Protein Synthesis Worksheet
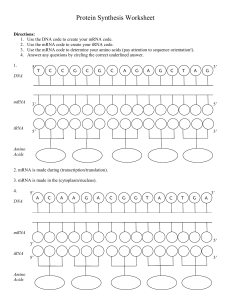
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
Sickle Cell Anemia and Cystic Fibrosis
... Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene. This gene provides the code for a protein that helps produce digestive juices and mucus. 1. Using what you know about DNA, what does it mean for there to be “a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene”? 2. The most common mutation in t ...
... Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene. This gene provides the code for a protein that helps produce digestive juices and mucus. 1. Using what you know about DNA, what does it mean for there to be “a mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene”? 2. The most common mutation in t ...
Clinical Feature: Diagnosis and Genetic Variance in Familial
... glutamine substitution resulting from a missense mutation at the 3500 codon. Often the levels of LDL-C are not as high as in heterozygous FH, and this is one feature which reduces the utility of the MEDPED criteria for diagnosis. In these patients the remnant lipoproteins which depend on ApoE rather ...
... glutamine substitution resulting from a missense mutation at the 3500 codon. Often the levels of LDL-C are not as high as in heterozygous FH, and this is one feature which reduces the utility of the MEDPED criteria for diagnosis. In these patients the remnant lipoproteins which depend on ApoE rather ...
regulation of cell cycle
... Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) a small RNA chain (73-93 nucleotides) that transfers a specific amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation. It has a 3' terminal site for amino acid attachment. This covalent linkage is catalyzed by an amin ...
... Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) a small RNA chain (73-93 nucleotides) that transfers a specific amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation. It has a 3' terminal site for amino acid attachment. This covalent linkage is catalyzed by an amin ...
10DNAtoProt
... 1. During the process of translation: A. the peptide is ‘passed’ from the tRNA in the P-site to the tRNA in the A-site. B. incoming tRNAs must first bind to the E-site. C. initiation begins with the binding of the ribosomal SSU to the poly-A tail of the mRNA. D. the mRNA is translated by one ribosom ...
... 1. During the process of translation: A. the peptide is ‘passed’ from the tRNA in the P-site to the tRNA in the A-site. B. incoming tRNAs must first bind to the E-site. C. initiation begins with the binding of the ribosomal SSU to the poly-A tail of the mRNA. D. the mRNA is translated by one ribosom ...
CLOUSTON SYNDROME: FIRST CASE IN RUSSIA
... gene. We performed whole gene sequencing using primers flanking the open reading frame of the gene, which revealed a heterozygous non synonymous substitution c.263C>T (Figure 2, upper chromatogram). At the protein level, the mutation leads to the amino acid substitution p.A88V. This is one of the mu ...
... gene. We performed whole gene sequencing using primers flanking the open reading frame of the gene, which revealed a heterozygous non synonymous substitution c.263C>T (Figure 2, upper chromatogram). At the protein level, the mutation leads to the amino acid substitution p.A88V. This is one of the mu ...
The Importance of DNA and RNA - Emmanuel Biology 12
... The unwound DNA exposes two parental strands of DNA which are antiparallel. This means they are orientated in different directions and must be replicated by different mechanisms. The leading strand elongates towards the replication fork (in the direction of unwinding) by the simple addition of nucle ...
... The unwound DNA exposes two parental strands of DNA which are antiparallel. This means they are orientated in different directions and must be replicated by different mechanisms. The leading strand elongates towards the replication fork (in the direction of unwinding) by the simple addition of nucle ...
Slide 1
... 11.5 Complex assemblies of proteins control eukaryotic transcription Regulatory proteins that bind to control sequences – Transcription factors promote RNA polymerase binding to the promoter – Activator proteins bind to DNA enhancers and interact with other transcription factors – Silencers are r ...
... 11.5 Complex assemblies of proteins control eukaryotic transcription Regulatory proteins that bind to control sequences – Transcription factors promote RNA polymerase binding to the promoter – Activator proteins bind to DNA enhancers and interact with other transcription factors – Silencers are r ...
The types of muscular dystrophy
... overnight with a mixture of MLPA probes MLPA probes consist of two separate oligonucleotides, each containing one of the PCR primer sequences The two probe oligonucleotides hybridize to immediately adjacent target sequences Only when the two probe oligonucleotides are both hybridised to their adjace ...
... overnight with a mixture of MLPA probes MLPA probes consist of two separate oligonucleotides, each containing one of the PCR primer sequences The two probe oligonucleotides hybridize to immediately adjacent target sequences Only when the two probe oligonucleotides are both hybridised to their adjace ...
Slide 1 - Loyola Blakefield
... DNA Cloning • Produces gene-sized pieces of DNA in multiple identical copies. • Plasmids, circular DNA pieces separate from the main chromosome, are used • Human growth hormone is mass-produced this way ...
