General Astrophysics And Comparative Planetology
... 2.1 A Parallel Giant Planet Search To understand an entire planetary system, giant planets must be detectable over a wide range of circumstellar separations. Jupiter and Saturn analogs in wide orbits around stars as old as the solar system are not detectable with any existing or planned ground-based ...
... 2.1 A Parallel Giant Planet Search To understand an entire planetary system, giant planets must be detectable over a wide range of circumstellar separations. Jupiter and Saturn analogs in wide orbits around stars as old as the solar system are not detectable with any existing or planned ground-based ...
Module 5 Modelling the universe - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Telescopes only now have sufficient accuracy to detect the slight wobble of some stars as a result of planets rotating around them. All the stars apart from the Sun are too far away for their planets, if they have any, to be seen. Size and distance are two problems with trying to see planets. Anothe ...
... Telescopes only now have sufficient accuracy to detect the slight wobble of some stars as a result of planets rotating around them. All the stars apart from the Sun are too far away for their planets, if they have any, to be seen. Size and distance are two problems with trying to see planets. Anothe ...
4. The Solar System
... orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit the Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
... orbits of Mars and Jupiter. • Comets are icy and are believed to have formed early in the solar system’s life. • Major planets orbit the Sun in same sense, and all but Venus rotate in that sense as well. • Planetary orbits lie almost in the same plane. ...
Pluto and Kuiper Belt Object Notes
... map every made of Pluto. It is unknown whether the bright areas are bright because they are high clouds near mountains or low haze and frost. What is known is that there are extreme contrasts on Pluto’s surface. 7) If you were standing on Pluto, the Sun would appear over 1000 times fainter than it d ...
... map every made of Pluto. It is unknown whether the bright areas are bright because they are high clouds near mountains or low haze and frost. What is known is that there are extreme contrasts on Pluto’s surface. 7) If you were standing on Pluto, the Sun would appear over 1000 times fainter than it d ...
Planets and Moons - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... and billions of stars held together by gravity. One galaxy can have hundreds of billions of stars and be as large as 200,000 light years across. • Galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias meaning "milky", a reference to the Milky Way. • Many galaxies are believed to have black holes at their active ...
... and billions of stars held together by gravity. One galaxy can have hundreds of billions of stars and be as large as 200,000 light years across. • Galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias meaning "milky", a reference to the Milky Way. • Many galaxies are believed to have black holes at their active ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 5. Universal Laws of Motion
... • Why are there two high tides on Earth each day? • The Moon’s gravity stretches Earth along the EarthMoon line, so that it bulges both toward and away from the Moon. • Why are tides on Earth caused primarily by the Moon rather than by the Sun? • Earth’s gravitational attraction to the sun is strong ...
... • Why are there two high tides on Earth each day? • The Moon’s gravity stretches Earth along the EarthMoon line, so that it bulges both toward and away from the Moon. • Why are tides on Earth caused primarily by the Moon rather than by the Sun? • Earth’s gravitational attraction to the sun is strong ...
Astronomy 110 Lecture 2.
... Some stars never cross the observer’s horizon and thus never appear to rise or set so they are always either above or below the horizon. If they are above the horizon they are called circumpolar and are always visible throughout the year. If they are below the horizon – they cannot be seen from tha ...
... Some stars never cross the observer’s horizon and thus never appear to rise or set so they are always either above or below the horizon. If they are above the horizon they are called circumpolar and are always visible throughout the year. If they are below the horizon – they cannot be seen from tha ...
Volume XXVI - Royal Asiatic Society
... always there. It is composed of the first seven of the twenty eight zodiacal constellations or lunar mansions, known in China 4,500 years ago. It covers a quarter of the zodiac occupying approximately the position of the constellations, Virgo, Libra and Scorpio. The fifth of its seven asterisms is S ...
... always there. It is composed of the first seven of the twenty eight zodiacal constellations or lunar mansions, known in China 4,500 years ago. It covers a quarter of the zodiac occupying approximately the position of the constellations, Virgo, Libra and Scorpio. The fifth of its seven asterisms is S ...
CHP 4
... A(n) _______________ is a single conjecture that can be tested. a. hypothesis b. paradigm c. natural law d. model e. theory A(n) _______________ is a description of some natural phenomenon that can't be right or wrong. It is merely a convenient way to think about a natural phenomenon. a. hypothesis ...
