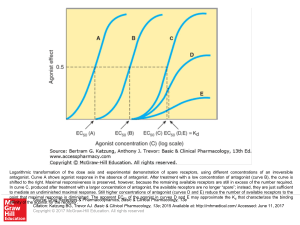
Unit_5_Topic_8_Grey_matter_Objectives
... 8. Compare mechanisms of coordination in plants and animals, ie nervous and hormonal, including the role of IAA in photostropism (details of individual mammalian hormones are not required). 9. Locate and state the functions of the regions of the human brain’s cerebral hemispheres (ability to see, th ...
... 8. Compare mechanisms of coordination in plants and animals, ie nervous and hormonal, including the role of IAA in photostropism (details of individual mammalian hormones are not required). 9. Locate and state the functions of the regions of the human brain’s cerebral hemispheres (ability to see, th ...
Nervous System
... 50. What term is given to functionally related bundles of axons in the white matter? 51. Are tracts distinguishable in the brain or spinal cord with routine processing? 52. What is neuropil? 53. What is the location of white matter in the spinal cord? 54. What term applies to groups of nerve cell b ...
... 50. What term is given to functionally related bundles of axons in the white matter? 51. Are tracts distinguishable in the brain or spinal cord with routine processing? 52. What is neuropil? 53. What is the location of white matter in the spinal cord? 54. What term applies to groups of nerve cell b ...
Endocrine System PowerPoint
... Some receptors are on only a relatively small number of cells e.g. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone receptors Cells can have receptors for more than one type of hormone ...
... Some receptors are on only a relatively small number of cells e.g. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone receptors Cells can have receptors for more than one type of hormone ...
5 pairs of sacral nerves
... Parasympathomimetics •AKA – cholinergic agents •Cholinergic = parasympathetic •Classic – acetylcholine •Does not stay long in body, rapidly destroyed after receptor binding •Direct acting – bind to cholinergic receptors to produce rest/digest response – AKA muscarinic agonist •Indirect acting – avo ...
... Parasympathomimetics •AKA – cholinergic agents •Cholinergic = parasympathetic •Classic – acetylcholine •Does not stay long in body, rapidly destroyed after receptor binding •Direct acting – bind to cholinergic receptors to produce rest/digest response – AKA muscarinic agonist •Indirect acting – avo ...
nervous system
... • Depolarization of presynaptic membrane causes influx of Ca2+ • Increased Ca2+ in cell causes synaptic vesicles to fuse to cell membrane and release neurotransmitters via exocytosis • Neurotransmitters diffuse to postsynaptic cell • Postsynaptic membrane has gated channels that open when neurotran ...
... • Depolarization of presynaptic membrane causes influx of Ca2+ • Increased Ca2+ in cell causes synaptic vesicles to fuse to cell membrane and release neurotransmitters via exocytosis • Neurotransmitters diffuse to postsynaptic cell • Postsynaptic membrane has gated channels that open when neurotran ...
It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
B6 Brain and Mind revised - Blackpool Aspire Academy
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... • Humans born with all our neurons that slowly die over our lifetime. • What two areas of the brain does new research suggest can regrow? – Hippocampus and olfactory bulb ...
... • Humans born with all our neurons that slowly die over our lifetime. • What two areas of the brain does new research suggest can regrow? – Hippocampus and olfactory bulb ...
The Nervous System
... low dosages can lead to paralysis or Alzheimer’s disease Dopamine – involved with learning, emotional arousal; low levels are linked to schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease Serotonin – may result in depression ...
... low dosages can lead to paralysis or Alzheimer’s disease Dopamine – involved with learning, emotional arousal; low levels are linked to schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease Serotonin – may result in depression ...
Chapter 2 - WordPress.com
... Synapse – when an impulse reaches its terminal buttons, it triggers the release of chemical messengers (neurotransmitters). The chemicals move across to be received by the receiving cell (muscle, gland, or another neuron) ...
... Synapse – when an impulse reaches its terminal buttons, it triggers the release of chemical messengers (neurotransmitters). The chemicals move across to be received by the receiving cell (muscle, gland, or another neuron) ...
Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission
... Instead, that electrical signal triggers chemical changes that can cross the synapse and affect the postsynaptic cell. When the electrical impulse reaches the presynaptic axon terminal, it causes membranous sacs, called vesicles, to move toward the membrane of the axon terminal. When the vesicles re ...
... Instead, that electrical signal triggers chemical changes that can cross the synapse and affect the postsynaptic cell. When the electrical impulse reaches the presynaptic axon terminal, it causes membranous sacs, called vesicles, to move toward the membrane of the axon terminal. When the vesicles re ...
MPTP - Columbia University
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... a) Reflex actions can happen with/without the participation of the brain. b) Grey matter is shaped like the wings of a bird/butterfly. c) Grey matter is found in the centre/on the outside of the spinal cord. 7. Name the different parts of the brain. 8. What is the function of the skull? 9. Complete ...
... a) Reflex actions can happen with/without the participation of the brain. b) Grey matter is shaped like the wings of a bird/butterfly. c) Grey matter is found in the centre/on the outside of the spinal cord. 7. Name the different parts of the brain. 8. What is the function of the skull? 9. Complete ...
Kinase clamping
... neuronal silencing—while the native receptor was unaffected. Considering the wide range of natural ligands that bind various GPCRs, receptors could be engineered to be activated by essentially any ligand using this strategy. Other scientists are already using the receptors generated in this study as ...
... neuronal silencing—while the native receptor was unaffected. Considering the wide range of natural ligands that bind various GPCRs, receptors could be engineered to be activated by essentially any ligand using this strategy. Other scientists are already using the receptors generated in this study as ...
Salomon Z
... presynaptic receptors and if that phenomenon could be observed for other transmitters as well. It turned out that in the central nervous system, dopamine release like norepinepherine release was equally modulated presynaptically. For dopamine the presynaptic receptors are of the D2 and D3 sub-type a ...
... presynaptic receptors and if that phenomenon could be observed for other transmitters as well. It turned out that in the central nervous system, dopamine release like norepinepherine release was equally modulated presynaptically. For dopamine the presynaptic receptors are of the D2 and D3 sub-type a ...
A Project by Rose Software Ltd
... Thus, low levels of V3 activity strengthen sexual openness, also, intensity of adventurousness of males can be predicted from the length of D4DR (dopamine 4 receptor gene), and that is (D4) where low dose of cocain expresses its effect via strengthening openness in a similar manner (also in females ...
... Thus, low levels of V3 activity strengthen sexual openness, also, intensity of adventurousness of males can be predicted from the length of D4DR (dopamine 4 receptor gene), and that is (D4) where low dose of cocain expresses its effect via strengthening openness in a similar manner (also in females ...
Concept Mapping Back Print
... receptor protein The drug molecule binds to the reuptake receptor that would normally remove the neurotransmitter molecules from the synapse and end the impulse. As a result, the impulse continues and the postsynaptic neuron is overstimulated. ...
... receptor protein The drug molecule binds to the reuptake receptor that would normally remove the neurotransmitter molecules from the synapse and end the impulse. As a result, the impulse continues and the postsynaptic neuron is overstimulated. ...
Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
Jeopardy
... receptor is an allosteric modulatory site, in addition to the benzodiazepine, this needs to be present to alter the function of the GABA A receptor ...
... receptor is an allosteric modulatory site, in addition to the benzodiazepine, this needs to be present to alter the function of the GABA A receptor ...
receptor
... Group 4: While on the T, Joe reviews for a Spanish quiz. He looks at flashcards with vocabulary to test his memory. Model the neurons and their connections to see the flashcards and test language memory. Group 5: At basketball practice, Joe warms up by practicing his free throw. Model the neurons an ...
... Group 4: While on the T, Joe reviews for a Spanish quiz. He looks at flashcards with vocabulary to test his memory. Model the neurons and their connections to see the flashcards and test language memory. Group 5: At basketball practice, Joe warms up by practicing his free throw. Model the neurons an ...
The Nervous System
... Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Soma (cell body): the neuron’s life supp ...
... Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Soma (cell body): the neuron’s life supp ...
Losartar is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist drug used mainly to
... account for its nephroprotective effects.[4] Effects on TGF-β expression may also ...
... account for its nephroprotective effects.[4] Effects on TGF-β expression may also ...
Nervous Dia rams
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...