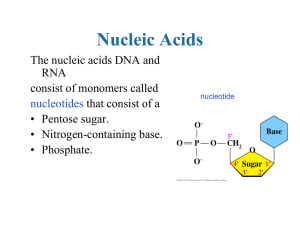
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
... • Lagging strand: Okazaki fragments to form daughter strand (discontinuous) • RNA replication requires primers ...
A new classification scheme of the genetic code
... second row. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that there was a period during code evolution where the third position was not needed at all. Assuming this, we can cancel each second row and are left with a pure doublet code that encodes 4x4=16 amino acids (or 15 plus a termination codon). Perhap ...
... second row. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that there was a period during code evolution where the third position was not needed at all. Assuming this, we can cancel each second row and are left with a pure doublet code that encodes 4x4=16 amino acids (or 15 plus a termination codon). Perhap ...
Cavalor Nutri Plus
... acids necessary for the health, growth, and development of the bones and the stress resistance of the sport horse. Cavalor Nutri Plus can be used as ration balancer for Sport Horses. 3. Directions of use Dosage per animal per day: ...
... acids necessary for the health, growth, and development of the bones and the stress resistance of the sport horse. Cavalor Nutri Plus can be used as ration balancer for Sport Horses. 3. Directions of use Dosage per animal per day: ...
EXAM B
... 8. A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an) A.chromosomal mutation. B.inversion. C.point mutation. D.translocation. ...
... 8. A mutation that involves a single nucleotide is called a(an) A.chromosomal mutation. B.inversion. C.point mutation. D.translocation. ...
Transamination, Deamination,urea cycle
... • first two reactions leading to the synthesis of urea occur in the mitochondria, whereas the remaining cycle enzymes are located in the cytosol • One nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by free ammonia, and the other nitrogen by aspartate ...
... • first two reactions leading to the synthesis of urea occur in the mitochondria, whereas the remaining cycle enzymes are located in the cytosol • One nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by free ammonia, and the other nitrogen by aspartate ...
Amino Acids : BCAA FLASH ZERO 360GR - BIOTECH
... BioTechUSA’s flavoured BCAA Flash Zero amino acid powder contains 2:1:1 ratio of leucine, isoleucine and valine amino acids, which greatly enhance each other’s effect on building muscles and energising, and they have a natural, specific proportion in muscles. We have also added vitamin B6 to the pro ...
... BioTechUSA’s flavoured BCAA Flash Zero amino acid powder contains 2:1:1 ratio of leucine, isoleucine and valine amino acids, which greatly enhance each other’s effect on building muscles and energising, and they have a natural, specific proportion in muscles. We have also added vitamin B6 to the pro ...
2770 October 2007 Mid-Term Test
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
... All of the following functions of an enzyme are true EXCEPT: A) Enzymes help to catalyze nearly all metabolic reactions. B) Enzyme activity is sensitive to enzyme and substrate concentration. C) Enzymes are sensitive to temperature and pH changes. D. An increased activity of an enzyme increases the ...
The Central Dogma Activity (Student Sheet)
... The objective of this lesson is to explore and then demonstrate the principle of The Central Dogma. By the end of the activity, you should be able to identify and explain the relationship between DNA and protein by describing the three processes involved in the Central Dogma as well as explain the p ...
... The objective of this lesson is to explore and then demonstrate the principle of The Central Dogma. By the end of the activity, you should be able to identify and explain the relationship between DNA and protein by describing the three processes involved in the Central Dogma as well as explain the p ...
DHaganTalk1
... Protein Secondary Structure • Once the primary structure has been established it is referred to as the “backbone” of the protein. • The secondary structure can be defined as the regular, repeated patters of folding of the protein backbone. The two most common folding patterns are the alpha helix an ...
... Protein Secondary Structure • Once the primary structure has been established it is referred to as the “backbone” of the protein. • The secondary structure can be defined as the regular, repeated patters of folding of the protein backbone. The two most common folding patterns are the alpha helix an ...
02-3 Carbon Compounds
... Amino acids are linked together into a polypeptide. 1. Primary Structure (single strand) 2. Secondary Structure (alpha helix or pleated sheet) 3. Tertiary Structure (folded helixes, sheets) 4. Quartenary Structure (2 or more polypeptides together) ...
... Amino acids are linked together into a polypeptide. 1. Primary Structure (single strand) 2. Secondary Structure (alpha helix or pleated sheet) 3. Tertiary Structure (folded helixes, sheets) 4. Quartenary Structure (2 or more polypeptides together) ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 18 – Microbial
... Figure 18.18 Two strains of E. coli are shown in this figure. One is a human pathogen and one is not. Explain why genome size cannot be used to determine which is pathogenic. The nonpathogenic strain is K-12, with 4.64 million bp, and the pathogenic strain is O157:H7, with a 5.53 million bp genome. ...
