CHAPTER 35 Human Body Systems: The levels of organization in
... 1. Somatic Nervous System: regulates activities under conscious control. Wiggle a toe or make a fist. 2. Autonomic Nervous System: regulates involuntary responses- will speed up your heart rate when you are running. The Autonomic nervous system has 2 parts: Sympathetic nervous system and parasympath ...
... 1. Somatic Nervous System: regulates activities under conscious control. Wiggle a toe or make a fist. 2. Autonomic Nervous System: regulates involuntary responses- will speed up your heart rate when you are running. The Autonomic nervous system has 2 parts: Sympathetic nervous system and parasympath ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... amount of stress present and will cause transient changes in heart rate and systemic arteries and veins. Epinephrine is a constant in regulating heart rate, vasoconstriction in systemic arteries and veins and vasodilation of muscles and liver. ...
... amount of stress present and will cause transient changes in heart rate and systemic arteries and veins. Epinephrine is a constant in regulating heart rate, vasoconstriction in systemic arteries and veins and vasodilation of muscles and liver. ...
sex hormone production by testis and ovary
... ● Individuals with Y chromosome with SRY gene will develop as males ● In the absence of Y Female development is the ‘default pathway’ ...
... ● Individuals with Y chromosome with SRY gene will develop as males ● In the absence of Y Female development is the ‘default pathway’ ...
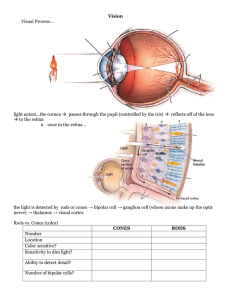
Vision Lecture Notes
... from these, the brain (frontal, parietal and temporal lobes) assembles the image ● parallel processing – the brain processes several aspects of a problem simultaneously ...
... from these, the brain (frontal, parietal and temporal lobes) assembles the image ● parallel processing – the brain processes several aspects of a problem simultaneously ...
Brain Scan Imaging
... body with outstanding clarity. • A magnetic resonance imaging system uses a powerful magnet, radio signals and sophisticated computer software technology. Because certain atoms in our cells respond or “resonate” lightly in the presence of magnetic fields, the MRI is able to use that response to crea ...
... body with outstanding clarity. • A magnetic resonance imaging system uses a powerful magnet, radio signals and sophisticated computer software technology. Because certain atoms in our cells respond or “resonate” lightly in the presence of magnetic fields, the MRI is able to use that response to crea ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
... motor neuron response Involuntary, does NOT involve the brain ...
... motor neuron response Involuntary, does NOT involve the brain ...
Problem Set
... linked to increased susceptibility to anxiety disorders in humans, suggesting there is decreased function of the NPSR in humans with this mutation. Mice with this mutation also show increased ...
... linked to increased susceptibility to anxiety disorders in humans, suggesting there is decreased function of the NPSR in humans with this mutation. Mice with this mutation also show increased ...
Lecture 5
... Delirium ____________________________________withdrawal Emotional disturbances still there, but physical symptoms of withdrawal are mainly gone Sleep problems and mood swings still Protracted withdrawal ____________________________________cued withdrawal Can last for years, even decades after the us ...
... Delirium ____________________________________withdrawal Emotional disturbances still there, but physical symptoms of withdrawal are mainly gone Sleep problems and mood swings still Protracted withdrawal ____________________________________cued withdrawal Can last for years, even decades after the us ...
Antidepressant_agents
... only as new enzyme is biosynthesized) Have a rapid rate of elimination, excess drug is rapidly metabolized Inhibition occurs slowly ...
... only as new enzyme is biosynthesized) Have a rapid rate of elimination, excess drug is rapidly metabolized Inhibition occurs slowly ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... pathways 3. Somatosensory cortex D. Physiology of motor pathways 1. Direct (pyramidal) pathways 2. Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways ...
... pathways 3. Somatosensory cortex D. Physiology of motor pathways 1. Direct (pyramidal) pathways 2. Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways ...
Additional Science B6 Module – What You Should Know
... a. sensory neurons carrying impulses from receptors to the CNS b. motor neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to effectors I understand that within the CNS, impulses are passed from sensory neurons to motor neurons through relay neurons I describe the nervous pathway of a spinal reflex arc to inclu ...
... a. sensory neurons carrying impulses from receptors to the CNS b. motor neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to effectors I understand that within the CNS, impulses are passed from sensory neurons to motor neurons through relay neurons I describe the nervous pathway of a spinal reflex arc to inclu ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
Curriculum
... tissue and cell culture systems to address many complex mechanisms in simplified versions. But this is important and in some instances, it is a prerequisite for many translational research related to human health and diseases. Like any other model organisms, Drosophila possesses many unique characte ...
... tissue and cell culture systems to address many complex mechanisms in simplified versions. But this is important and in some instances, it is a prerequisite for many translational research related to human health and diseases. Like any other model organisms, Drosophila possesses many unique characte ...
Estimating Dynamic Neural Interactions in Awake Behaving Animals
... with millisecond precision. It is likely that the correlated activity organizes dynamically during behavior and cognition, and this may be independent from spike rates of individual neurons. Consequently current analysis tools must be extended so that they can directly estimate timevarying neural in ...
... with millisecond precision. It is likely that the correlated activity organizes dynamically during behavior and cognition, and this may be independent from spike rates of individual neurons. Consequently current analysis tools must be extended so that they can directly estimate timevarying neural in ...
Principles of Biology ______Lake Tahoe
... 1. neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that is not part of an ion channel a. activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in postsynaptic cell b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens m ...
... 1. neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that is not part of an ion channel a. activates a signal transduction pathway involving a second messenger in postsynaptic cell b. slower onset but last longer 2. eg. when norepinephrine binds to its receptor, a G protein is activated, which ultimately opens m ...
Autonomic nervous system
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
Slide 1
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
What structures comprise the sympathetic division?
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
Effects of Titanium Particle Radiation on the Cerebral Cortex
... executive functions such as planning, decision making, and social behavior. We analyzed the effects of oxygen and titanium (5 and 30cGy) ion exposure on cognitive performance and a dance of morphometric parameters in the mPFC neurons in Thy1-EGFP (6-month old) mice six weeks following irradiation. O ...
... executive functions such as planning, decision making, and social behavior. We analyzed the effects of oxygen and titanium (5 and 30cGy) ion exposure on cognitive performance and a dance of morphometric parameters in the mPFC neurons in Thy1-EGFP (6-month old) mice six weeks following irradiation. O ...
action potentials - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Membrane potential is the electrical charge difference across the membrane. Resting potential is the steady state membrane potential of a neuron. Voltage (electric potential difference): force that causes charged particles to move between two points. The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 mi ...
... Membrane potential is the electrical charge difference across the membrane. Resting potential is the steady state membrane potential of a neuron. Voltage (electric potential difference): force that causes charged particles to move between two points. The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 mi ...
Brain - People
... • What if a neuron works like an antenna ? • If so the neuron-neuron interaction is coming from the electromagnetic field emitted and received by each neuron • A mean-field approach is likely to be valid, due to the close proximity of a large number of neuron and the slow decay of the electromagneti ...
... • What if a neuron works like an antenna ? • If so the neuron-neuron interaction is coming from the electromagnetic field emitted and received by each neuron • A mean-field approach is likely to be valid, due to the close proximity of a large number of neuron and the slow decay of the electromagneti ...