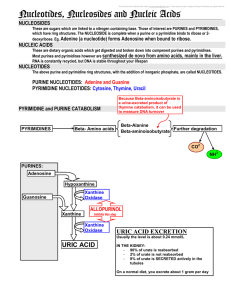
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... ANEUPLOIDY is an abnormal number of chromosomes, commonly found in cancerous cells ...
... ANEUPLOIDY is an abnormal number of chromosomes, commonly found in cancerous cells ...
Gene, Protein Synthesis & Gene Regulation
... The code is composed of codons Codon is composed of 3 bases ( e.g. ACG or UAG). Each codon is translated into one amino acid. ...
... The code is composed of codons Codon is composed of 3 bases ( e.g. ACG or UAG). Each codon is translated into one amino acid. ...
You Asked for it….. - Mr. Smith’s Science Page
... • DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break) • Each side acts as a template • New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules • Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand. Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis) ...
... • DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break) • Each side acts as a template • New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules • Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand. Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis) ...
Figure 5.x3 James Watson and Francis Crick
... the nucleus to the ribosomes where the proteins are assembled. It is a partial copy of ONLY the information needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment of mRNA and in the assembly of proteins. Transfer RNA ...
... the nucleus to the ribosomes where the proteins are assembled. It is a partial copy of ONLY the information needed for that specific job. It is read 3 bases at a time – codon. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – found in ribosomes and helps in the attachment of mRNA and in the assembly of proteins. Transfer RNA ...
Chapter 8
... b. DNA replication only happens once before the cell divides. A given gene may produce an RNA many times or not at all during a specific cell cycle. c. DNA replication copies the entire length of the chromosome while RNA manufacture only copies part of the chromosome. 10. If a DNA nucleotide sequenc ...
... b. DNA replication only happens once before the cell divides. A given gene may produce an RNA many times or not at all during a specific cell cycle. c. DNA replication copies the entire length of the chromosome while RNA manufacture only copies part of the chromosome. 10. If a DNA nucleotide sequenc ...
... 11. Which type of conservation measures – in situ or ex-situ will help the larger number of species to survive? Explain. (2) 12. What is interspecific hybridization. Give an example? (2) 13. What are the advantages of breeding for disease-resistance in plants? (2) 14. Which law of Mendel is universa ...
Lecture 11-Chargaff
... If so, the implication was that the structure of DNA was too simple and too regular to contribute to genetic variation: attention thereafter focused on protein as the probable hereditary substance ...
... If so, the implication was that the structure of DNA was too simple and too regular to contribute to genetic variation: attention thereafter focused on protein as the probable hereditary substance ...
From Gene to Protein
... The key terms: gene expression, transcription, and translation. The major events of transcription. How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription. The steps to translation. How point mutations can change the amino acid sequence of a protein. ...
... The key terms: gene expression, transcription, and translation. The major events of transcription. How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription. The steps to translation. How point mutations can change the amino acid sequence of a protein. ...
Elements in Cells
... • When a plant first absorbs these elements from the soil or atmosphere, or when it breaks down products within the cell, the elements are in the form of simple molecules or ions. • These simple forms may be converted to very large, complex molecules through the metabolism of the cells. • The lar ...
... • When a plant first absorbs these elements from the soil or atmosphere, or when it breaks down products within the cell, the elements are in the form of simple molecules or ions. • These simple forms may be converted to very large, complex molecules through the metabolism of the cells. • The lar ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
... 1. What are the 2 pyrimidines? ____________, and the 2 purines? __________, which is a double ring structure and which is a single ring? ___________________ What are Chargaff’s rules? ______________ 2. How many H bonds are there between A and T? ______ and how many between C and G? ________ 3. Which ...
Randy Carroll
... by binding it to promoters. It adds one nucleotide at a time until the termination signal drops by. ...
... by binding it to promoters. It adds one nucleotide at a time until the termination signal drops by. ...
C. The Synthesis of Protein
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
Ch17WordLectureOutline w pics
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
没有幻灯片标题
... at the molecular level: phylogenetic trees are made by using the number of residues that differ. 8.2.5 Highly conserved residues usually play important roles in protein structure and/or function. (need to be further exploited, e.g. How does it determine the 3D structure?). 8.2.6 Homologous proteins ...
... at the molecular level: phylogenetic trees are made by using the number of residues that differ. 8.2.5 Highly conserved residues usually play important roles in protein structure and/or function. (need to be further exploited, e.g. How does it determine the 3D structure?). 8.2.6 Homologous proteins ...
