* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT ONE - TeacherWeb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
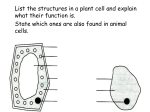
Fall Semester Final Exam STUDY GUIDE NAME ________________________ BIOCHEMISTRY Define: 1. Monomer 2. Polymer 3. Lipid 4. Fatty acid 5. Protein 6. Amino acid 7. Nucleic Acid 8. Nucleotide 9. Polysaccharide 10. Monosaccharide 11. Chemical Reaction 12. Reactant 13. Product 14. Activation energy 15. Catalyst 16. Enzyme 17. Substrate 1. Describe the difference between “organic” and “inorganic” and give examples of each type of compound. 2. What property allows carbon compounds to exist in so many different forms? 3. List the four main types of organic compounds. Describe the main job of each and name its monomer. A. B. C. D. 5. Diagram how an enzyme changes the activation energy of a chemical reaction. 6. What are enzymes? How are they used in the body? 7. Enzymes are very specific. Each enzyme will react with only one type of substrate. Why is this? 1 8. Describe how enzyme activity (how well it works) depends on temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. 9. What are the two types of nucleic acids and their functions? 10. Name structures A, B, and C 11. Where is the “code” in this molecule? CELL BIOLOGY Define: 1. Cytoplasm 2. Organelle 3. Prokaryotic cell 4. Eukaryotic cell 5. Cytoskeleton 6. Nucleus 7. Endoplasmic reticulum 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Ribosome Vesicle Mitochondria Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Cell membrane 1. How does the image through a microscope compare to the orientation of the specimen on a slide? When a slide is moved to the left, the image moves in which direction? 2 2. List the three parts of the cell theory. 3. Compare and contrast the structure of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. 4. Name the parts of this cell and give the job or jobs of each part 5. Name the parts that a plant cell has that animal cells like the one above don’t. What are the jobs of these plant parts? 6. Diagram and describe how the E.R. and Golgi work to secrete a protein. 3 CELL TRANSPORT 5. Define the terms 1. Phospholipids 2. Selective permeability 3. Passive transport 4. Diffusion 5. Concentration gradient 6. Osmosis 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Facilitated diffusion Active transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Equilibrium 1. Diagram and describe a phospholipid, labeling the polar and nonpolar parts. (1a) 2. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion so important to living cells? 3. What is osmosis? 4. Draw a diagram of a typical plasma membrane and label the parts Use the following key to explain how osmosis would affect these blood cells KEY: A. The cell would shrink B. The cell would swell C. The cell would stay the same 5. 6. 4 8. This diagram illustrates the cell membrane of a cell that normally contains 3.0% Calcium that has been placed in a 1.0 % solution. Exactly what is happening and why? Cell Energy and Aerobic Cellular Respiration Define: 1. ATP 2. Photosynthesis 3. Chlorophyll 4. Thylakoid 5. Light-dependent reactions 6. Light-independent reactions 7. Chloroplast 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Spongy Mesophyll Palisade Mesophyll Stomata Cellular respiration Aerobic Glycolysis Anaerobic 1. Draw the molecule ATP and explain its importance. (1g) 2. Describe the difference between aerobic and anaerobic. 3. Fill in the blanks 4. Write the balanced equation for aerobic cellular respiration. 5 5. What does “glycolysis” mean? Where does glycolysis take place? 7. Draw and label the structure of a chloroplast. 8. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis. 9. Label the structures in a leaf cross section and explain what each does for the plant during photosynthesis. (1f) 10. What is the job of the molecule known as NADPH? DNA Replication Define: 1. Double helix 2. Sugar phosphate backbone 3. Nitrogenous base 4. Hydrogen bonds 5. Antiparallel 6. Base pairing rules 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Semiconservative Replication DNA polymerase Helicase Ligase 1. Describe the evidence that lead Watson and Crick to determine the structure of DNA. 2. Draw the opposite strand of this DNA strand SUGAR -- A | P | SUGAR -- C | P | SUGAR -- T | P 6 Transcription Translation, and Protein Synthesis 1. Describe the sequence of the Central Dogma of Biology. 2. Identify the two main kinds of RNA and their functions. (5a/4a) 3. Predict the sequence of amino acids from a sequence of codons in RNA. (4b) mRNA: AUG UGU UAC AUU CAA AAC UGC CCC UUA GGA UAG 4. Describe what is happening in each step of the diagram on the next page. 5. Distinguish and identify the different types of mutations. (4c) 6. Explain why mutations may or may not show up in the characteristics of an organism. (4c) 7. Describe the different affects that mutations have on germ cells and somatic cells. (4c) 8. Describe the difference between introns and exons in eukaryotic RNA. (4b) 9. Draw the general structure of a protein and describe how proteins are different. (5a/4e) 7 Investigation and Experimentation 1. In science, a logical way to solve a problem (question) of nature is called the __________ _______________________. 2. List the five major steps to this method and briefly describe each. A. B. C. D. E. 3. What is the purpose of a control in a scientific experiment. 4. Distinguish between a hypothesis and a theory. 6. Can an experiment ever be called a failure? Explain. 8. A. B. C. D. Define or explain Biology Science Scientific Method Control E. F. G. H. Variable Hypothesis Theory Law Mitosis Define: Chromatid Metastasize Histone benign Chromatin haploid asexual reproduction diploid 1. Name and diagram the 5 phases of mitosis. 2. What makes up a chromosome and how many does each human body cell contain? 3. Explain the difference between meiosis and mitosis 4. 8 Genetics Define: Cross trait Heterozygous phenotype genome genotype cross over allele homozygous P generation F1 generation 1. Explain sex linked genes 2. What is codominance 3. In pea plants, spherical seeds (S) are dominant to dented seeds (s). In a genetic cross of two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? 4. In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. Cross a homozygous brown eyed with a heterozygous brown eyed person. Complete the Punnett square. a. What are the ratios for the genotypes (Homozygous dominant : Heterozygous)? b. What is the probability the two will have blue eyed children? 9