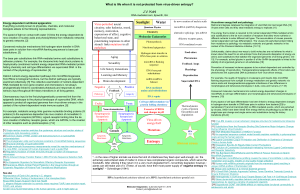
From Gene to Protein
... (Translation) • Initiation: brings mRNA, tRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits together • Elongation: three-step cycle that adds amino acids one by one to the initial amino acid, requires cooperation of several • Termination: release of the polypeptide chain from the complex. ...
... (Translation) • Initiation: brings mRNA, tRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits together • Elongation: three-step cycle that adds amino acids one by one to the initial amino acid, requires cooperation of several • Termination: release of the polypeptide chain from the complex. ...
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments
... nucleotides (codons ). Since there are four (codons). bases, there are 64 possible codons. codons. • One mRNA codon indicates the starting point of translation and codes for methionine. methionine. Three stop codons indicate the end of translation. The other 60 codons code only for particular amino ...
... nucleotides (codons ). Since there are four (codons). bases, there are 64 possible codons. codons. • One mRNA codon indicates the starting point of translation and codes for methionine. methionine. Three stop codons indicate the end of translation. The other 60 codons code only for particular amino ...
Molecules of Life
... D Melba Moore is a celebrity spokesperson for sickle-cell anemia organizations. Right, range of symptoms for a person with two mutated genes for hemoglobin’s beta chain. Fig. 3-19d, p. 47 ...
... D Melba Moore is a celebrity spokesperson for sickle-cell anemia organizations. Right, range of symptoms for a person with two mutated genes for hemoglobin’s beta chain. Fig. 3-19d, p. 47 ...
Document
... D Melba Moore is a celebrity spokesperson for sickle-cell anemia organizations. Right, range of symptoms for a person with two mutated genes for hemoglobin’s beta chain. Fig. 3-19d, p. 47 ...
... D Melba Moore is a celebrity spokesperson for sickle-cell anemia organizations. Right, range of symptoms for a person with two mutated genes for hemoglobin’s beta chain. Fig. 3-19d, p. 47 ...
The RNA origin of transfer RNA aminoacylation and beyond
... in vitro translation apparatus. Despite the simplicity of the concept, the codon reassignments require two major technical challenges; (i) preparation of aminoacyl-tRNAs with non-proteinogenic amino acids, and (ii) making vacant codons to which the above amino acids are reassigned. Although there ar ...
... in vitro translation apparatus. Despite the simplicity of the concept, the codon reassignments require two major technical challenges; (i) preparation of aminoacyl-tRNAs with non-proteinogenic amino acids, and (ii) making vacant codons to which the above amino acids are reassigned. Although there ar ...
Self-Quiz 3 Questions
... A sequence of nucleotides that contain a start and stop codon in any order A reading frame that contains a start codon, a number of codons for amino acids, and then a stop codon A reading frame with multiple start codons A sequence of nucleotides without any stop codons Assume that all the following ...
... A sequence of nucleotides that contain a start and stop codon in any order A reading frame that contains a start codon, a number of codons for amino acids, and then a stop codon A reading frame with multiple start codons A sequence of nucleotides without any stop codons Assume that all the following ...
1030ExamFinal
... 54. The type of RNA that carries each amino acid to the ribosome is: A. MicroRNA (miRNA) B. Transfer RNA (tRNA) C. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) D. Messenger RNA (mRNA) E. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) 55. The process used by cells to convert an RNA "message" into a sequence of amino acids is: A. Transcription ...
... 54. The type of RNA that carries each amino acid to the ribosome is: A. MicroRNA (miRNA) B. Transfer RNA (tRNA) C. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) D. Messenger RNA (mRNA) E. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) 55. The process used by cells to convert an RNA "message" into a sequence of amino acids is: A. Transcription ...
Evolution and Genetic Engineering Keystone Vocabulary
... population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a completely different amino acid sequence than what would be normal. The earli ...
... population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a completely different amino acid sequence than what would be normal. The earli ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. • More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. • More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... Retroviral integrase catalyses the integration of viral DNA into host target DNA.[10] Viruses enter cells and they steal metabolic energy to replicate.[11] ...
... Retroviral integrase catalyses the integration of viral DNA into host target DNA.[10] Viruses enter cells and they steal metabolic energy to replicate.[11] ...
12.3 notes
... The Roles of RNA and DNA • DNA is like the master plan of the cell • If DNA is damaged, the whole cell could die • RNA is like copies of this master plan that can be taken all around the cell to be made into product or proteins • If RNA is damaged, it’s okay, more can be ...
... The Roles of RNA and DNA • DNA is like the master plan of the cell • If DNA is damaged, the whole cell could die • RNA is like copies of this master plan that can be taken all around the cell to be made into product or proteins • If RNA is damaged, it’s okay, more can be ...