... A(n) _______________ is a single conjecture that can be tested. a. hypothesis b. paradigm c. natural law d. model e. theory A(n) _______________ is a description of some natural phenomenon that can't be right or wrong. It is merely a convenient way to think about a natural phenomenon. a. hypothesis ...
Sunstruck
... The Sun is humanity’s star. It is classified as a G2V star (see stellar classification) along the main sequence. The Sun was once considered to be a fairly dim star compared to most other stars in the universe. Recent discoveries have shown, however, that there are many more red dwarf stars than exp ...
... The Sun is humanity’s star. It is classified as a G2V star (see stellar classification) along the main sequence. The Sun was once considered to be a fairly dim star compared to most other stars in the universe. Recent discoveries have shown, however, that there are many more red dwarf stars than exp ...
Celestia DATA WORKSHEET
... speed, it will still take you about 8 minutes to reach earth. Thus, light leaving the sun takes 8 minutes of space travel to reach us. Now, you may find this hard to believe, but at this incredible speed, it will take 4.5 years of you sitting there watching this screen, before you would reach the ve ...
... speed, it will still take you about 8 minutes to reach earth. Thus, light leaving the sun takes 8 minutes of space travel to reach us. Now, you may find this hard to believe, but at this incredible speed, it will take 4.5 years of you sitting there watching this screen, before you would reach the ve ...
Chapter 16 Lives of the Stars (Low Mass)
... follows the red giant branch in stars whose masses are similar to the Sun's. Horizontal-branch stars are powered by helium fusion in the core and by hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core. The thermostat is temporarily fixed. ...
... follows the red giant branch in stars whose masses are similar to the Sun's. Horizontal-branch stars are powered by helium fusion in the core and by hydrogen fusion in a shell around the core. The thermostat is temporarily fixed. ...
Printable Version of this information
... What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a dry season. People have paid attention to seasons ...
... What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a dry season. People have paid attention to seasons ...
ziggynotes
... Knowing the orbital period and distance to this very large “Moon”, you can at least constrain a few orbital parameters. Let us hypothesize that Ziggy is much more massive than the “Moon”, so that Ziggy is essentially stationary while the “Moon” orbits us. We roughly know the radius of the Moon’s orb ...
... Knowing the orbital period and distance to this very large “Moon”, you can at least constrain a few orbital parameters. Let us hypothesize that Ziggy is much more massive than the “Moon”, so that Ziggy is essentially stationary while the “Moon” orbits us. We roughly know the radius of the Moon’s orb ...
CHAPTER 8 Survey of Solar Systems
... has about the same relative thickness as 3 CDs stacked together. The planets also all travel around the Sun in the same direction: counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s North Pole, and this is the same direction in which the Sun itself spins. As the planets orbit the Sun, each also spins ...
... has about the same relative thickness as 3 CDs stacked together. The planets also all travel around the Sun in the same direction: counterclockwise, as seen from above the Earth’s North Pole, and this is the same direction in which the Sun itself spins. As the planets orbit the Sun, each also spins ...
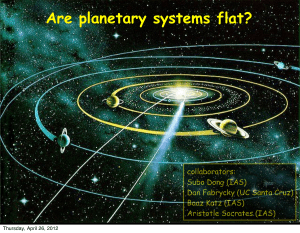
Are planetary systems flat?
... • circular orbits cannot remain circular, and are excited to high inclination and eccentricity •circular orbits are chaotic ...
... • circular orbits cannot remain circular, and are excited to high inclination and eccentricity •circular orbits are chaotic ...
Lecture
... lifetime ( 90% of its total lifespan) • Second stage: Fusing of helium (He) to make carbon (C) • The life of some stars (like our Sun) stops after this stage, but others will continue processing heavier and heavier elements than carbon in their cores. • For the massive stars (more than 8 solar masse ...
... lifetime ( 90% of its total lifespan) • Second stage: Fusing of helium (He) to make carbon (C) • The life of some stars (like our Sun) stops after this stage, but others will continue processing heavier and heavier elements than carbon in their cores. • For the massive stars (more than 8 solar masse ...
The Stability of Exomoons in the Habitable Zone
... In the investigation into the habitability of extrasolar objects, the main focus has long been on exoplanets, while exomoons have only been considered properly during the last few years. A reason for this is the obvious difficulty in detecting objects that do not primarily orbit a star, but rather a ...
... In the investigation into the habitability of extrasolar objects, the main focus has long been on exoplanets, while exomoons have only been considered properly during the last few years. A reason for this is the obvious difficulty in detecting objects that do not primarily orbit a star, but rather a ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.