- EdShare - University of Southampton
... Alkenes are unsaturated compounds that can be used in organic synthesis. They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to comp ...
... Alkenes are unsaturated compounds that can be used in organic synthesis. They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to comp ...
CHMY_271_practice_exam_3
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. Br ...
... 11. (6 pt) If the following alkyl halide were to undergo elimination, predict the major product in each case, and explain your answer. You do not need to draw out the mechanism, but knowing the mechanism will help you to predict reasonable products. Br ...
Exam 1
... For chap 12: 12.1 (Grignard only) For chap 14: 14. 18 14.20, 14.21 (color) For chap 16: 16.2,16.5, 16.6-16.16, 16.20, 16.22-16.23 For chap 17: 17.2, 17.3, 17.4 & 17.7 For chap 19; 19.21, 19.22 (Azo dye reaction) Know and be able draw the arrow pushing mechanism for these reactions: Electrophilic Aro ...
... For chap 12: 12.1 (Grignard only) For chap 14: 14. 18 14.20, 14.21 (color) For chap 16: 16.2,16.5, 16.6-16.16, 16.20, 16.22-16.23 For chap 17: 17.2, 17.3, 17.4 & 17.7 For chap 19; 19.21, 19.22 (Azo dye reaction) Know and be able draw the arrow pushing mechanism for these reactions: Electrophilic Aro ...
Chem 30CL - Lecture 1c - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... The iso-propyl group in the auxiliary generates steric hindrance for the approach from the same side in the enolate (the high-lighted atom is the one which is deprotonated) ...
... The iso-propyl group in the auxiliary generates steric hindrance for the approach from the same side in the enolate (the high-lighted atom is the one which is deprotonated) ...
Chemguide – answers ALCOHOLS: THE TRIIODOMETHANE
... 1. a) Either: Add iodine solution followed by enough sodium hydroxide solution to remove the colour of the iodine. Warm very gently if nothing happens in the cold. Or: Add potassium iodide solution followed by sodium chlorate(I) solution (sodium hypochlorite solution). Warm very gently if nothing ha ...
... 1. a) Either: Add iodine solution followed by enough sodium hydroxide solution to remove the colour of the iodine. Warm very gently if nothing happens in the cold. Or: Add potassium iodide solution followed by sodium chlorate(I) solution (sodium hypochlorite solution). Warm very gently if nothing ha ...
Chapter 9. Addition Reactions of Alkenes
... The reaction below, which provides compound M as its major product, appears to defy the principles that we discussed in class. Draw the structures of the intermediate carbocations that form in this reaction, then clearly but briefly explain why M, and not L, is the major product of this reaction. Hi ...
... The reaction below, which provides compound M as its major product, appears to defy the principles that we discussed in class. Draw the structures of the intermediate carbocations that form in this reaction, then clearly but briefly explain why M, and not L, is the major product of this reaction. Hi ...
Elimination reactions under acidic conditions
... 4. In each of these reactions, there is more than one alkene that could form. Draw out all possible products, and then circle the one you would predict to be the major product. (Don’t worry about cis/trans isomers.) ...
... 4. In each of these reactions, there is more than one alkene that could form. Draw out all possible products, and then circle the one you would predict to be the major product. (Don’t worry about cis/trans isomers.) ...
Exam - Chemistry With BT
... requires more than one step. Show all the steps of the synthesis in the right sequence. Give the reagents used and the reaction conditions utilized (including acid base catalysis). Show the structures of all intermediate products. ...
... requires more than one step. Show all the steps of the synthesis in the right sequence. Give the reagents used and the reaction conditions utilized (including acid base catalysis). Show the structures of all intermediate products. ...
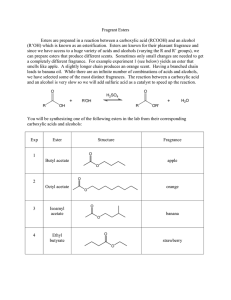
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 18. How are oxidizing agents chemoselective? Explain with suitable examples. 19. Explain the mechanism of Aldol condensation and Wittig reaction. 20. Discuss the mechanism of Baeyer Villiger reaction with suitable example. 21. Discuss on the electroorganic synthesis by reduction with suitable exampl ...
