Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer – a
... DNA polymerase – an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of double stranded DNA. DNA sequence – the relative order of base pairs, whether in a fragment of DNA, a gene, a chromosome, or an entire genome. Double Helix – the shape that two linear strands of DNA assume when bonded together. Dye blobs – a ...
... DNA polymerase – an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of double stranded DNA. DNA sequence – the relative order of base pairs, whether in a fragment of DNA, a gene, a chromosome, or an entire genome. Double Helix – the shape that two linear strands of DNA assume when bonded together. Dye blobs – a ...
A SHORT HISTORY OF BIOINFORMATICS
... European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), and the University of Heidelberg. Paradigm Genetics Inc., a company focussed on the application of genomic technologies to enhance worldwide food and fiber production, is founded in Research Triangle Park, NC. deCode ...
... European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), and the University of Heidelberg. Paradigm Genetics Inc., a company focussed on the application of genomic technologies to enhance worldwide food and fiber production, is founded in Research Triangle Park, NC. deCode ...
L5 mRNA to Amino Acids File
... amino acid it codes for is identified in the box. Amino acids are repeated many times in the table as there are 64 possible codons and only 20 different amino acids. ...
... amino acid it codes for is identified in the box. Amino acids are repeated many times in the table as there are 64 possible codons and only 20 different amino acids. ...
Genetics
... Most gene regulation occurs in the transcription step. ‘Transcription factor’ genes produce proteins that bind to ‘control element’ segments of the targeted gene to activate/inactivate its expression. They can regulate which sections of DNA are copied, the number of mRNA transcripts produced, and ...
... Most gene regulation occurs in the transcription step. ‘Transcription factor’ genes produce proteins that bind to ‘control element’ segments of the targeted gene to activate/inactivate its expression. They can regulate which sections of DNA are copied, the number of mRNA transcripts produced, and ...
I. TRANSCRIPTION
... – Inherited blood disorder (autosomal recessive) – Can cause mild severe anemia, poor appetite, slow growth, bone abnormalities, enlarged heart – Nucleated (immature) red blood cells – More than 200 mutations identified ...
... – Inherited blood disorder (autosomal recessive) – Can cause mild severe anemia, poor appetite, slow growth, bone abnormalities, enlarged heart – Nucleated (immature) red blood cells – More than 200 mutations identified ...
Organic Compounds
... – 11 of the 20 amino acids (nonessential) can be synthesized within the body and therefore do not need to be supplied by the diet – 9 of the 20 amino acids (essential) cannot by can synthesized by the body and therefore need to be obtained through hydrolysis of dietary proteins during the digestive ...
... – 11 of the 20 amino acids (nonessential) can be synthesized within the body and therefore do not need to be supplied by the diet – 9 of the 20 amino acids (essential) cannot by can synthesized by the body and therefore need to be obtained through hydrolysis of dietary proteins during the digestive ...
2.4.measuring evolution of populations
... • Sickle cell anemia – inherit a mutation in gene coding for hemoglobin • oxygen-carrying blood protein • recessive allele = HsHs – normal allele = Hb ...
... • Sickle cell anemia – inherit a mutation in gene coding for hemoglobin • oxygen-carrying blood protein • recessive allele = HsHs – normal allele = Hb ...
Networks, not building blocks – the idea of the
... spontaneous capability exists not only in connection with the relationship of phenotype and molecular function, but also within the molecular network itself. This capability is effected both retrospectively – with epigenetic processes and inheritance without DNA – and prospectively – by the regulati ...
... spontaneous capability exists not only in connection with the relationship of phenotype and molecular function, but also within the molecular network itself. This capability is effected both retrospectively – with epigenetic processes and inheritance without DNA – and prospectively – by the regulati ...
2.4 Molecules to Metabolism NOTES - Proteins
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. Understandings: • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on riboso ...
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. Understandings: • Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. • There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on riboso ...
Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Culture (SILAC)
... amino acid is supplied to cells in culture instead of the natural amino acid, it is incorporated into all newly synthesized proteins. After a number of cell divisions, each instance of this particular amino acid will be replaced by its isotope-labeled analog. Since there is hardly any chemical diffe ...
... amino acid is supplied to cells in culture instead of the natural amino acid, it is incorporated into all newly synthesized proteins. After a number of cell divisions, each instance of this particular amino acid will be replaced by its isotope-labeled analog. Since there is hardly any chemical diffe ...
17 - Doctor Jade Main
... a. photosynthesis involves only oxidations; respiration involves only reductions. b. in photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is oxidized for form sugar; in respiration, sugar is reduced to form carbon dioxide. c. photosynthesis involves only reductions; respiration involves only oxidations. d. in photosyn ...
