Protein Synthesis Webquest
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. 1. How does the mRNA leave the nucleus? ...
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. 1. How does the mRNA leave the nucleus? ...
Biology Spring Semester Review
... 3. Predict the genotypes of parents based on the phenotype of the offspring. 4. A homozygous black and a homozygous white dog are crossed. Describe the phenotype of the offspring if the mode of inheritance is: complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance. 5. Be able to use a Punnett Squ ...
... 3. Predict the genotypes of parents based on the phenotype of the offspring. 4. A homozygous black and a homozygous white dog are crossed. Describe the phenotype of the offspring if the mode of inheritance is: complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance. 5. Be able to use a Punnett Squ ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... Clones are genetically identical copies o Each identical recombinant DNA molecule is called a gene clone o In 1997, Dolly was the 1st mammal (sheep) cloned Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the process allowing replication of DNA outside living organisms in a special machine Heat is used to sep ...
... Clones are genetically identical copies o Each identical recombinant DNA molecule is called a gene clone o In 1997, Dolly was the 1st mammal (sheep) cloned Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the process allowing replication of DNA outside living organisms in a special machine Heat is used to sep ...
Protein Synthesis
... 2. Proteins are made of chains of ___________ __________ held together by ___________ bonds. 3. How many amino acids are there? 4. The function of a protein depends on its _________________ structure. 5. Each combination of three nucleotides on mRNA is called a _____________ and codes for a specific ...
... 2. Proteins are made of chains of ___________ __________ held together by ___________ bonds. 3. How many amino acids are there? 4. The function of a protein depends on its _________________ structure. 5. Each combination of three nucleotides on mRNA is called a _____________ and codes for a specific ...
File
... A string of ribosomes carrying out multiple translation on the same mRNA strand is called a polyribosome ...
... A string of ribosomes carrying out multiple translation on the same mRNA strand is called a polyribosome ...
Advances in Genetics
... • Put normal allele in a cold virus • Inhale the cold virus • The virus infects your nasal cells • The normal allele goes into the nucleus • The cell can make the normal protein ...
... • Put normal allele in a cold virus • Inhale the cold virus • The virus infects your nasal cells • The normal allele goes into the nucleus • The cell can make the normal protein ...
Intro to Genetics
... you expect to find in the organism’s gametes? a. 4 b. 6 c. 10 d. 12 12. During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up side by side? a. prophase b. telophase I c. metaphase II d. anaphase II 13. The division of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is called a. mitosis. b. binary fissi ...
... you expect to find in the organism’s gametes? a. 4 b. 6 c. 10 d. 12 12. During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up side by side? a. prophase b. telophase I c. metaphase II d. anaphase II 13. The division of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is called a. mitosis. b. binary fissi ...
finalexamcrib201213NED 33.5 KB
... 5) Primary purpose of genetic control: efficiency in transcript expression to product. 6) Requirements to allow gene transcription (solely) in euks. 7) Requirements to allow translation (solely) of modified transcripts in euks. 8) Necessity for protein-protein interactions and protein-dna interactio ...
... 5) Primary purpose of genetic control: efficiency in transcript expression to product. 6) Requirements to allow gene transcription (solely) in euks. 7) Requirements to allow translation (solely) of modified transcripts in euks. 8) Necessity for protein-protein interactions and protein-dna interactio ...
Transgenic and knockout mice
... in which one or more genes have been turned off through a gene knockout Important animal models for studying the role of genes which have been sequenced, but have unknown functions By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behaviour or cond ...
... in which one or more genes have been turned off through a gene knockout Important animal models for studying the role of genes which have been sequenced, but have unknown functions By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behaviour or cond ...
L3_Viral Vector and Non
... • This allows either the gene product or the converted prodrug to transport between cells, such that therapeutic efficacy may be achieved even when targeting only a fraction of the cells within a tumor. ...
... • This allows either the gene product or the converted prodrug to transport between cells, such that therapeutic efficacy may be achieved even when targeting only a fraction of the cells within a tumor. ...
chapter 8
... Bacteria can transfer genes from one strain to another by three different mechanisms ...
... Bacteria can transfer genes from one strain to another by three different mechanisms ...
