Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... 27. Describe what determines whether a ribosome will be free in the cytosol or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. 28. Describe two properties of RNA that allow it to perform so many different functions. 29. Compare protein synthesis in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. 30. Define point mutati ...
... 27. Describe what determines whether a ribosome will be free in the cytosol or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. 28. Describe two properties of RNA that allow it to perform so many different functions. 29. Compare protein synthesis in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. 30. Define point mutati ...
Bio 262- Genetics Study Guide
... Recessive: Moving back and out of view. In genetics, a recessive gene is a gene that does not express its instructions when paired with a dominant gene. Recombination: The process by which progeny derive a combination of genes different from that of either parent. In higher organisms, this can occur ...
... Recessive: Moving back and out of view. In genetics, a recessive gene is a gene that does not express its instructions when paired with a dominant gene. Recombination: The process by which progeny derive a combination of genes different from that of either parent. In higher organisms, this can occur ...
molecular biology and phylogeny
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
Lecture ** - Telomeres
... SR: T loops and the origins of telomeres. (2004) T. de Lange Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biology 5: 323-329 The "problem" of linear chromosome ends: a) 5'->3' DNA replication of "lagging strand" b) How does cell discriminate between DNA double-strand breaks (which are also “ends”) and the natural ends of ...
... SR: T loops and the origins of telomeres. (2004) T. de Lange Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biology 5: 323-329 The "problem" of linear chromosome ends: a) 5'->3' DNA replication of "lagging strand" b) How does cell discriminate between DNA double-strand breaks (which are also “ends”) and the natural ends of ...
Replication Transcription Translation
... • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • 1 Strand DNA 2 Strands RNA • The primary enzyme involved in this process is RNA Polymerase ...
... • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • 1 Strand DNA 2 Strands RNA • The primary enzyme involved in this process is RNA Polymerase ...
Do Now: - South Orange
... Translation • Cell uses information from mRNA to produce proteins • tRNA will be our “translator” • mRNA “words” are read in 3 nucleotide sequences known as codons • tRNA has only one specific aa for every complimentary mRNA codon, known as an anticodon ...
... Translation • Cell uses information from mRNA to produce proteins • tRNA will be our “translator” • mRNA “words” are read in 3 nucleotide sequences known as codons • tRNA has only one specific aa for every complimentary mRNA codon, known as an anticodon ...
Advance Molecular Biology (LS6421, 1999)
... mature sperm. Further changes are made after fertilization. In females, the maternal pattern is imposed during oogenesis. (3). Methylation pattern of germ cells: (1) the previous pattern is erased by a genome-wide demethylation; (2) pattern specific for each sex is imposed. (4). Imprinting describes ...
... mature sperm. Further changes are made after fertilization. In females, the maternal pattern is imposed during oogenesis. (3). Methylation pattern of germ cells: (1) the previous pattern is erased by a genome-wide demethylation; (2) pattern specific for each sex is imposed. (4). Imprinting describes ...
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
... • Liver Disease – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
... • Liver Disease – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
Genetic Engineering
... separate during meiosis in plants. For example, polyploid plants have many sets of ...
... separate during meiosis in plants. For example, polyploid plants have many sets of ...
History of Molecular Evolution
... prediction of the Classic School. However, it also seemed to contradict the Balance School and the allimportant role for selection in evolution. This was because the amount of genetic variation was so large that most organisms would be carrying a huge genetic load of detrimental mutations. These dif ...
... prediction of the Classic School. However, it also seemed to contradict the Balance School and the allimportant role for selection in evolution. This was because the amount of genetic variation was so large that most organisms would be carrying a huge genetic load of detrimental mutations. These dif ...
Exam 3
... (DNA Polymerase III, DNA Polymerase I, DNA gyrase, helicase, single strand binding (SSB) proteins, primase, ligase. How is leading and lagging strand synthesis different? What is a replisome? How do bacterial chromosomes replicate? What is the oriC, ter, initiation proteins? Explain why it is advant ...
... (DNA Polymerase III, DNA Polymerase I, DNA gyrase, helicase, single strand binding (SSB) proteins, primase, ligase. How is leading and lagging strand synthesis different? What is a replisome? How do bacterial chromosomes replicate? What is the oriC, ter, initiation proteins? Explain why it is advant ...