... Figure 18.18 Two strains of E. coli are shown in this figure. One is a human pathogen and one is not. Explain why genome size cannot be used to determine which is pathogenic. The nonpathogenic strain is K-12, with 4.64 million bp, and the pathogenic strain is O157:H7, with a 5.53 million bp genome. ...
Molecular Biology Final Exam (Set A)
... In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. This is unfavorable, since the bases are largely hydrophobic. Instead, RNA folds up on itself, forming internal basepairs wherever its sequence allows. Since ...
... In contrast, RNA is almost always single-stranded. As an elongated single strand, its nitrogenous bases would be exposed to the water solvent. This is unfavorable, since the bases are largely hydrophobic. Instead, RNA folds up on itself, forming internal basepairs wherever its sequence allows. Since ...
Chapter 15 - Dr. Jennifer Capers
... how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations • Frameshift mutations • Indicates importance of reading frame ...
... how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations • Frameshift mutations • Indicates importance of reading frame ...
ppt - cse.sc.edu
... Acidic versus alkaline (basic) Mass Amino acid full names, three letter and single letter abbreviations – Alanine, ALA, A ...
... Acidic versus alkaline (basic) Mass Amino acid full names, three letter and single letter abbreviations – Alanine, ALA, A ...
Unit Three “Cell Proliferation and Genetics”
... From Gene to Protein • The way in which the “Control Center” of the cell, which is the DNA in the nucleus, enables the efficient operation of the remainder of the cell is via Protein Synthesis • Recall that proteins maintain the proper function of the cell by acting as enzyme that regulate the vita ...
... From Gene to Protein • The way in which the “Control Center” of the cell, which is the DNA in the nucleus, enables the efficient operation of the remainder of the cell is via Protein Synthesis • Recall that proteins maintain the proper function of the cell by acting as enzyme that regulate the vita ...
Big slides
... RNA has a Different shape than DNA • RNA is a SINGLE STRANDED molecule…not a double helix. • It can twist into many different shapes.. • With many different possible shapes… • You have many different….? ...
... RNA has a Different shape than DNA • RNA is a SINGLE STRANDED molecule…not a double helix. • It can twist into many different shapes.. • With many different possible shapes… • You have many different….? ...
classsssssss
... boy with IDDM is brought to the emergency room in coma. His breathing is rapid and deep, and his breath has a fruity odor. His blood glucose is 36.5 mM (normal: 4-6 mM; 70-110 mg/dL). The physician administers IV fluids, insulin, potassium chloride. A rapid effect of insulin in this situation is to ...
... boy with IDDM is brought to the emergency room in coma. His breathing is rapid and deep, and his breath has a fruity odor. His blood glucose is 36.5 mM (normal: 4-6 mM; 70-110 mg/dL). The physician administers IV fluids, insulin, potassium chloride. A rapid effect of insulin in this situation is to ...
Comparison of p53 Structure: Wild type vs. mutant
... • Notice that the portion of the protein that directly interacts with the DNA is highly conserved (purple) • Other protein regions are less highly conserved ...
... • Notice that the portion of the protein that directly interacts with the DNA is highly conserved (purple) • Other protein regions are less highly conserved ...
Introductory Biological Sequence Analysis Through Spreadsheets
... structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins are sequences of letters -- 4 letters in the case of DNA (ATGC) and RNA (AUGC) and 20 letters representing the sequence of amino acids which ...
... structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins are sequences of letters -- 4 letters in the case of DNA (ATGC) and RNA (AUGC) and 20 letters representing the sequence of amino acids which ...
Practice - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Alanine and Glutamine in the Blood. Normal human blood plasma contains all the amino acids require for the synthesis of body proteins, but not in equal concentration. Alanine and glutamine are present in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. Suggest why? Answer : Muscle tissue can conv ...
... Alanine and Glutamine in the Blood. Normal human blood plasma contains all the amino acids require for the synthesis of body proteins, but not in equal concentration. Alanine and glutamine are present in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. Suggest why? Answer : Muscle tissue can conv ...
Amino Acids
... Buffer pairs: the –COOH/-COO- pair can serve as a buffer in the pH region around pK1, and the –NH3/ NH2 pair can buffer in the region around pK2 When pH=pK: when pH = pK1(2.3), equal amounts of forms I and II exist in solution. When pH = pK2 (9.1), equal amounts of form II and form III. Isoelectric ...
... Buffer pairs: the –COOH/-COO- pair can serve as a buffer in the pH region around pK1, and the –NH3/ NH2 pair can buffer in the region around pK2 When pH=pK: when pH = pK1(2.3), equal amounts of forms I and II exist in solution. When pH = pK2 (9.1), equal amounts of form II and form III. Isoelectric ...
Mutation Notes
... affects several amino acids Ex. (GCA-TCA GCA-GTC-A -Deletion – base is removed, affects several amino acids ...
... affects several amino acids Ex. (GCA-TCA GCA-GTC-A -Deletion – base is removed, affects several amino acids ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.