Question 1
... The purpose of this assignment is for you to understand basic gene expression data analysis techniques. We will use WEKA data mining to perform two types of gene expression data analysis 1. Molecular classification of leukemia cancer. We will build a classifier to identify whether a diseased tissue ...
... The purpose of this assignment is for you to understand basic gene expression data analysis techniques. We will use WEKA data mining to perform two types of gene expression data analysis 1. Molecular classification of leukemia cancer. We will build a classifier to identify whether a diseased tissue ...
Adapted
... A simple plasmid DNA with expression promoter can be used A plasmid with T-DNA in needed for host genome integration No –TDNA is required ...
... A simple plasmid DNA with expression promoter can be used A plasmid with T-DNA in needed for host genome integration No –TDNA is required ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • To determine which genes are transcribed under different situations, researchers isolate mRNA from particular cells and use the mRNA as templates to build a cDNA library. • This cDNA can be compared to other collections of DNA by hybridization. • This will reveal which genes are active at differen ...
... • To determine which genes are transcribed under different situations, researchers isolate mRNA from particular cells and use the mRNA as templates to build a cDNA library. • This cDNA can be compared to other collections of DNA by hybridization. • This will reveal which genes are active at differen ...
Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Human Glycine-N-acyltransferase Gene GLYATL1, Which Activates Transcriptional Activity of HSE Pathway
... insights into the evolution and genetics of these important detoxifying systems. Third, it may relate to the pathogenesis and possibly the treatment of certain organic acidemias. Finally, it does provide a useful model for studying mechanisms of enzymatic transfer reactions. During the past five dec ...
... insights into the evolution and genetics of these important detoxifying systems. Third, it may relate to the pathogenesis and possibly the treatment of certain organic acidemias. Finally, it does provide a useful model for studying mechanisms of enzymatic transfer reactions. During the past five dec ...
Human Chromosomes Mr. Alvarez March 15, 2013
... • Human genes associated with color vision are located on the X chromosome • Most common type of color blindness is RedGreen color blindness – Effects 1 in 10 males – Effects 1 in 100 females ...
... • Human genes associated with color vision are located on the X chromosome • Most common type of color blindness is RedGreen color blindness – Effects 1 in 10 males – Effects 1 in 100 females ...
Nucleic Acids - saddleback.edu
... • Each chromosome contains a different DNA molecule, and during cell mitosis (division) the DNA is replicated (duplicated) so that each new cell receives a complete copy. • The number of chromosomes varies from organism to organism. For example, a horse has 64 chromosomes (32 pairs), a cat has 38 ...
... • Each chromosome contains a different DNA molecule, and during cell mitosis (division) the DNA is replicated (duplicated) so that each new cell receives a complete copy. • The number of chromosomes varies from organism to organism. For example, a horse has 64 chromosomes (32 pairs), a cat has 38 ...
Genetics
... At this point it must be mentioned that there may also be spontaneous changes in a gene regardless of the inherited disease, by genes during fetus development. This can also lead to a disease. One speaks of a "spontaneous mutation" that occurs in a brand new family member, but it can then be passed ...
... At this point it must be mentioned that there may also be spontaneous changes in a gene regardless of the inherited disease, by genes during fetus development. This can also lead to a disease. One speaks of a "spontaneous mutation" that occurs in a brand new family member, but it can then be passed ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
Gene Section CDKN2a (cyclin dependent kinase 2a) / p16
... Malignant melanoma arises de novo or from a preexisting benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but also may involve other sites. Oncogenesis Familial melanoma (comprising between 8 and 12% of all melanoma cases) is a genodermatosis transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait. CDKN2a has be ...
... Malignant melanoma arises de novo or from a preexisting benign nevus, which occurs most often in the skin but also may involve other sites. Oncogenesis Familial melanoma (comprising between 8 and 12% of all melanoma cases) is a genodermatosis transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait. CDKN2a has be ...
Leukaemia Section t(2;11)(q37;q23) in AML Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... cytoskeletal dynamics and secretion. The SEPT2 gene codes for a protein with 361 amino acids and a molecular weight of 41.5 kDa. SEPT2 was identified as a gene expressed in early embryonic mouse brain and down-regulated during development. It is ubiquitously expressed in cell lines and tissues with ...
... cytoskeletal dynamics and secretion. The SEPT2 gene codes for a protein with 361 amino acids and a molecular weight of 41.5 kDa. SEPT2 was identified as a gene expressed in early embryonic mouse brain and down-regulated during development. It is ubiquitously expressed in cell lines and tissues with ...
Chapter 14 Transposons, Plasmids, and Bacteriophage
... occurs, in case after c+ gene has been transferred but before d gene has entered recipient cell. ...
... occurs, in case after c+ gene has been transferred but before d gene has entered recipient cell. ...
Exam Study Guide semester 2
... the characteristics of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and examples of each the structure of the cell membrane (color plate cell membrane) the location, function and description and be able to identify diagrams of all organelles of plant and animal cells (know the cell chart) contributions ...