... a. photosynthesis involves only oxidations; respiration involves only reductions. b. in photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is oxidized for form sugar; in respiration, sugar is reduced to form carbon dioxide. c. photosynthesis involves only reductions; respiration involves only oxidations. d. in photosyn ...
Curiosity is the Key to Discovery
... does not result in the replacement of one Amino Acid by another in Protein. Many mutations are silent. (Synonymous Substitution) ...
... does not result in the replacement of one Amino Acid by another in Protein. Many mutations are silent. (Synonymous Substitution) ...
chap-4 - Workforce3One
... – Can accumulate to levels that interfere with bacterial growth – Expressed protein may form insoluble aggregates, inclusion bodies ...
... – Can accumulate to levels that interfere with bacterial growth – Expressed protein may form insoluble aggregates, inclusion bodies ...
Protein Production
... Specific proteins are produced from instructions contained in genes Genes = specific regions along one strand of the double-stranded DNA molecules Each gene can only produce one specific protein ...
... Specific proteins are produced from instructions contained in genes Genes = specific regions along one strand of the double-stranded DNA molecules Each gene can only produce one specific protein ...
Aim: What is positive feedback of bacterial operons?
... pathways, synthesizing end products. (tryptophan synthesis). Inducible enzymes usually function in catabolic pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negat ...
... pathways, synthesizing end products. (tryptophan synthesis). Inducible enzymes usually function in catabolic pathways, digesting nutrients to simpler molecules. (lactose metabolism). Both repressible and inducible operons demonstrate negative control because active repressors can only have negat ...
HERE
... 1. sub-populations may have different allele frequencies 2. causes _____________________________ across regions 3. ________________________ differences between populations ...
... 1. sub-populations may have different allele frequencies 2. causes _____________________________ across regions 3. ________________________ differences between populations ...
Udvardy, A.1,Bosnyák, E.1, Trájer, E.1, Protzner, A.1, Komka, Zs.1
... subarray consists of 64 through-holes, which means that 3072 nanocapillary quick reaction time (QRT) PCR can be run at one time. To measure the polimorphisms fluorescently signaled Taqman probes are used. The isolated DNA (150ng) from whole blood is mixed with OpenArray MasterMix and loaded into the ...
... subarray consists of 64 through-holes, which means that 3072 nanocapillary quick reaction time (QRT) PCR can be run at one time. To measure the polimorphisms fluorescently signaled Taqman probes are used. The isolated DNA (150ng) from whole blood is mixed with OpenArray MasterMix and loaded into the ...
DNA to mRNA to Protein Assignment
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as ...
Lung Cancer and the KRAS G12V Mutation This material will help
... The most common mutations in KRAS occur at positions 12, 13, and 61. All three of these amino acid positions are important in turning on the protein . When a mutation occurs at any one of these positions, the growth pathway cannot be turned off. This can cause cells to grow out of control and lead t ...
... The most common mutations in KRAS occur at positions 12, 13, and 61. All three of these amino acid positions are important in turning on the protein . When a mutation occurs at any one of these positions, the growth pathway cannot be turned off. This can cause cells to grow out of control and lead t ...
Regulation
... Regulation Occurs at Any Level Transcription* - Binding RNA Polymerase at P site mRNA - amount of Turn over Alter Sigma’s “Strength of P” Translation Step ...
... Regulation Occurs at Any Level Transcription* - Binding RNA Polymerase at P site mRNA - amount of Turn over Alter Sigma’s “Strength of P” Translation Step ...
TALK
... • Genome streamlining occurs when selection is able to act to directly reduce the amount of DNA which serves no useful function for the cell. Introns, inteins, transposons and pesudogenes are examples of "selfish DNA", which persist because their impact on cellular replication efficiency is too smal ...
... • Genome streamlining occurs when selection is able to act to directly reduce the amount of DNA which serves no useful function for the cell. Introns, inteins, transposons and pesudogenes are examples of "selfish DNA", which persist because their impact on cellular replication efficiency is too smal ...
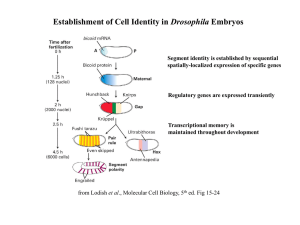
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... Aggressive techniques for inserting foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells: o Electroporation = a brief electric pulse applied to a cell solution causes temporary holes in the plasma membrane, through which the DNA can enter o Thin needles can inject DNA directly into a eukaryotic cell o DNA Gun = DNA is ...
... Aggressive techniques for inserting foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells: o Electroporation = a brief electric pulse applied to a cell solution causes temporary holes in the plasma membrane, through which the DNA can enter o Thin needles can inject DNA directly into a eukaryotic cell o DNA Gun = DNA is ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.