Basic Concepts of Human Genetics
... • Now , there are mainly two kinds of makers used today. (1) SNPs (Single nucleotide polymorphism): 1 bp in length; there are two alleles in human population. The two alleles may be any two from {A,G,C,T}. • Most of the SNPs were found from DNA sequences of a few individuals (Human Genome project). ...
... • Now , there are mainly two kinds of makers used today. (1) SNPs (Single nucleotide polymorphism): 1 bp in length; there are two alleles in human population. The two alleles may be any two from {A,G,C,T}. • Most of the SNPs were found from DNA sequences of a few individuals (Human Genome project). ...
bonds form when water is removed to hold acids together.
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a _____________________. 25. _______________ bonds form when water is removed t ...
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of _____________ in a process called __________________. 24. Chains of amino acids make ________________________ which can join together to make a _____________________. 25. _______________ bonds form when water is removed t ...
NATIONAL BRAIN RESEARCH CENTRE(NBRC) NH-8, Manesar-122050, HARYANA
... A 200 W lamp is connected to 100 volts supply. The number of electrons passing through the lamp in one minute is(charge of an electron =1.6 X 10-19C): (1) 1x1019 (3) 7.5x1020 ...
... A 200 W lamp is connected to 100 volts supply. The number of electrons passing through the lamp in one minute is(charge of an electron =1.6 X 10-19C): (1) 1x1019 (3) 7.5x1020 ...
1) From DNA to protein 2) Gene mutation
... 8.1 From DNA to protein: gene expression • Beadle and Tatum used Neurospora to test hypothesis that specific gene expression → specific enzyme activity. • Neurospora is haploid for most of its life cycle—all alleles are expressed as phenotypes. • Wild-type strains like Neurospora are prototrophs ...
... 8.1 From DNA to protein: gene expression • Beadle and Tatum used Neurospora to test hypothesis that specific gene expression → specific enzyme activity. • Neurospora is haploid for most of its life cycle—all alleles are expressed as phenotypes. • Wild-type strains like Neurospora are prototrophs ...
8.6 Gene Expression and Regulation
... transcribed. • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of g ...
... transcribed. • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of g ...
g.ML-6 DNA Replication1
... is critical in that it will disrupt RNA synthesis and processing and the cell should have sufficient metabolic reserve to complete the cell cycle. Problems: 1. The basic goal is to make 1 and only 1 copy of each chromosome with high fidelity (on average 1 error in 109 base pairs). 2. Unwind before a ...
... is critical in that it will disrupt RNA synthesis and processing and the cell should have sufficient metabolic reserve to complete the cell cycle. Problems: 1. The basic goal is to make 1 and only 1 copy of each chromosome with high fidelity (on average 1 error in 109 base pairs). 2. Unwind before a ...
Paper Title
... 1. Introduction Non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can have severe effect on protein functionality. A lot of genetic diseases are caused by single point nucleotide mutation such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia. The identification of potentially deleterious ...
... 1. Introduction Non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can have severe effect on protein functionality. A lot of genetic diseases are caused by single point nucleotide mutation such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia. The identification of potentially deleterious ...
Exam Handout for PHAR2811 students, 2009
... 4. A; those proteins (A, D & E) with molecular weights >50,000 will be excluded from the gel filtration beads and hence elute faster. 5. A; Telomerase actually does the opposite it fills in and extends the telomeres using the RNA contained in the enzyme as a template and its reverse transcriptase ac ...
... 4. A; those proteins (A, D & E) with molecular weights >50,000 will be excluded from the gel filtration beads and hence elute faster. 5. A; Telomerase actually does the opposite it fills in and extends the telomeres using the RNA contained in the enzyme as a template and its reverse transcriptase ac ...
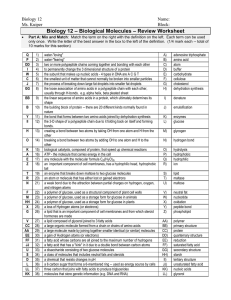
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... the subunit that makes up nucleic acids - 4 types in DNA are A C G T the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken into smaller particles the process of breaking down large fat droplets into smaller fat droplets the loose association of amino acids in a polypeptide chain with each other ...
... the subunit that makes up nucleic acids - 4 types in DNA are A C G T the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken into smaller particles the process of breaking down large fat droplets into smaller fat droplets the loose association of amino acids in a polypeptide chain with each other ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.