File
... uses the genetic information in mRNA to build proteins. The mRNA carries the “code” (or instructions) to the ribosome [organelle in the cell which builds proteins]; Ribosome is made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
... uses the genetic information in mRNA to build proteins. The mRNA carries the “code” (or instructions) to the ribosome [organelle in the cell which builds proteins]; Ribosome is made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
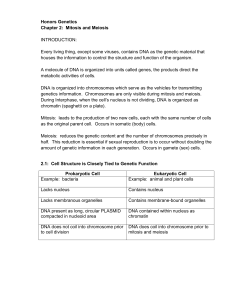
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromosomes which serve as the vehicles for transmitting genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cel ...
... A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromosomes which serve as the vehicles for transmitting genetics information. Chromosomes are only visible during mitosis and meiosis. During Interphase, when the cel ...
Proteins
... uses the genetic information in mRNA to build proteins. The mRNA carries the “code” (or instructions) to the ribosome [organelle in the cell which builds proteins]; Ribosome is made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
... uses the genetic information in mRNA to build proteins. The mRNA carries the “code” (or instructions) to the ribosome [organelle in the cell which builds proteins]; Ribosome is made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). ...
3 " ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ - 1 - G 2 ¢ 2 2 – 1. Biological catalysts are (A
... 13. How many polypeptide chain(s) is (are) in one molecule of the collagen helix? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 14. A protein has an isoelectric point (pI) of 7. The net charge of this protein will be (A) + at pH 5 and – at pH 9 (B) – at pH 5 and + at pH 9 (C) + at both pH 5 and 9 (D) – at both pH 5 and 9 ...
... 13. How many polypeptide chain(s) is (are) in one molecule of the collagen helix? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 14. A protein has an isoelectric point (pI) of 7. The net charge of this protein will be (A) + at pH 5 and – at pH 9 (B) – at pH 5 and + at pH 9 (C) + at both pH 5 and 9 (D) – at both pH 5 and 9 ...
Wrap up Genes and Expression
... region of the opsin gene cluster (Nathans, et. al. 1989) shown to cause 50% of the cases of blue cone monochromacy. The locus control region is approximately 4 kilobases upstream of the red opsin gene, and 43 kilobases upstream of the green opsin gene. The 579 base region was mapped to the X-chromos ...
... region of the opsin gene cluster (Nathans, et. al. 1989) shown to cause 50% of the cases of blue cone monochromacy. The locus control region is approximately 4 kilobases upstream of the red opsin gene, and 43 kilobases upstream of the green opsin gene. The 579 base region was mapped to the X-chromos ...
The CENTRAL DOGMA in Biology
... Translation is the process that creates, or synthesizes, proteins from the genetic code, which is now in mRNA form. The mRNA is read in triplet, _________ base pairs at a time. Each triplet, called a ________________, codes for a specific amino acid that will be added to the protein. For example: co ...
... Translation is the process that creates, or synthesizes, proteins from the genetic code, which is now in mRNA form. The mRNA is read in triplet, _________ base pairs at a time. Each triplet, called a ________________, codes for a specific amino acid that will be added to the protein. For example: co ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... Occur only in bacterial genomes Contain more than one gene Contain more than one promoter Were discovered in the 19th century Contain long intergenic sequences ...
... Occur only in bacterial genomes Contain more than one gene Contain more than one promoter Were discovered in the 19th century Contain long intergenic sequences ...
No Slide Title
... in terms of the difference in free energies between the free and the bound states, can be described as DG°binding = -RT ln ([A]/Kd) It is also often useful to describe the difference in binding affinity between a wild type protein and a mutant of the same protein, which is an intrinsic property inde ...
... in terms of the difference in free energies between the free and the bound states, can be described as DG°binding = -RT ln ([A]/Kd) It is also often useful to describe the difference in binding affinity between a wild type protein and a mutant of the same protein, which is an intrinsic property inde ...
Answers chapter 9
... elaborate mechanisms that exist to replicate DNA accurately and to repair any incorrectly incorporated or damaged bases. On the other hand, reducing the mutation rate to zero would not only require an enormous investment (to produce enough repair enzymes with sufficient activity to detect and repair ...
... elaborate mechanisms that exist to replicate DNA accurately and to repair any incorrectly incorporated or damaged bases. On the other hand, reducing the mutation rate to zero would not only require an enormous investment (to produce enough repair enzymes with sufficient activity to detect and repair ...
Chapter08_MBP1022H
... • dissect away undesirable tissues and membranes • mince and digest the extracellular matrix (ECM) with one or more proteinases (eg. trypsin, collagenase) • isolate free cells (eg. by filtration or centrifugation) and plate onto petri dishes under appropriate growth medium •very rich media- 9 essent ...
