chapter 17 and 18 study guide
... Promoter? A specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA that binds RNA polymerase, positioning it to start transcribing RNA at the appropriate place Repressor? A protein that inhibits gene transcription; in prokaryotes repressors bind to the DNA in or near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind ...
... Promoter? A specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA that binds RNA polymerase, positioning it to start transcribing RNA at the appropriate place Repressor? A protein that inhibits gene transcription; in prokaryotes repressors bind to the DNA in or near the promoter; in eukaryotes repressors can bind ...
Document
... mRNA (messenger-RNA) nucleotides scattered next to it. This represents the contents of the nucleus. 4. Now, on the left side of the membrane (in the "cytoplasm"), place the "ribosome" surface in a horizontal position across the bottom of that area, and scatter the yellow tRNA (transfer-RNA) pieces a ...
... mRNA (messenger-RNA) nucleotides scattered next to it. This represents the contents of the nucleus. 4. Now, on the left side of the membrane (in the "cytoplasm"), place the "ribosome" surface in a horizontal position across the bottom of that area, and scatter the yellow tRNA (transfer-RNA) pieces a ...
SMU-DDE-Assignments-Scheme of Evaluation PROGRAM msc
... promoter called CAP site. • By themselves, both RNA polymerase and cAMP CAP complex have relatively low affinity for their respective binding sites in lac promoter DNA. Interaction between residues in CAP and α subunit of RNA polymerase forms a protein protein complex that binds much more stably to ...
... promoter called CAP site. • By themselves, both RNA polymerase and cAMP CAP complex have relatively low affinity for their respective binding sites in lac promoter DNA. Interaction between residues in CAP and α subunit of RNA polymerase forms a protein protein complex that binds much more stably to ...
BIOCHEMISTRY - Mexico Central School District
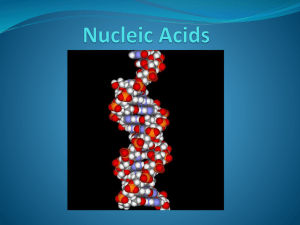
... Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids ...
... Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids ...
DNA and RNA
... information, form specific structures in a cell or carry out specific roles in a cell. Found in all living things and viruses.* The two most common are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). ...
... information, form specific structures in a cell or carry out specific roles in a cell. Found in all living things and viruses.* The two most common are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... For example, if the the haemagglutinine of the current H5N1 virus has one amino acid changed, its conformation would be changed. The conformation may become much easier to combine with the receptor protein on the surface of the human cells. Then, human would become susceptible to the infection of t ...
... For example, if the the haemagglutinine of the current H5N1 virus has one amino acid changed, its conformation would be changed. The conformation may become much easier to combine with the receptor protein on the surface of the human cells. Then, human would become susceptible to the infection of t ...
Document
... was published simultaneously in the journals Nature (Lander ES et al: Nature 409:860-921, 2001) and ...
... was published simultaneously in the journals Nature (Lander ES et al: Nature 409:860-921, 2001) and ...
TRANSLATION Protein synthesis is the final step in the decoding
... three consecutive nucleotides (a codon) in the mRNA encodes a particular amino acid. Decoding of mRNA to produce a polypeptide chain is also termed translation. Translation occurs on subcellular particles called ribosomes. Each ribosome is made up of two nonidentical subunits (`large' and `small') e ...
... three consecutive nucleotides (a codon) in the mRNA encodes a particular amino acid. Decoding of mRNA to produce a polypeptide chain is also termed translation. Translation occurs on subcellular particles called ribosomes. Each ribosome is made up of two nonidentical subunits (`large' and `small') e ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section A: The
... nucleotides making up a genetic message must be three times the number of amino acids making up the protein product. • It would take at least 300 nucleotides to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long. ...
... nucleotides making up a genetic message must be three times the number of amino acids making up the protein product. • It would take at least 300 nucleotides to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long. ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... ii. Each protein will fold into a final shape called a conformation based on its amino acid sequence 1. Proteins will naturally fold into the lowest possible energy conformation 2. Each protein has one single stable conformation, but there can be slight changes based on interactions with other molec ...
