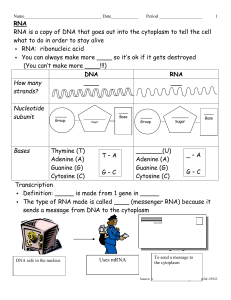
ap biology review guide big idea #2
... subjected to temperatures over 95 degrees C to make the double-stranded DNA separate. The temperature is then lowered slightly to allow primers to anneal before the Taq polymerase catalyzes the reactions to incorporate new nucleotides into the complementary strands. The cycle is then repeated over a ...
... subjected to temperatures over 95 degrees C to make the double-stranded DNA separate. The temperature is then lowered slightly to allow primers to anneal before the Taq polymerase catalyzes the reactions to incorporate new nucleotides into the complementary strands. The cycle is then repeated over a ...
Schedule
... Each amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon. A substitution mutation may change one codon but it may still code for the same amino acid; hence no effect (silent mutation). • A change in the codon may result in a different amino acid with similar properties, and it does not affect the ove ...
... Each amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon. A substitution mutation may change one codon but it may still code for the same amino acid; hence no effect (silent mutation). • A change in the codon may result in a different amino acid with similar properties, and it does not affect the ove ...
Gene7-07
... cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either in the sense of the original codon or to give an acceptable substitute for the origin ...
... cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either in the sense of the original codon or to give an acceptable substitute for the origin ...
learning objectives
... A. Introns 1. Prokaryotic DNA is made up of a continuous sequence of genes with no interruptions. 2. Eukaryotic DNA is constructed differently because it possesses gene sequences that code for amino acids, called exons, plus intervening, nonusable sequences of nucleotides, called introns. 3. Intron ...
... A. Introns 1. Prokaryotic DNA is made up of a continuous sequence of genes with no interruptions. 2. Eukaryotic DNA is constructed differently because it possesses gene sequences that code for amino acids, called exons, plus intervening, nonusable sequences of nucleotides, called introns. 3. Intron ...
Frameshift Mutations
... – RNA has uracil instead of thymine. – RNA is a single-stranded structure. ...
... – RNA has uracil instead of thymine. – RNA is a single-stranded structure. ...
Genetic information determines structure
... Describe the two binding sites of tRNA. Why is this important to the process of translation? Follow the steps in translating a six amino acid protein from start to finish. Define the term mutation. Distinguish between a point (base substitution) and a frame shift (base deletion or insertion) mutatio ...
... Describe the two binding sites of tRNA. Why is this important to the process of translation? Follow the steps in translating a six amino acid protein from start to finish. Define the term mutation. Distinguish between a point (base substitution) and a frame shift (base deletion or insertion) mutatio ...
Chapter 8
... A gene must be able to make copies of itself; mutate; store information that determines the characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that determines the characteristics of cells and organisms; 2) ...
... A gene must be able to make copies of itself; mutate; store information that determines the characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that determines the characteristics of cells and organisms; 2) ...
Final Report
... Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant function of these enzyme complexes leads to an array of diseases, including vascular disease and certain cancers. Noxo1’s role ...
... Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant function of these enzyme complexes leads to an array of diseases, including vascular disease and certain cancers. Noxo1’s role ...
List of protein families currently covered by SVMProt
... It has 16 alanines (n1=16) and 14 glutamic acids (n2=14). The composition for these two amino acids are n1×100.00/(n1+n2)=53.33 and n2×100.00/(n1+n2)=46.67 respectively. There are 15 transitions from A to E or from E to A in this sequence and the percent frequency of these transitions is (15/29)×100 ...
... It has 16 alanines (n1=16) and 14 glutamic acids (n2=14). The composition for these two amino acids are n1×100.00/(n1+n2)=53.33 and n2×100.00/(n1+n2)=46.67 respectively. There are 15 transitions from A to E or from E to A in this sequence and the percent frequency of these transitions is (15/29)×100 ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... Translation (__________synthesis): process of making a protein Proteins are made up of ________ _______ (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... Translation (__________synthesis): process of making a protein Proteins are made up of ________ _______ (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
bio 1406 final exam review
... 76. DNA fingerprints look like –the order of bases in a particular gene. 77. muscle and bone cells are different because they are differentiated 78. the simplest bacterial transposons are – insertion sequences 79. viroids are naked strands of RNA 80. Prions are infectious protein particles 81. a Pr ...