... • dissect away undesirable tissues and membranes • mince and digest the extracellular matrix (ECM) with one or more proteinases (eg. trypsin, collagenase) • isolate free cells (eg. by filtration or centrifugation) and plate onto petri dishes under appropriate growth medium •very rich media- 9 essent ...
1. Assuming simple dominance, out of a total of 160 offspring, how
... 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What is the name of mode of inhe ...
... 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What is the name of mode of inhe ...
CP Biology Cumulative Final Exam Study Guide write all answers on
... 21. What does the term semipermeable mean? 22. What is the function of the plasma membrane? 23. What is the function of the proteins embedded in the plasma membrane? 24. Explain the terms active transport and passive transport. 25. Describe what would happen to a plant cell placed in hypotonic and h ...
... 21. What does the term semipermeable mean? 22. What is the function of the plasma membrane? 23. What is the function of the proteins embedded in the plasma membrane? 24. Explain the terms active transport and passive transport. 25. Describe what would happen to a plant cell placed in hypotonic and h ...
15 Guided Reading
... - Because DNA molecules are too large to analyze, what must scientists do first? ...
... - Because DNA molecules are too large to analyze, what must scientists do first? ...
The F plasmid and conjugation
... Plasmids can carry genes that confer resistance to antibiotics and toxic substances. Plasmids are not needed for reproduction or normal growth, but they can be beneficial. Plasmids can carry genes from one bacteria to another. Bacteria can thus become resistant to a drug, put the resistance gene in ...
... Plasmids can carry genes that confer resistance to antibiotics and toxic substances. Plasmids are not needed for reproduction or normal growth, but they can be beneficial. Plasmids can carry genes from one bacteria to another. Bacteria can thus become resistant to a drug, put the resistance gene in ...
Lecture 24 Evolution Genotype vs. Phenotype Ontogeny Genotype
... “Selfish Gene” • An organism is a gene’s way of making more copies of itself • A gene (or collection of genes) will tend to persist in a population if they tend to produce physical characteristics & behavior that are relatively successful at producing more copies of itself • Nevertheless, it is phys ...
... “Selfish Gene” • An organism is a gene’s way of making more copies of itself • A gene (or collection of genes) will tend to persist in a population if they tend to produce physical characteristics & behavior that are relatively successful at producing more copies of itself • Nevertheless, it is phys ...
DNA – RNA – PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
... This sequence would be read three bases at a time as: UCG-CAC-GGU The codons represent the different amino acids: UCG = Serine, CAC = Histidine, GGU = Glycine THE GENETIC CODE ...
... This sequence would be read three bases at a time as: UCG-CAC-GGU The codons represent the different amino acids: UCG = Serine, CAC = Histidine, GGU = Glycine THE GENETIC CODE ...
Savannah Gonzales - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
... lead toforDMD Codes a protein complex called dystrophin. Located in skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles Most are deletions that cause frame-shift Small amounts are present in nerve cells in the ...
... lead toforDMD Codes a protein complex called dystrophin. Located in skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles Most are deletions that cause frame-shift Small amounts are present in nerve cells in the ...
UNIT ONE - TeacherWeb
... 2. What property allows carbon compounds to exist in so many different forms? ...
... 2. What property allows carbon compounds to exist in so many different forms? ...
Protein Folding Lab with Balloons
... include the words mRNA, tRNA, amino acid, and final protein structure. 4. Given that there are only so many amino acids (20), why are there so many different types of proteins (hundreds of thousands)? ...
... include the words mRNA, tRNA, amino acid, and final protein structure. 4. Given that there are only so many amino acids (20), why are there so many different types of proteins (hundreds of thousands)? ...
Gene Regulation of Eukaryotes
... Proto-oncogene - is a normal gene that can become an oncogene due to mutations or increased expression. ...
... Proto-oncogene - is a normal gene that can become an oncogene due to mutations or increased expression. ...
Study Guide for Cells and Traits Test This is a picture of active
... Growth of the human body results from cell division. ...
... Growth of the human body results from cell division. ...
Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between
... 28. If a solution is hypotonic to the cell, which of the following will happen a. Nothing. The phospholipid membrane stops the solutes from moving. b. The water moves into the cell because it has a greater number of solutes. c. ...
... 28. If a solution is hypotonic to the cell, which of the following will happen a. Nothing. The phospholipid membrane stops the solutes from moving. b. The water moves into the cell because it has a greater number of solutes. c. ...
Integration of Bioinformatics into Inquiry Based Learning
... beneficial to our learning experience. It was interesting to use the same computers that real scientists used to do their research. The using of bioinformatics was key in the expansion of our minds. It helped us get more involved with the concepts we were learning since it made everything more reali ...
... beneficial to our learning experience. It was interesting to use the same computers that real scientists used to do their research. The using of bioinformatics was key in the expansion of our minds. It helped us get more involved with the concepts we were learning since it made everything more reali ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.