other conditions, such as spina bifida, Tay Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, and cystic fibrosis. Screening can also determine the gender of the fetus. 3 types of fetal testing: 1. amniotic fluid sample (amn ...
Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn McCarty 1928
... somatic cells had twice the DNA as gametes but gametes and somatic cells varied in its amount of protein. ...
... somatic cells had twice the DNA as gametes but gametes and somatic cells varied in its amount of protein. ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? 11. RNA contains the sugar _________. 12. List ...
... 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eukaryotic cell? 11. RNA contains the sugar _________. 12. List ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Provide groups of students (2-3 is best) with a student version of the β-globin gene map, a dry erase marker or highlighter, and the β-globin protein sequence. You may also wish to provide a codon chart. Ask them to find the protein sequence and highlight it on the gene strip. We suggest you answer ...
... Provide groups of students (2-3 is best) with a student version of the β-globin gene map, a dry erase marker or highlighter, and the β-globin protein sequence. You may also wish to provide a codon chart. Ask them to find the protein sequence and highlight it on the gene strip. We suggest you answer ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... 13. A DNA segment is changed from- AATTAG- toAAATAG. What kind of mutation is this? Point mutation (or substitution) 14. What four things can cause a mutation? o Mistakes in DNA replication o radiation o chemicals o high temperatures 15. Where does translation and transcription take place in the cel ...
... 13. A DNA segment is changed from- AATTAG- toAAATAG. What kind of mutation is this? Point mutation (or substitution) 14. What four things can cause a mutation? o Mistakes in DNA replication o radiation o chemicals o high temperatures 15. Where does translation and transcription take place in the cel ...
Biology Standards (For the Year) *DO NOT LOSE THIS!* CST
... increases the chances that at least some organisms can survive changes in an environment. 8c) Genetic drift through the Bottleneck Effect or the Founder Effect decreases the size of a gene pool and its diversity. This can decrease the chances of survival of the species. 8d) Speciation can occur due ...
... increases the chances that at least some organisms can survive changes in an environment. 8c) Genetic drift through the Bottleneck Effect or the Founder Effect decreases the size of a gene pool and its diversity. This can decrease the chances of survival of the species. 8d) Speciation can occur due ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.