Unit 7 Molecular Genetics Chp 17 Protein Synthesis
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
... A tRNA molecule consists of a strand of about 80 nucleotides that folds back on itself to form a three-dimensional structure. ...
(PTH), or parathormone, is secreted
... Escherichia Coli. Physical Appearance: Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. Formulation: The protein (1 mg/ml) was lyophilized after extensive dialyses against 1.15 mg sodium citrate, sodium chloride 7.31 mg, 0.21 mg citric acid, 0.1117 EDTA-Na2, 0.2 mg Tween 80 and 50 mg Mannit ...
... Escherichia Coli. Physical Appearance: Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. Formulation: The protein (1 mg/ml) was lyophilized after extensive dialyses against 1.15 mg sodium citrate, sodium chloride 7.31 mg, 0.21 mg citric acid, 0.1117 EDTA-Na2, 0.2 mg Tween 80 and 50 mg Mannit ...
Review Materials for Gene to Protein and DNA
... either UAA or TAA, depending on wobble in the first base. ...
... either UAA or TAA, depending on wobble in the first base. ...
Antibody
... • A collective name for the proteins expressed by the genome • Dynamic and functional information • It varies with cell type, developmental stage, and environmental condition such as the presence of hormones. • Regulation of mRNA synthesis, alternative splicing, mRNA stability, rate of protein synth ...
... • A collective name for the proteins expressed by the genome • Dynamic and functional information • It varies with cell type, developmental stage, and environmental condition such as the presence of hormones. • Regulation of mRNA synthesis, alternative splicing, mRNA stability, rate of protein synth ...
... reserve substances for the energy supply in case of hunger. Above all, the body regenerates them from the muscular apparatus, the spleen and the liver. It is mostly these organs that they are adducted in times of hunger – and also in the case of false diets or fasting cures – with the help of glucon ...
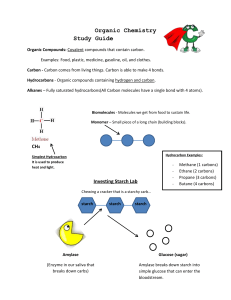
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fatsoluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. ...
... Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fatsoluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. ...
CHAPTER 12 - powerpoint
... • When a stop codon—UAA, UAG, or UGA— enters the A site, a release factor and a water molecule enter the A site, instead of an amino acid. • The newly completed protein then separates from the ribosome. ...
... • When a stop codon—UAA, UAG, or UGA— enters the A site, a release factor and a water molecule enter the A site, instead of an amino acid. • The newly completed protein then separates from the ribosome. ...
Bio 120 Principles of Evolution Discussion Exercise 2 Optimality of
... UGA codes for tryptophan rather than serving as a stop codon. Moreover, it is quite possible that code evolution was more common when the code was first being established. If such evolution occurred, did it in some way optimize the code so that it functions better than a random code? One suggestion ...
... UGA codes for tryptophan rather than serving as a stop codon. Moreover, it is quite possible that code evolution was more common when the code was first being established. If such evolution occurred, did it in some way optimize the code so that it functions better than a random code? One suggestion ...
Why do we eat
... that our bodies need -- hormone, enzyme, muscle fiber. We can use protein as a source of energy, but this is inefficient. Usually the body does not use proteins as an energy source because proteins are too valuable for muscle, enzymes, antibodies, hair, cartilage, hormones, etc. The body can break p ...
... that our bodies need -- hormone, enzyme, muscle fiber. We can use protein as a source of energy, but this is inefficient. Usually the body does not use proteins as an energy source because proteins are too valuable for muscle, enzymes, antibodies, hair, cartilage, hormones, etc. The body can break p ...
EXAM 1
... 11. When a nucleotide is added to a growing DNA or RNA polymer, what is removed? a. Nothing; the nucleotide is added intact b. One base c. One phosphate d. XTwo phosphates 12. During synthesis of a growing DNA or RNA polymer, the new nucleotide is a. Xattached by the 5’ phosphate of the new nucleot ...
... 11. When a nucleotide is added to a growing DNA or RNA polymer, what is removed? a. Nothing; the nucleotide is added intact b. One base c. One phosphate d. XTwo phosphates 12. During synthesis of a growing DNA or RNA polymer, the new nucleotide is a. Xattached by the 5’ phosphate of the new nucleot ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.