Introduction and Review
... ribonucleoprotein particles called spliceosomes. mRNA contains a “leader sequence” at its 5’ end, before the coding region. The coding region begins with a translational initiation codon (AUG). A methylated guanosine cap is added to the 5’ end of the mRNA by capping enzymes. The cap is attached by a ...
... ribonucleoprotein particles called spliceosomes. mRNA contains a “leader sequence” at its 5’ end, before the coding region. The coding region begins with a translational initiation codon (AUG). A methylated guanosine cap is added to the 5’ end of the mRNA by capping enzymes. The cap is attached by a ...
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
... a. Nucleotides – 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base b. Nucleic Acid – nucleotides joined by covalent bonds 1) Store and transmit genetic info a) RNA – Ribonucleic Acid b) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid 4. Proteins – made of C, H, O, N a. Amino Acids – 1) 20 different amino acids 2) a ...
... a. Nucleotides – 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base b. Nucleic Acid – nucleotides joined by covalent bonds 1) Store and transmit genetic info a) RNA – Ribonucleic Acid b) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid 4. Proteins – made of C, H, O, N a. Amino Acids – 1) 20 different amino acids 2) a ...
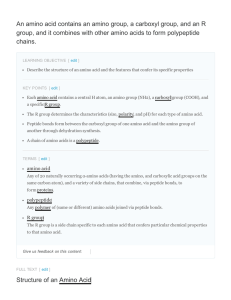
An amino acid contains an amino group, a carboxyl
... The name "amino acid" is derived from the amino group and carboxylacidgroup in their basic structure. There are 21 amino acids present in proteins, each with a specific R group or side chain. Ten of these are considered essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and ...
... The name "amino acid" is derived from the amino group and carboxylacidgroup in their basic structure. There are 21 amino acids present in proteins, each with a specific R group or side chain. Ten of these are considered essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and ...
Biochemistry Review Packet
... gain/lose _____________________. h. ________________ are charged atoms that have gained or lost ________________________. i. ____________________ are more than one atom joined together. 5. ___, ___, ___, & ___ make up 96% of living matter. 6. Draw the number of bonds that each element from #5 needs ...
... gain/lose _____________________. h. ________________ are charged atoms that have gained or lost ________________________. i. ____________________ are more than one atom joined together. 5. ___, ___, ___, & ___ make up 96% of living matter. 6. Draw the number of bonds that each element from #5 needs ...
Gene Regulation and Mutation Notes and Questions
... • It may or may not have serious effects on an organism. It depends on where the mutation occurs and how it affects the protein for which it codes • It can be harmless • Muscular dystrophy is an example of a disease caused by a point mutation. (nonsense – early STOP codon due to the wrong amino acid ...
... • It may or may not have serious effects on an organism. It depends on where the mutation occurs and how it affects the protein for which it codes • It can be harmless • Muscular dystrophy is an example of a disease caused by a point mutation. (nonsense – early STOP codon due to the wrong amino acid ...
BIOLOGY SAMPLE TEST 1 1. In this type of mutation, one or two
... C. pancreas D. thyroid gland E. gonads ...
... C. pancreas D. thyroid gland E. gonads ...
File
... excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. • Intron presence can determine which exons stay or go • Increases efficiency and flexibility of cell • snRNA’s have big role in alternative splicing Starting to get hard to define a gene! ...
... excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. • Intron presence can determine which exons stay or go • Increases efficiency and flexibility of cell • snRNA’s have big role in alternative splicing Starting to get hard to define a gene! ...
Chapter 1-The Chemical Nature of Cells
... DNA causes to be produced. The sequence of N-bases along one of the chain of nucleotides carries a set of information that controls the production of polypeptide and is a code. o Code comprises of four bases o Operates with three letters at a time o Eg AAA means amino acid phenylalanine is added t ...
... DNA causes to be produced. The sequence of N-bases along one of the chain of nucleotides carries a set of information that controls the production of polypeptide and is a code. o Code comprises of four bases o Operates with three letters at a time o Eg AAA means amino acid phenylalanine is added t ...
DNA Mutations
... A synonym is a word having the same or nearly the same meaning as another; so a synonym mutation is a different codon that still codes for the same amino acid. Example: ...
... A synonym is a word having the same or nearly the same meaning as another; so a synonym mutation is a different codon that still codes for the same amino acid. Example: ...
Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... 5. Amino acids are linked together by bonds C. Proteins Are Chains of 1. Proteins composed of one or more 2. Polypeptides are long chains of 3. Each protein has a , defined amino acid sequence D. The Shape of Globular Proteins 1. Globular protein chains are up into complex shapes a. Examine three di ...
... 5. Amino acids are linked together by bonds C. Proteins Are Chains of 1. Proteins composed of one or more 2. Polypeptides are long chains of 3. Each protein has a , defined amino acid sequence D. The Shape of Globular Proteins 1. Globular protein chains are up into complex shapes a. Examine three di ...
Genetics Introduction:
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.