... DNA Cloning • Produces gene-sized pieces of DNA in multiple identical copies. • Plasmids, circular DNA pieces separate from the main chromosome, are used • Human growth hormone is mass-produced this way ...
genetic code-unit-1.- study mat-2012
... represented by more than one codon. For example, the three amino acids-arginine, serine and leucine-each have six synonymous codons. However, for many of the synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant, whereas the third can vary; for example, all co ...
... represented by more than one codon. For example, the three amino acids-arginine, serine and leucine-each have six synonymous codons. However, for many of the synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant, whereas the third can vary; for example, all co ...
ENG - Hong Kong Academy of Medicine
... What is BRCA gene mutation? Is it common in Hong Kong? BRCA gene mutation is one of the known genetic factors that would raise the risks of developing certain cancers. It can be further subdivided into BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 mutations. According to the latest local data, there are only 8.5% of 914 select ...
... What is BRCA gene mutation? Is it common in Hong Kong? BRCA gene mutation is one of the known genetic factors that would raise the risks of developing certain cancers. It can be further subdivided into BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 mutations. According to the latest local data, there are only 8.5% of 914 select ...
Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
Schedule of Lecture and Laboratory Sessions
... 36. To examine the notion of cell “competency” for transformation 37. To understand that conjugation, transformation, and transduction are rare events ...
... 36. To examine the notion of cell “competency” for transformation 37. To understand that conjugation, transformation, and transduction are rare events ...
Close Reading for Macromolecules
... acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functiona ...
... acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functiona ...
Differentiation in Germline Cells
... • Mutations in germline cells are passed onto offspring. – For example: Cystic Fibrosis • A gene mutation on chromosome 7 may become the recessive form (leading to production of thick and sticky mucus). This mutant allele is passed onto gametes during meiosis. If the other parent is a carrier of the ...
... • Mutations in germline cells are passed onto offspring. – For example: Cystic Fibrosis • A gene mutation on chromosome 7 may become the recessive form (leading to production of thick and sticky mucus). This mutant allele is passed onto gametes during meiosis. If the other parent is a carrier of the ...
DNA and Genes - Mr. Boettcher`s Class
... • 1) Traits are passed from one generation of a species to the next generation • 2) Genes are the units of hereditary and determine traits of living things • 3) Living things that reproduce sexually inherit genes in pairs, with one set being contributed by both parents • 4) Some genes are dominant, ...
... • 1) Traits are passed from one generation of a species to the next generation • 2) Genes are the units of hereditary and determine traits of living things • 3) Living things that reproduce sexually inherit genes in pairs, with one set being contributed by both parents • 4) Some genes are dominant, ...
Lan Mai - New Treatments of Cancers using Gene Expression and Regulation
... progress, providing valuable information that could be used to develop new and more effective treatments. Also, abnormal DNA methylation’s ability to silence tumor-suppressor genes can be fixed clinically. It might be possible “to reverse the epigenetic changes and restore gene function to a cell” ( ...
... progress, providing valuable information that could be used to develop new and more effective treatments. Also, abnormal DNA methylation’s ability to silence tumor-suppressor genes can be fixed clinically. It might be possible “to reverse the epigenetic changes and restore gene function to a cell” ( ...
Document
... 13- …………….blocks the MRNA transcription. a. Repressor protein. b. Inducer. c. RNA polymerase. d. All of the above are correct. 14- Initiation, elongation and termination are the stages of………... a. Polymerase action. b. DNA transcription. c. Protein synthesis. d. DNA replication. ...
... 13- …………….blocks the MRNA transcription. a. Repressor protein. b. Inducer. c. RNA polymerase. d. All of the above are correct. 14- Initiation, elongation and termination are the stages of………... a. Polymerase action. b. DNA transcription. c. Protein synthesis. d. DNA replication. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
DNA and Genes - Mr. Boettcher`s Class
... A Brief History into DNA • (1866) Heritable Traits: a scientist monk named Gregory Mendel, noted that parents inherited parents’ traits, and that some traits were more common than others. These traits became known as dominant and recessive traits. Mendel is known as the father of Genetics • 6 Princ ...
... A Brief History into DNA • (1866) Heritable Traits: a scientist monk named Gregory Mendel, noted that parents inherited parents’ traits, and that some traits were more common than others. These traits became known as dominant and recessive traits. Mendel is known as the father of Genetics • 6 Princ ...
Simultaneous detection of alpha-thalassemia and beta
... allowed the unequivocal association of Hb Porto Alegre with Mediterranean haplotype I8, and with framework 18 and also revealed its segregation, in cis, with the codon 27 novel intragenic polymorphism. Because of historical data, we hypothesized whether Hb Porto Alegre described in Brazil could have ...
... allowed the unequivocal association of Hb Porto Alegre with Mediterranean haplotype I8, and with framework 18 and also revealed its segregation, in cis, with the codon 27 novel intragenic polymorphism. Because of historical data, we hypothesized whether Hb Porto Alegre described in Brazil could have ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.























