Neuroimaging Tutorial
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test Name
... 15. Stimulated digestion is to inhibited digestion as the ________ nervous system is to the ________ nervous system. A) somatic; autonomic B) autonomic; somatic C) central; peripheral D) sympathetic; parasympathetic E) parasympathetic; sympathetic 16. Motor neurons are to the ________ nervous system ...
... 15. Stimulated digestion is to inhibited digestion as the ________ nervous system is to the ________ nervous system. A) somatic; autonomic B) autonomic; somatic C) central; peripheral D) sympathetic; parasympathetic E) parasympathetic; sympathetic 16. Motor neurons are to the ________ nervous system ...
Editöre Mektuplar / Letters to the Editor
... nuclear plant crisis is of interest. Mental disorders are important clinical problems in patients exposed to radionuclides in the nuclear plant crisis. The treatment of these cases is interesting. Referring to previous publications on a similar nuclear plant crisis, the Chernobyl crisis, a complexit ...
... nuclear plant crisis is of interest. Mental disorders are important clinical problems in patients exposed to radionuclides in the nuclear plant crisis. The treatment of these cases is interesting. Referring to previous publications on a similar nuclear plant crisis, the Chernobyl crisis, a complexit ...
351 Pharmacology 3rd sf
... or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must change its function upon binding in such a way that the function of the b ...
... or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must change its function upon binding in such a way that the function of the b ...
Biology and Behaviour 40s
... neuron passes the message to a motor neuron that controls your leg muscles. Nerve impulses travel down the motor neuron and stimulate the appropriate leg muscle to contract. The response is a muscular jerk that happens quickly and does not involve your brain. Humans have lots of hard-wired reflexes ...
... neuron passes the message to a motor neuron that controls your leg muscles. Nerve impulses travel down the motor neuron and stimulate the appropriate leg muscle to contract. The response is a muscular jerk that happens quickly and does not involve your brain. Humans have lots of hard-wired reflexes ...
NALTREXONE[1].
... for their drug of abuse. These are caused by the communication between the frontal lobe and the reward’s pathway Memories associated with the drug can trigger a craving to get high Not fully understood how it works to reduce cravings, but some researchers believe it works by affecting neural pat ...
... for their drug of abuse. These are caused by the communication between the frontal lobe and the reward’s pathway Memories associated with the drug can trigger a craving to get high Not fully understood how it works to reduce cravings, but some researchers believe it works by affecting neural pat ...
L1: Intro to Pharm- Objectives Describe what is meant by a drug`s
... Agonist: drug that binds to receptor and stimulates cellular activity Antagonist: drug that binds to receptor and inhibits the action of agonists ...
... Agonist: drug that binds to receptor and stimulates cellular activity Antagonist: drug that binds to receptor and inhibits the action of agonists ...
Histology Laboratories Molecules to Systems
... Lodish, H. et al. Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman, New York, 2000. Mizoguti, H. Color Slide Atlas of Histology. Nihon Shashin Shinbunsha, Tokyo. Young, B. and Heath, J. W. Wheater’s Functional Histology. Churchill ...
... Lodish, H. et al. Molecular Cell Biology. W. H. Freeman, New York, 2000. Mizoguti, H. Color Slide Atlas of Histology. Nihon Shashin Shinbunsha, Tokyo. Young, B. and Heath, J. W. Wheater’s Functional Histology. Churchill ...
1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
neuron
... Neuron Communication With Other Neurons • In order for one neuron to communicate with another it must pass a junction or gap called the synapse between the axon which is sending the signal and the dendrite which is receiving the signal. • At the ends of the axon, the terminal buttons release neur ...
... Neuron Communication With Other Neurons • In order for one neuron to communicate with another it must pass a junction or gap called the synapse between the axon which is sending the signal and the dendrite which is receiving the signal. • At the ends of the axon, the terminal buttons release neur ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... each end; one is an axon and the other is a dendrite; located within specialized parts of the eye, nose and ears; Unipolar Neurons – single nerve fiber that extends from the cell body then divides into two branches; one connecting to a peripheral body part and functioning as a dendrite, and the othe ...
... each end; one is an axon and the other is a dendrite; located within specialized parts of the eye, nose and ears; Unipolar Neurons – single nerve fiber that extends from the cell body then divides into two branches; one connecting to a peripheral body part and functioning as a dendrite, and the othe ...
Physical Development Use pp. 411-417, 445-448, and 455
... _______________ outlive _______________ by about 5 years. Sensory abilities decline with age. _______________ pitches cannot be distinguished as clearly. The retina receives about _______________ as much light as it used to because the _______________ is now less transparent. In the elderly, the imm ...
... _______________ outlive _______________ by about 5 years. Sensory abilities decline with age. _______________ pitches cannot be distinguished as clearly. The retina receives about _______________ as much light as it used to because the _______________ is now less transparent. In the elderly, the imm ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... vesicles with the presynaptic membrane 4. Acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane 5. When binding occurs, they open up their channels and depolarize the postsynaptic membrane 6. The spreading depolarization fires an action potentia ...
