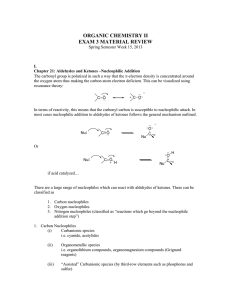
organic chemistry ii
... In cases where enolate formation can take place at non-equivalent carbons the reaction can take place under (i) thermodynamic or (ii) kinetic conditions (i) a thermodynamic enolate is the more stable (more substituted) enolate which can be formed upon reaction with only a mildly strong base such as ...
... In cases where enolate formation can take place at non-equivalent carbons the reaction can take place under (i) thermodynamic or (ii) kinetic conditions (i) a thermodynamic enolate is the more stable (more substituted) enolate which can be formed upon reaction with only a mildly strong base such as ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... pi bond up to the oxygen. (eg: ) Alternatively, if start with the minor resonance contributor: attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation. (eg: ) After the carbonyl is attacked by the nucleophile, the negatively charged oxygen has the capacity to act as a nucleophile. However, most commonly the ox ...
... pi bond up to the oxygen. (eg: ) Alternatively, if start with the minor resonance contributor: attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation. (eg: ) After the carbonyl is attacked by the nucleophile, the negatively charged oxygen has the capacity to act as a nucleophile. However, most commonly the ox ...
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is an organic reaction of an aldehyde
... The MBH reaction in general is any reaction of electron deficient alkenes and sp2 hybridized carbon electrophiles such as aldehydes, ketones and aldimines catalyzed by a nucleophile. Under special reaction conditions the reaction is also found to extend to alkyl halides as the electrophilic reagent. ...
... The MBH reaction in general is any reaction of electron deficient alkenes and sp2 hybridized carbon electrophiles such as aldehydes, ketones and aldimines catalyzed by a nucleophile. Under special reaction conditions the reaction is also found to extend to alkyl halides as the electrophilic reagent. ...
7-1 EXPERIMENT 7: Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds – Achiral
... Although various methods for this conversion are possible, the most frequently employed is the use of complex metal hydride reagents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4). These particular reagents are also soluble in organic solvents and are not as reactive as a s ...
... Although various methods for this conversion are possible, the most frequently employed is the use of complex metal hydride reagents such as lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4). These particular reagents are also soluble in organic solvents and are not as reactive as a s ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... be a site that is attacked by nucleophiles. And, since the oxygen bears a partial negative charge, it is likely to be a site of electrophilic attack. Since ordinary carbanions (R: −) and hydride ions (H: −) are very poor leaving groups (unlike ...
... be a site that is attacked by nucleophiles. And, since the oxygen bears a partial negative charge, it is likely to be a site of electrophilic attack. Since ordinary carbanions (R: −) and hydride ions (H: −) are very poor leaving groups (unlike ...
Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions
... Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Markovnikov’s Rule: The major product obtained from the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the grea ...
... Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Markovnikov’s Rule: The major product obtained from the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the grea ...
Chapter 18
... Upon application of light, a cis/trans interconversion occurs which is converted into an electrochemical impulse by affecting the concentration of Ca2+ crossing a cell membrane ...
... Upon application of light, a cis/trans interconversion occurs which is converted into an electrochemical impulse by affecting the concentration of Ca2+ crossing a cell membrane ...
I. ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Carbonyl compounds are
... Drawing the structure of the reacting enol-aldehyde pair, as shown above, the mechanism of the condensation becomes clear. It is also possible to utilize two different aldehydes or ketones in an aldol-type condensation reaction. In order to minimize self-condensations, generally one reactant is cho ...
... Drawing the structure of the reacting enol-aldehyde pair, as shown above, the mechanism of the condensation becomes clear. It is also possible to utilize two different aldehydes or ketones in an aldol-type condensation reaction. In order to minimize self-condensations, generally one reactant is cho ...
06 MC /08 MC /08 NMR
... Multiple Choice. (2 points each): Write the best answer in the box provided. l. Which of the following alkenes is expected to have the highest heat of hydrogenation? (Least stable isomer) A) l-pentene B) trans-2-pentene C) cis-2-pentene D) 2-methyl-2-butene ofthe following is not a possible reaction ...
... Multiple Choice. (2 points each): Write the best answer in the box provided. l. Which of the following alkenes is expected to have the highest heat of hydrogenation? (Least stable isomer) A) l-pentene B) trans-2-pentene C) cis-2-pentene D) 2-methyl-2-butene ofthe following is not a possible reaction ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
... The Wittig is unique in that the alkoxide oxygen in the tetrahedral intermediate attacks the phosphonium center forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form tr ...
... The Wittig is unique in that the alkoxide oxygen in the tetrahedral intermediate attacks the phosphonium center forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to form tr ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... 7. Using Curved Arrows in Polar Reaction Mechanisms 8. Describing a Reaction: Equilibria, Rates, and Energy Changes, Bond Dissociation Energies, and Energy Diagrams , Transition States, and Intermediates Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity- You should know; ...
... 7. Using Curved Arrows in Polar Reaction Mechanisms 8. Describing a Reaction: Equilibria, Rates, and Energy Changes, Bond Dissociation Energies, and Energy Diagrams , Transition States, and Intermediates Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity- You should know; ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... • Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to produce alcohols. • The reducing agent of choice is LiAlH4 - lithium aluminium hydride • Able to transfer a hydride ion to the partially positive carbon atom of the carbonyl group • Musty be carried out in anhydrous conditions (in ether) ...
... • Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced to produce alcohols. • The reducing agent of choice is LiAlH4 - lithium aluminium hydride • Able to transfer a hydride ion to the partially positive carbon atom of the carbonyl group • Musty be carried out in anhydrous conditions (in ether) ...
Nomenclature - Clydebank High School
... This is the opposite of a condensation reaction. We are splitting the ester - back into the alkanol and alkanoic acid. We must add back the water which is removed in the condensation reaction. This is not very successful with water alone so we add a dilute acid to catalyse it e.g. HCl or H2SO4. (Or ...
... This is the opposite of a condensation reaction. We are splitting the ester - back into the alkanol and alkanoic acid. We must add back the water which is removed in the condensation reaction. This is not very successful with water alone so we add a dilute acid to catalyse it e.g. HCl or H2SO4. (Or ...
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... Since thioacetals are quite stable toward hydrolysis, there is no special need to remove the H2O formed during the reaction. Since it is more difficult to equilibrate thioacetals than acetal via protonation, double bond migration in thioacetalization of enones is not usually observed. ...
... Since thioacetals are quite stable toward hydrolysis, there is no special need to remove the H2O formed during the reaction. Since it is more difficult to equilibrate thioacetals than acetal via protonation, double bond migration in thioacetalization of enones is not usually observed. ...
Chapter 21 aldehydes and ketones
... • Nucleophilic trends in carbonyl attack are not the same as in straightforward substitution reactions at sp3 carbon atoms. • Cl¯, Br¯, and I¯ are good nucleophiles in substitution reactions at sp3 hybridized carbons, but they are ineffective nucleophiles in addition. • When these nucleophiles add t ...
... • Nucleophilic trends in carbonyl attack are not the same as in straightforward substitution reactions at sp3 carbon atoms. • Cl¯, Br¯, and I¯ are good nucleophiles in substitution reactions at sp3 hybridized carbons, but they are ineffective nucleophiles in addition. • When these nucleophiles add t ...