... ii. Each protein will fold into a final shape called a conformation based on its amino acid sequence 1. Proteins will naturally fold into the lowest possible energy conformation 2. Each protein has one single stable conformation, but there can be slight changes based on interactions with other molec ...
Nerve activates contraction
... nucleotides making up a genetic message must be three times the number of amino acids making up the protein product. • It would take at least 300 nucleotides to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long. ...
... nucleotides making up a genetic message must be three times the number of amino acids making up the protein product. • It would take at least 300 nucleotides to code for a polypeptide that is 100 amino acids long. ...
CH 3 RG 2014 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... 11. The flow of genetic information is from DNA RNA protein. Use this figure to explain the process. Label the nucleus, DNA, mRNA, ribosome, and amino acids. ...
... 11. The flow of genetic information is from DNA RNA protein. Use this figure to explain the process. Label the nucleus, DNA, mRNA, ribosome, and amino acids. ...
Lecture20_Translation
... The ribosome enhances the rate of peptide bond formation by properly positioning and orienting the substrates and/or excluding water from the active site rather than by chemical ...
... The ribosome enhances the rate of peptide bond formation by properly positioning and orienting the substrates and/or excluding water from the active site rather than by chemical ...
Genetics and Critical Illness
... - thought to be related to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) - influence severity of injury by controlling induction of TNF, NF kappa B and toll receptors - TT LNPEP rs XXX -> inherited mutation that is able to predict the SIRS response to bypass - important genetic polymorphisms: IL-6, TNF alph ...
... - thought to be related to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) - influence severity of injury by controlling induction of TNF, NF kappa B and toll receptors - TT LNPEP rs XXX -> inherited mutation that is able to predict the SIRS response to bypass - important genetic polymorphisms: IL-6, TNF alph ...
One Gene - One Polypeptide
... sequence of nucleotides into a specific polypeptide involves a variety of enzymes, protein factors, ATP, amino acids, and cellular organelles. This process can be summarized in two general steps; transcription and translation. During transcription the sequence of nucleotides in a gene in DNA is copi ...
... sequence of nucleotides into a specific polypeptide involves a variety of enzymes, protein factors, ATP, amino acids, and cellular organelles. This process can be summarized in two general steps; transcription and translation. During transcription the sequence of nucleotides in a gene in DNA is copi ...
Transcription & Translation
... Delivers amino acid to ribosome Reads mRNA codon Has a matching ‘anticodon’ One tRNA for each amino acid ...
... Delivers amino acid to ribosome Reads mRNA codon Has a matching ‘anticodon’ One tRNA for each amino acid ...
0c5168dab2ecd61778b5bb175973dab5 UNPDF
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bond ...
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bond ...
OCHeM.com ©1999 Thomas Poon Amino Acids, Peptides, and
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
... Be able to predict the structure of any amino acid based on its pKa values and the pH of the surrounding solution. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the major form of an amino acid at any pH. In general, if the pKa < pH a protic functional group will be “more acidic than th ...
7.1 Solutions File
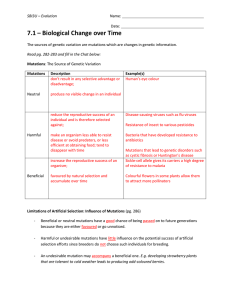
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... Law of Segregation -during fertilization gametes randomly pair to produce four sets of alleles (monohyrid) TT=homozygous dominant, Tt=heterozygous, tt=homozygous recessive Genotype is the combination of alleles, Phenotype is the physical expression of alleles Law of Independent Assortment -g ...
LYSINURIC PROTEIN INTOLERANCE
... Plasma and urinary amino acid analysis will show an anomalous profile with hypoaminoacidemia which exclusively affects the dibasic AAs, with elevated excretion of these amino acids, particularly lysine, in the urine. There is also an increase in the excretion of orotic acid. The mutational study of ...
... Plasma and urinary amino acid analysis will show an anomalous profile with hypoaminoacidemia which exclusively affects the dibasic AAs, with elevated excretion of these amino acids, particularly lysine, in the urine. There is also an increase in the excretion of orotic acid. The mutational study of ...
DNA - Moodle
... (AUG is the) start codon some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation ...
... (AUG is the) start codon some (nonsense) codons code for the end of translation ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.