... 18. How are oxidizing agents chemoselective? Explain with suitable examples. 19. Explain the mechanism of Aldol condensation and Wittig reaction. 20. Discuss the mechanism of Baeyer Villiger reaction with suitable example. 21. Discuss on the electroorganic synthesis by reduction with suitable exampl ...
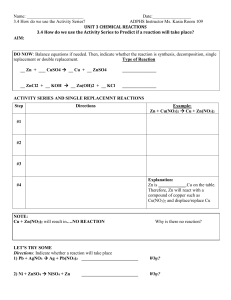
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
Exam 2 Review Sheet for Friday, March 2 Exam Chem 1120, Spring
... • Define and use the following terms: catenation, hybridization, homologous, saturated, unsaturated, condensed structural formula, general structural formula, radicals, isomers. • Explain why there are so many carbon compounds. • List and explain the different types of hybridization that carbon unde ...
... • Define and use the following terms: catenation, hybridization, homologous, saturated, unsaturated, condensed structural formula, general structural formula, radicals, isomers. • Explain why there are so many carbon compounds. • List and explain the different types of hybridization that carbon unde ...
Slide 1
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
... presence of base or by heating a mixture of the reactants at high temperatures ranging from 150-220°C in the absence of catalyst.(1) ...
Name - Clark College
... The first step of the reaction is the straightforward process of the pi bond (Lewis Base) going after a proton (Lewis Acid) from sulfuric acid, to create the 3° carbocation. At this point the available Lewis bases to go after the carbocation are the alcohol and the hydrogen sulfate ion. The alcohol ...
... The first step of the reaction is the straightforward process of the pi bond (Lewis Base) going after a proton (Lewis Acid) from sulfuric acid, to create the 3° carbocation. At this point the available Lewis bases to go after the carbocation are the alcohol and the hydrogen sulfate ion. The alcohol ...
File
... Deduce a reaction pathway for the two-stage conversion of 1-bromopropane to 1-butylamine (butan-1-amine). Your answer should include an equation for each stage of the reaction and the reaction conditions for the second stage. ...
... Deduce a reaction pathway for the two-stage conversion of 1-bromopropane to 1-butylamine (butan-1-amine). Your answer should include an equation for each stage of the reaction and the reaction conditions for the second stage. ...
How to study organic chemistry?
... Which type of systems act as E+ or Nu-? Same system act as E+ or Nu- depending on which system it reacts. Acidity and Basicity: General idea of order of acidity and basicity. Bronsted & Lewis theory. Effect of back-bonding , aromaticity, SIR,etc. ...
... Which type of systems act as E+ or Nu-? Same system act as E+ or Nu- depending on which system it reacts. Acidity and Basicity: General idea of order of acidity and basicity. Bronsted & Lewis theory. Effect of back-bonding , aromaticity, SIR,etc. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Multiple bonds are treated as attachments of multiple single bonds C ...
... Multiple bonds are treated as attachments of multiple single bonds C ...
Formative 3.5 2014
... (ii) Amino acids can form polymers because at each end of the molecule is a functional group that can react with a functional group from neighbouring molecules. (b) To be able to form enantiomers a molecule must have a chiral atom – one to which four different groups are attached. This enables the f ...
... (ii) Amino acids can form polymers because at each end of the molecule is a functional group that can react with a functional group from neighbouring molecules. (b) To be able to form enantiomers a molecule must have a chiral atom – one to which four different groups are attached. This enables the f ...
org test 1
... b. Methanoic acid and Ethanoic acid. c. Aniline and Ethylamine 13. Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophlic addition reaction than propanal? Explain. 14. Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling points: CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3CH2 OCH2CH3, C ...
... b. Methanoic acid and Ethanoic acid. c. Aniline and Ethylamine 13. Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophlic addition reaction than propanal? Explain. 14. Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling points: CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3CH2 OCH2CH3, C ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.