Lab - Protein Synthesis
... Transcription & Translation Background: The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence in ...
... Transcription & Translation Background: The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence in ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Genetics Vocab Card Definitions
... Describes genes that each have equal effect in making the character they control appear in offspring. The genes for A and B blood groups are codominant and give rise to the AB blood group if they are both inherited ...
... Describes genes that each have equal effect in making the character they control appear in offspring. The genes for A and B blood groups are codominant and give rise to the AB blood group if they are both inherited ...
sample written evaluation
... functional gene classes and proteome-wide. In the case of functional gene class analysis, each class was divided into two subclasses, those above the MCU median and those below. The Mantel-Haenzel procedure was used to determine the probability amino acid distribution departs from equal usage. Exclu ...
... functional gene classes and proteome-wide. In the case of functional gene class analysis, each class was divided into two subclasses, those above the MCU median and those below. The Mantel-Haenzel procedure was used to determine the probability amino acid distribution departs from equal usage. Exclu ...
Chapter 8 Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... *Mutation Examples – be able to identify the type of mutation causing disorders and diseases 1. Fragile X syndrome is caused by genes that have undergone insertions of a string of 3 or 4 nucleotides repeated over and over. Specifically, a locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nu ...
... *Mutation Examples – be able to identify the type of mutation causing disorders and diseases 1. Fragile X syndrome is caused by genes that have undergone insertions of a string of 3 or 4 nucleotides repeated over and over. Specifically, a locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nu ...
Introduction - Cedar Crest College
... This bond provides the energy for making the peptide bond that will join adjacent amino acids. ...
... This bond provides the energy for making the peptide bond that will join adjacent amino acids. ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
Slide 1
... homologous chromosomes breaks and binds to the other. Usually this sort of mutation is lethal ...
... homologous chromosomes breaks and binds to the other. Usually this sort of mutation is lethal ...
gida bi̇yoteknoloji̇si̇-2
... amino acid of synthesized polypeptide chain. • Formyl group is removed after the tRNA attaches to the initiation codon. Thus, the first a.a becomes methionine. • After the protein synthesis is completed, methionine is usualy removed from the protein by methionine aminopeptidase. ...
... amino acid of synthesized polypeptide chain. • Formyl group is removed after the tRNA attaches to the initiation codon. Thus, the first a.a becomes methionine. • After the protein synthesis is completed, methionine is usualy removed from the protein by methionine aminopeptidase. ...
- thevignanam
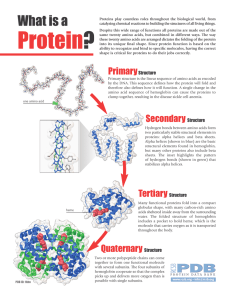
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
... • If a protein is made up of more than one polypeptide chain it is said to have quaternary structure. • This refers to the spatial arrangement of the polypeptide subunits and the nature of the interactions between them. ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... First, the tRNA binds an amino acid (there are several tRNAs for every amino acid) Then, the tRNA and the amino acid attach to the mRNA template in the ribosome Translation typically starts with Methionine, which is encoded by the sequence AUG As the amino acids attach to each other, the tRNA moves ...
... First, the tRNA binds an amino acid (there are several tRNAs for every amino acid) Then, the tRNA and the amino acid attach to the mRNA template in the ribosome Translation typically starts with Methionine, which is encoded by the sequence AUG As the amino acids attach to each other, the tRNA moves ...
AQA Biology Question number Answer Marks Guidance 1 a i (In all
... Intron non-coding (DNA)/only exons coding (So) not translated/no change in mRNA produced/no effect (on protein)/no effect on amino acid sequence ...
... Intron non-coding (DNA)/only exons coding (So) not translated/no change in mRNA produced/no effect (on protein)/no effect on amino acid sequence ...
Proteins…
... Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
... Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
Class11 POGIL Translation Full Win17 KEY v1
... a. What parts of the enzymes must be different between different members of this family? The amino acid R-group binding sites and the anticodon binding sites. b. Are the reactions catalyzed by different members of this family the same or different? How do you know? The reactions are the same – they ...
... a. What parts of the enzymes must be different between different members of this family? The amino acid R-group binding sites and the anticodon binding sites. b. Are the reactions catalyzed by different members of this family the same or different? How do you know? The reactions are the same – they ...
4.7.08 105 lecture
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase promoter – the genetic information in the DNA that tells where, when, and how much the gene should be expressed. ------------------------------coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the codi ...
g. ¶I - wwphs
... The type of covalent bond linking one amino acid to another ‘-tC Fourth level of protein organization; globular, with multiple polypeptide chains i’ Breaking weak bonds in large molecules (such as protein) to disrupt three-dimensional shapes such that they no longer function 4’ The sequence of amino ...
... The type of covalent bond linking one amino acid to another ‘-tC Fourth level of protein organization; globular, with multiple polypeptide chains i’ Breaking weak bonds in large molecules (such as protein) to disrupt three-dimensional shapes such that they no longer function 4’ The sequence of amino ...
How Did Life Begin? And What is Life?
... As a community committed to the Augustinian ideals of truth, unity and love, God School prides itself on maintaining the highest standards of academic integrity and does not tolerate any forms of academic dishonesty or misconduct. ...
... As a community committed to the Augustinian ideals of truth, unity and love, God School prides itself on maintaining the highest standards of academic integrity and does not tolerate any forms of academic dishonesty or misconduct. ...
organic molecules webquest
... questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_nucleicacids.html 1. The __________________ are the building blocks of living organisms. 2. ________________ is just one type of nucleic acid. 3. List 4 types of nucleic acids (NA’s): o o o o Draw pictures of the four nucleic acids below: ...
... questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_nucleicacids.html 1. The __________________ are the building blocks of living organisms. 2. ________________ is just one type of nucleic acid. 3. List 4 types of nucleic acids (NA’s): o o o o Draw pictures of the four nucleic acids below: ...
Handout 2: Glossary
... gene cloning The process of synthesizing multiple copies of a particular DNA sequence using a bacterial cell or another organism as a host. genetic code The set of sixty-four codons corresponding to each of the 20 amino acids. genetic engineering The technique of altering the genetic makeup of cells ...
... gene cloning The process of synthesizing multiple copies of a particular DNA sequence using a bacterial cell or another organism as a host. genetic code The set of sixty-four codons corresponding to each of the 20 amino acids. genetic engineering The technique of altering the genetic makeup of cells ...
organic macromolecules webquest
... these questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_carbos.html 1. Carbohydrates are made up of the following elements: a. ...
... these questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_carbos.html 1. Carbohydrates are made up of the following elements: a. ...
1 - UCSB CLAS
... PLP-catalyzed transaminations? a. Pyruvate b. Oxaloacetate 2. (Ch 24, #16) Which of the following compounds is more easily decarboxylated? O ...
... PLP-catalyzed transaminations? a. Pyruvate b. Oxaloacetate 2. (Ch 24, #16) Which of the following compounds is more easily decarboxylated? O ...
WHAT`S A CARBOHYDRATE
... “R” represents the “Radical” side chain that is different for each amino acid. The “R” group can either be one atom (H) or a group of atoms. ...
... “R” represents the “Radical” side chain that is different for each amino acid. The “R” group can either be one atom (H) or a group of atoms. ...
Protein?
... same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its unique final shape. Since protein function is based on the ability to recognize and bind to specific molecules, having the correct shape is critical for ...
... same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its unique final shape. Since protein function is based on the ability to recognize and bind to specific molecules, having the correct shape is critical for ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.