DNA Function: Information Transmission
... ● Multicellular eukaryotes must also develop and maintain -each cell type contains the same genome but expresses a different subset of genes…how is this accomplished?? ● Gene expression in both eukaryotes & prokaryotes is often regulated at the stage of ...
... ● Multicellular eukaryotes must also develop and maintain -each cell type contains the same genome but expresses a different subset of genes…how is this accomplished?? ● Gene expression in both eukaryotes & prokaryotes is often regulated at the stage of ...
The Central Dogma Dry Lab
... Following is the base sequence of a gene on one strand of a DNA molecule (the SENSE STRAND): A A T G C C A G T G G T T C G C A C 1. What is the sequence of the complementary DNA strand (i.e. the NONSENSE STRAND)? 2. What is the sequence of the mRNA transcribed from this gene? 3. Use the provided gen ...
... Following is the base sequence of a gene on one strand of a DNA molecule (the SENSE STRAND): A A T G C C A G T G G T T C G C A C 1. What is the sequence of the complementary DNA strand (i.e. the NONSENSE STRAND)? 2. What is the sequence of the mRNA transcribed from this gene? 3. Use the provided gen ...
slides available - The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering
... • For recessive diseases 75% of the embryos will be normal • For dominant diseases 50% of the embryos will be normal • If one parent is homozygous mutant: 0% of embryos will be normal ...
... • For recessive diseases 75% of the embryos will be normal • For dominant diseases 50% of the embryos will be normal • If one parent is homozygous mutant: 0% of embryos will be normal ...
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) **Long molecule made up of units
... ***It is the order of the nitrogen bases that make up the genetic code*** DNA molecules are very long and must be folded into a space only one one-thousandth of its length. They are found in the nucleus of the cell. Example: ** The chromosome of a bacterial cell in the human colon contains 4,639,221 ...
... ***It is the order of the nitrogen bases that make up the genetic code*** DNA molecules are very long and must be folded into a space only one one-thousandth of its length. They are found in the nucleus of the cell. Example: ** The chromosome of a bacterial cell in the human colon contains 4,639,221 ...
Gene Mutation
... cultured in the absence of certain chemicals such as folic acid, which is normally present in the culture medium. ...
... cultured in the absence of certain chemicals such as folic acid, which is normally present in the culture medium. ...
Vocabulary:
... will be turned “on” or “off.” Say what? Our genes are like light switches? Kind of! Every cell in your body (with the exception of a few) has the same DNA. Your skin cell looks way ...
... will be turned “on” or “off.” Say what? Our genes are like light switches? Kind of! Every cell in your body (with the exception of a few) has the same DNA. Your skin cell looks way ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... transcriptase & fluorescent nucleotides are added cDNA is made from RNA cDNA is applied to well that contain DNA from a cell; cDNA will bind to DNA that is complementary in the wells Rinse unbound cDNA – fluorescent spots show DNA that is being expressed by the cell; no glow = unexpressed DNA ...
... transcriptase & fluorescent nucleotides are added cDNA is made from RNA cDNA is applied to well that contain DNA from a cell; cDNA will bind to DNA that is complementary in the wells Rinse unbound cDNA – fluorescent spots show DNA that is being expressed by the cell; no glow = unexpressed DNA ...
Document
... • Functionally related genes co-induced: – evidence for induction of specific biological pathways ...
... • Functionally related genes co-induced: – evidence for induction of specific biological pathways ...
13 Packet
... sequences, is called an operon. One control sequence, the promoter, is a binding site for an enzyme needed in DNA transcription. The other control sequence, the operator, switches the promoter on and off. A protein called the repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables pr ...
... sequences, is called an operon. One control sequence, the promoter, is a binding site for an enzyme needed in DNA transcription. The other control sequence, the operator, switches the promoter on and off. A protein called the repressor turns the operator off by binding to it. This process enables pr ...
Slide 1
... of reproductive cells (meiosis I) so that each cell gets one of the factors. Dominance: Sometimes one factor dominates the other factor. A dominant trait masks/suppresses the alternative (recessive) trait for a particular feature. Conversely, a recessive trait is masked or suppressed by the dominant ...
... of reproductive cells (meiosis I) so that each cell gets one of the factors. Dominance: Sometimes one factor dominates the other factor. A dominant trait masks/suppresses the alternative (recessive) trait for a particular feature. Conversely, a recessive trait is masked or suppressed by the dominant ...
Gene Section NET1 (neuroepithelial cell transforming gene 1) in Oncology and Haematology
... amino acid 387-503. The 596 amino acid sequence is: ...
... amino acid 387-503. The 596 amino acid sequence is: ...
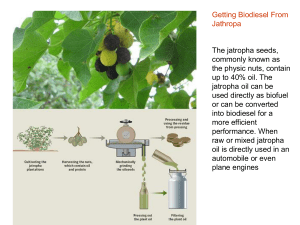
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics
... a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
... a 3-letter sequence called a CODON. • Each CODON specifies a SINGLE Amino Acid. • There is 1 start codon for initiation of protein synthesis and 3 stop codons for ending protein synthesis for a specific protein. • A given amino acid can have more than one codon sequence. ...
Sin título de diapositiva
... All the Genes • Any human gene can now be found in the genome by similarity searching with over 90% certainty. • However, the sequence still has many gaps – one is unlikely to find a complete and uninterrupted genomic segment for any gene – still can’t identify pseudogenes with certainty ...
... All the Genes • Any human gene can now be found in the genome by similarity searching with over 90% certainty. • However, the sequence still has many gaps – one is unlikely to find a complete and uninterrupted genomic segment for any gene – still can’t identify pseudogenes with certainty ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... Imagine two populations of squirrels on opposite sides of a river. The squirrels on the west side have bushier tails than those on the east side as a result of three different genes that code for tail bushiness. If a tree falls over the river and the squirrels are able to scamper across it to mate w ...
... Imagine two populations of squirrels on opposite sides of a river. The squirrels on the west side have bushier tails than those on the east side as a result of three different genes that code for tail bushiness. If a tree falls over the river and the squirrels are able to scamper across it to mate w ...
Adaptations homework - Kinross High School
... 2. a) Exposure to radiation can cause mutation. The pie chart below shows the contribution of various sources of radiation to the total exposure. ...
... 2. a) Exposure to radiation can cause mutation. The pie chart below shows the contribution of various sources of radiation to the total exposure. ...
Ch. 8 Power Point
... • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a gene. – Replication makes one copy; DNA transcription can make many copie ...
... • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a gene. – Replication makes one copy; DNA transcription can make many copie ...
DNA - hdueck
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.