Early History The Composition of a Human Cell
... mutations can produce an altered subunit of the protein normally produced by that gene, which in turn can sometimes lead to altered structure and function. In a cell, that change or mutation will be inherited by any new cells created when the mutated cell divides. Whether that mutation results in a ...
... mutations can produce an altered subunit of the protein normally produced by that gene, which in turn can sometimes lead to altered structure and function. In a cell, that change or mutation will be inherited by any new cells created when the mutated cell divides. Whether that mutation results in a ...
Molecular Genetics And Otolaryngology
... recombinant DNA, vectors, probes, polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequence analysis and protein analysis. Molecular cloning requires the use of restriction endonucleases to cleave a DNA strand at a specific site. For example, EcoRI cleaves DNA at a palindromic site on each DNA strand. There are hundr ...
... recombinant DNA, vectors, probes, polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequence analysis and protein analysis. Molecular cloning requires the use of restriction endonucleases to cleave a DNA strand at a specific site. For example, EcoRI cleaves DNA at a palindromic site on each DNA strand. There are hundr ...
Document
... • He should have seen linkage if he had mated dwarf plants with wrinkled pea, but he apparently didn’t do this experiment. ...
... • He should have seen linkage if he had mated dwarf plants with wrinkled pea, but he apparently didn’t do this experiment. ...
DNA WebQuest - Pearland ISD
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
... Take the tour of DNA by clicking on “What is DNA?” and answer the questions below: 1. In what organelle (CELL PART) would I find your DNA (YOUR INSTRUCTIONS)? 2. What does DNA stand for? 3. The DNA molecule comes in the form of a ...
CAP5510 - Bioinformatics - UF CISE
... genes, compounds) that interact with each other to affect one another. As a result they serve a set of functions of that system. • Internal factors can alter the networks. – E.g., gene expression and regulation. ...
... genes, compounds) that interact with each other to affect one another. As a result they serve a set of functions of that system. • Internal factors can alter the networks. – E.g., gene expression and regulation. ...
1 Protein Synthesis Simulation Lab This lab was originally created
... 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only half as large as a DNA molecule. 6. What protein fragment would the mRNA sequence yo ...
... 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only half as large as a DNA molecule. 6. What protein fragment would the mRNA sequence yo ...
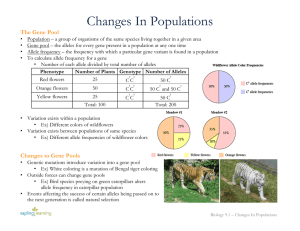
Changes In Populations
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
Model organisms: the genes we share
... The mouse would develop Huntington disease. To determine whether the mouse has HD, it could be made to run a maze, while researchers look for abnormal movements. A close look at the mouse brain could also reveal symptoms of Huntington disease. ...
... The mouse would develop Huntington disease. To determine whether the mouse has HD, it could be made to run a maze, while researchers look for abnormal movements. A close look at the mouse brain could also reveal symptoms of Huntington disease. ...
DNA Restriction and mechanism
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
... • The mammalian enzymes methylate the cytosine in mainly CG sequences to 5-methylcytosine (5-meC), but they do it efficiently only if the cytosine in the opposite strand already bears a methyl residue. The result is that CG sequences that are methylated perpetuate their methylated state following DN ...
Final Exam: Multiple Choice Portion Biochem Block Spring 2016
... d) fairly small (<< 1 M) because this acid is a weak acid 12. (3 pts) The distance between stacked bases of DNA is: a) 3 m b) 3 x 108 m/s c) 3 D d) 3 x 10-9 m e) 3.4 D f) 34 D 13. (3 pts) Cytochrome c peroxidase has an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.2. A reasonable value for the charge on this protein ...
... d) fairly small (<< 1 M) because this acid is a weak acid 12. (3 pts) The distance between stacked bases of DNA is: a) 3 m b) 3 x 108 m/s c) 3 D d) 3 x 10-9 m e) 3.4 D f) 34 D 13. (3 pts) Cytochrome c peroxidase has an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.2. A reasonable value for the charge on this protein ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.