... the characteristics of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and examples of each the structure of the cell membrane (color plate cell membrane) the location, function and description and be able to identify diagrams of all organelles of plant and animal cells (know the cell chart) contributions ...
Note 1
... around genes that play a role in controlling gene transcription and other related processes. ...
... around genes that play a role in controlling gene transcription and other related processes. ...
Lesson6.5_Translation Process
... How does translation occur? 1. The ribosome attaches to the mRNA molecule. 2. The tRNA attaches to the mRNA. The tRNA anticodon attaches to the mRNA codon. 3. The first two amino acids are joined/connected and the first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon ...
... How does translation occur? 1. The ribosome attaches to the mRNA molecule. 2. The tRNA attaches to the mRNA. The tRNA anticodon attaches to the mRNA codon. 3. The first two amino acids are joined/connected and the first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon ...
bio12_sm_07_2
... prokaryotic transcription it does not. 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA po ...
... prokaryotic transcription it does not. 6. DNA Replication and Transcription DNA replication Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA po ...
Gene Regulation - yayscienceclass
... Four of the many different types of human cells: They all share the same genome. What makes them different? ...
... Four of the many different types of human cells: They all share the same genome. What makes them different? ...
Final Exam Study Guide - Tacoma Community College
... 96. Compare and contrast base substitution mutations and base deletions and base insertions. 97. Discuss the causes of mutations, when they occur and why they are usually harmful, but occasionally beneficial. 98. Explain the evolutionary significance of mutations. ...
... 96. Compare and contrast base substitution mutations and base deletions and base insertions. 97. Discuss the causes of mutations, when they occur and why they are usually harmful, but occasionally beneficial. 98. Explain the evolutionary significance of mutations. ...
South Carolina State Biology Standards for 2008 aligned to Prentice
... B-4.8 Compare the consequences of mutations in body (somatic) cells with those in gametes. Recall the three main causes of mutations made by DNA or RNA “Polly” Polymerase? ...
... B-4.8 Compare the consequences of mutations in body (somatic) cells with those in gametes. Recall the three main causes of mutations made by DNA or RNA “Polly” Polymerase? ...
C2005/F2401 `09
... bacterium that causes anthrax (B. anthracis), and a few closely related other bacteria that are equally dangerous. Many techniques for detecting the anthrax bacillus depend on detecting anthrose. When B. anthracis cells are actively growing, the cells contain no anthrose. When the bacteria stop grow ...
... bacterium that causes anthrax (B. anthracis), and a few closely related other bacteria that are equally dangerous. Many techniques for detecting the anthrax bacillus depend on detecting anthrose. When B. anthracis cells are actively growing, the cells contain no anthrose. When the bacteria stop grow ...
Recitation Section 11 Answer Key Bacterial Genetics
... c. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains can interact d. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains are variants of the same protein e. DNA from one strain interacts with the protein from the other On the underlying level, this is a variant ...
... c. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains can interact d. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains are variants of the same protein e. DNA from one strain interacts with the protein from the other On the underlying level, this is a variant ...
Syllabus: AP Bio - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... school. Students are provided with the factual knowledge and conceptual framework as well as the conceptual skills to deal with the rapidly evolving field of biology today. Lab work is required as an important component of the course. These labs include important areas in modem biology. They are int ...
... school. Students are provided with the factual knowledge and conceptual framework as well as the conceptual skills to deal with the rapidly evolving field of biology today. Lab work is required as an important component of the course. These labs include important areas in modem biology. They are int ...
Unit 4
... 26. Describe the difference between procariotic and eucariotic mRNA. The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNA is that eukaryotic RNA is transcribed and translated separately, while prokaryotic RNA is translated during transcription. 28. Describe some biological functions of introns and ...
... 26. Describe the difference between procariotic and eucariotic mRNA. The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNA is that eukaryotic RNA is transcribed and translated separately, while prokaryotic RNA is translated during transcription. 28. Describe some biological functions of introns and ...
L5 mRNA to Amino Acids File
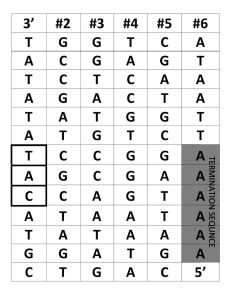
... amino acid it codes for is identified in the box. Amino acids are repeated many times in the table as there are 64 possible codons and only 20 different amino acids. ...
... amino acid it codes for is identified in the box. Amino acids are repeated many times in the table as there are 64 possible codons and only 20 different amino acids. ...
A SHORT HISTORY OF BIOINFORMATICS
... European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), and the University of Heidelberg. Paradigm Genetics Inc., a company focussed on the application of genomic technologies to enhance worldwide food and fiber production, is founded in Research Triangle Park, NC. deCode ...
... European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), and the University of Heidelberg. Paradigm Genetics Inc., a company focussed on the application of genomic technologies to enhance worldwide food and fiber production, is founded in Research Triangle Park, NC. deCode ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.