... vesicles with the presynaptic membrane 4. Acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane 5. When binding occurs, they open up their channels and depolarize the postsynaptic membrane 6. The spreading depolarization fires an action potentia ...
Brain Structure and Function
... only found within the CNS. control excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain and controlling spinal and cerebral reflexes. anxiety disorders decreased GABA can lead to seizure activity Benzodiazepines and ...
... only found within the CNS. control excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain and controlling spinal and cerebral reflexes. anxiety disorders decreased GABA can lead to seizure activity Benzodiazepines and ...
The Biological Basis of Behavior Why should Psychologists be
... stimulation and send a signal to the spinal cord where the information is passed on to an interneuron (within the spinal cord) and another neuron to the brain. The interneuron relays the message to a motor (efferent) neuron which signals the muscle to contract and move the finger. A short time later ...
... stimulation and send a signal to the spinal cord where the information is passed on to an interneuron (within the spinal cord) and another neuron to the brain. The interneuron relays the message to a motor (efferent) neuron which signals the muscle to contract and move the finger. A short time later ...
notes as
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
... and bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron thus changing their shape. – This opens up holes that allow specific ions in or out. • The effectiveness of the synapse can be changed – vary the number of vesicles of transmitter – vary the number of receptor molecules. • Syn ...
Convert - public.coe.edu
... Ligand-Receptors Binding Binding site specific point of ligand & receptor Affinity attraction physical & electrical fit NT or drug binds to receptor or activity of neuron excite or inhibit Drugs mimic or block NT message ~ ...
... Ligand-Receptors Binding Binding site specific point of ligand & receptor Affinity attraction physical & electrical fit NT or drug binds to receptor or activity of neuron excite or inhibit Drugs mimic or block NT message ~ ...
Biology of the Mind
... Neurons in the brain cluster into work groups called neural networks. The cell in each layer of a neural network connect with various cells in the next layer. With experience, networks can learn, as feedback strengthens or inhibits connections that produce certain results. One network is interconn ...
... Neurons in the brain cluster into work groups called neural networks. The cell in each layer of a neural network connect with various cells in the next layer. With experience, networks can learn, as feedback strengthens or inhibits connections that produce certain results. One network is interconn ...
Slide ()
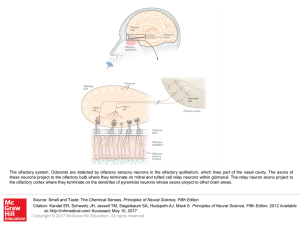
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Bill Deakin University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
... The Neuroscience and Psychiatry Unit aims to understand the neurobiology of common mental illness and new principles of treatment using neuroimaging together with cognitive and drug challenges. We will tailor the research training experiences to the individual needs of the ECNP visiting scientist. C ...
... The Neuroscience and Psychiatry Unit aims to understand the neurobiology of common mental illness and new principles of treatment using neuroimaging together with cognitive and drug challenges. We will tailor the research training experiences to the individual needs of the ECNP visiting scientist. C ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... DN: Name the functions of the dendrite, axon, myelin sheath and synapse. What is a neurotransmitter? Impulses are regulated ion gradients—these create action potentials. What is an ion channel? What is a gradient? Nerves can end at muscle tissue to deliver a stimulus to contract muscle. This enables ...
... DN: Name the functions of the dendrite, axon, myelin sheath and synapse. What is a neurotransmitter? Impulses are regulated ion gradients—these create action potentials. What is an ion channel? What is a gradient? Nerves can end at muscle tissue to deliver a stimulus to contract muscle. This enables ...
Plants and Pollinators
... • Light rays pass through lens and converge on retina at back of eye • The image that forms on the retina is upside down and reversed right to left ...
... • Light rays pass through lens and converge on retina at back of eye • The image that forms on the retina is upside down and reversed right to left ...
Opoid Analgesics Essay Research Paper Opioid AnalgesicsOpium
... The duration of pain may also help in deciding the choice of analgesic. There are three possible ways of altering the duration of the analgesia: a) Type of analgesic (e.g. fentanyl rapid onset lasts for 30 min. useful for pain immediately following operation; pethidine similar used during childbirth ...
... The duration of pain may also help in deciding the choice of analgesic. There are three possible ways of altering the duration of the analgesia: a) Type of analgesic (e.g. fentanyl rapid onset lasts for 30 min. useful for pain immediately following operation; pethidine similar used during childbirth ...
скачати - Essays, term papers, dissertation, diplomas - ua
... that is regulated by the opioid receptors present in this region of the brain. Opioids have also been typically used to as cough suppressants and sure enough this appears to be explained by the presence of large numbers of opioid receptors in the cough centre of the brain. What do we know about the ...
... that is regulated by the opioid receptors present in this region of the brain. Opioids have also been typically used to as cough suppressants and sure enough this appears to be explained by the presence of large numbers of opioid receptors in the cough centre of the brain. What do we know about the ...




![NALTREXONE[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008499817_1-96b3e8696c43dc1d94e990e6680b7eac-300x300.png)