... 76. DNA fingerprints look like –the order of bases in a particular gene. 77. muscle and bone cells are different because they are differentiated 78. the simplest bacterial transposons are – insertion sequences 79. viroids are naked strands of RNA 80. Prions are infectious protein particles 81. a Pr ...
Topic 12 (Ch9/7) – Microbial Genetics Genetics Chromosome
... • Copy of a structural gene or genes of DNA – Can encode for multiple proteins on one message ...
... • Copy of a structural gene or genes of DNA – Can encode for multiple proteins on one message ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... Translation is terminated with the stop codon is reached. There are three different stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG. The release factor recognizes the stop codon and releases the polypeptide strand. All the factors break apart and are reused. ...
... Translation is terminated with the stop codon is reached. There are three different stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG. The release factor recognizes the stop codon and releases the polypeptide strand. All the factors break apart and are reused. ...
R N A & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein) is called translation, which takes place on ribosomes Amino Acids are transported by ribosomes & tRNA molecules, which have specific regions that bond to AA The loop attachment has a sequence of 3 nucleotides called anticodons. The t ...
... The decoding of an mRNA message into a polypeptide chain (protein) is called translation, which takes place on ribosomes Amino Acids are transported by ribosomes & tRNA molecules, which have specific regions that bond to AA The loop attachment has a sequence of 3 nucleotides called anticodons. The t ...
Genetic Code and Transcription
... – Three stages of translation – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Translation ...
... – Three stages of translation – Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Translation ...
Protein Synthesis
... 1 – Transcription is the transfer of the information from DNA to RNA Step 2- Translation is the process of reading the information on DNA and converting it into the amino acid sequences of the protein The specific sequence of genes (bases) on DNA directly determine the sequence of RNA, and there ...
... 1 – Transcription is the transfer of the information from DNA to RNA Step 2- Translation is the process of reading the information on DNA and converting it into the amino acid sequences of the protein The specific sequence of genes (bases) on DNA directly determine the sequence of RNA, and there ...
Chapter 17
... between genetic variations in organisms and phenotypic variations in populations. [See SP 7.2] ...
... between genetic variations in organisms and phenotypic variations in populations. [See SP 7.2] ...
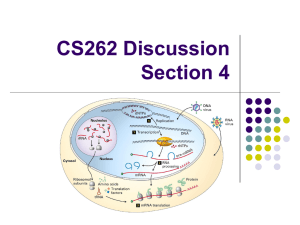
CS262 Discussion Section 4
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
Macromolecules pt 3
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a ...
... Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (Usually read N-C) Secondary structures are localized folds or helices that form within a region of a ...
From Gene to Protein—Transcription and Translation
... Draw a rectangle around the third codon in the messenger RNA. What is the anti-codon for that codon? The anti-codon for the third amino acid will be GAC Which amino acid will be the third amino acid in the hemoglobin protein? The third amino acid will be leucine. 12. Describe one similarity in the s ...
... Draw a rectangle around the third codon in the messenger RNA. What is the anti-codon for that codon? The anti-codon for the third amino acid will be GAC Which amino acid will be the third amino acid in the hemoglobin protein? The third amino acid will be leucine. 12. Describe one similarity in the s ...
Molecules of life
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
Side chains are negatively charged
... Genetic Code Properties • Purine (A,G) is heavier than Pyrimidine (C,T) • Transition within a type (Purines or Pyrimidineㄴ) is more likely than Translation between types • All AAs have more than one codon, except for Met and Trp • Codons for an AA are clustered – Two codons for an AA – same in the ...
... Genetic Code Properties • Purine (A,G) is heavier than Pyrimidine (C,T) • Transition within a type (Purines or Pyrimidineㄴ) is more likely than Translation between types • All AAs have more than one codon, except for Met and Trp • Codons for an AA are clustered – Two codons for an AA – same in the ...
File - Biology Class With Mrs. Caskey
... ____________________ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What ar ...
... ____________________ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What ar ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? electrons_ 13. Negatively charged particles of an atom are called this. active site or bonding site_ 14. This is the name for the region wher ...
... deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? electrons_ 13. Negatively charged particles of an atom are called this. active site or bonding site_ 14. This is the name for the region wher ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.