High Contrast - University of Arizona
... •Metrological Tolerancing & Stability •Wavefront/Mirror Sensing & Control ...
... •Metrological Tolerancing & Stability •Wavefront/Mirror Sensing & Control ...
How the Oceans Formed
... So, what do scientists theorize the Big Bang has to do with oceans, ocean features, or even ocean organisms? Somewhere out there, orbiting a mere 93 million miles from the Sun – really just a blink in astronomical distance – was a molten, rocky mass of hot magma. According to scientists, this molten ...
... So, what do scientists theorize the Big Bang has to do with oceans, ocean features, or even ocean organisms? Somewhere out there, orbiting a mere 93 million miles from the Sun – really just a blink in astronomical distance – was a molten, rocky mass of hot magma. According to scientists, this molten ...
Gravity Kepler`s Laws - historical remarks - UW
... Kepler had access to very good data from the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague. See table for today’s data. After many years of work Kepler found an intriguing correlation between the orbital periods and the length of the semimajor axis of orbits. ...
... Kepler had access to very good data from the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague. See table for today’s data. After many years of work Kepler found an intriguing correlation between the orbital periods and the length of the semimajor axis of orbits. ...
A Comparison of Atmospheric and Chemical Properties of Inner
... separation of the water budget from the other volatiles. If water were present as a condensed ocean, it would be removed in much smaller proportions compared to the atmospheric gases, and thus giant impacts preferentially remove CO2 and noble gases compared to water, which may explain the higher tha ...
... separation of the water budget from the other volatiles. If water were present as a condensed ocean, it would be removed in much smaller proportions compared to the atmospheric gases, and thus giant impacts preferentially remove CO2 and noble gases compared to water, which may explain the higher tha ...
Brightness and Temperature of Stars
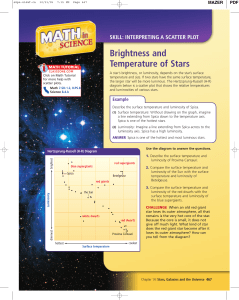
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
... A star’s brightness, or luminosity, depends on the star’s surface temperature and size. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star will be more luminous. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram below is a scatter plot that shows the relative temperatures and luminosities of variou ...
Astronomy Webquest _2 STARS
... time, the star will change into a ___________________________ and grow to more than 400 times its original size. As they expand, red giants engulf some of their close-orbiting planets. In the Sun's case, this will mean the fiery end of all the inner planets of our Solar System, which might also incl ...
... time, the star will change into a ___________________________ and grow to more than 400 times its original size. As they expand, red giants engulf some of their close-orbiting planets. In the Sun's case, this will mean the fiery end of all the inner planets of our Solar System, which might also incl ...
script
... The strength of the Lithium line can be calibrated with age, but it is generally not that good. In a solar type star the presence of Lithium most likely means it is young. But the processes that affect the strength of lithium are poorly known. For instance, strong Li is also found in some evolved gi ...
... The strength of the Lithium line can be calibrated with age, but it is generally not that good. In a solar type star the presence of Lithium most likely means it is young. But the processes that affect the strength of lithium are poorly known. For instance, strong Li is also found in some evolved gi ...
Solar System by Halfs
... 1. Examine the data above, your measures (in cm), the Actual distances in AU to the planets, and Bode’s Law predictions. How close are Bode’s Law predictions and your measurements to the ACTUAL AU distance? Hint: look at the ratios, not the actual measures. That is, Jupiter is 5.2 times as far as Ea ...
... 1. Examine the data above, your measures (in cm), the Actual distances in AU to the planets, and Bode’s Law predictions. How close are Bode’s Law predictions and your measurements to the ACTUAL AU distance? Hint: look at the ratios, not the actual measures. That is, Jupiter is 5.2 times as far as Ea ...
File
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
ph709-14
... inner edge begins around 25 AU away, farther than the average orbital distance of Uranus in the Solar System. Its outer edge appears to extend as far out as 550 AUs away from the star. ...
... inner edge begins around 25 AU away, farther than the average orbital distance of Uranus in the Solar System. Its outer edge appears to extend as far out as 550 AUs away from the star. ...
File
... • It didn’t match theory! – should have been a red supergiant. – was instead a B3 I – a blue giant! – Soon it was realized that evolved different because it was metal poor. It also probably lost outer material ...
... • It didn’t match theory! – should have been a red supergiant. – was instead a B3 I – a blue giant! – Soon it was realized that evolved different because it was metal poor. It also probably lost outer material ...
Practice Midterm 1
... 29. What conditions are required for a lunar eclipse? A) The phase of the Moon can be new or full, and the nodes of the Moon’s orbit must be nearly aligned with Earth and the Sun. B) The phase of the Moon must be new, and the nodes of the Moon’s orbit must be nearly aligned with Earth and the Sun. C ...
... 29. What conditions are required for a lunar eclipse? A) The phase of the Moon can be new or full, and the nodes of the Moon’s orbit must be nearly aligned with Earth and the Sun. B) The phase of the Moon must be new, and the nodes of the Moon’s orbit must be nearly aligned with Earth and the Sun. C ...
Planet X - The 2017 Arrival
... for all that Planet X does exist. He thinks it can be proven from analysis that will take less than two years. The professor believes Planet X is comprised mostly of hydrogen and helium gas, similar to a Brown Dwarf Star (a late-stage sun). He estimates that it would be much like Jupiter, although m ...
... for all that Planet X does exist. He thinks it can be proven from analysis that will take less than two years. The professor believes Planet X is comprised mostly of hydrogen and helium gas, similar to a Brown Dwarf Star (a late-stage sun). He estimates that it would be much like Jupiter, although m ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... Don’t worry…these stars can live up to 10 billion years. It is estimated that the sun is 4.6 billion years old. It still has 5 billion years of life left. • When yellow stars (medium sized) die, they swell up becoming very large. We then call these stars giant stars. • Giant star- When sun sized ...
... Don’t worry…these stars can live up to 10 billion years. It is estimated that the sun is 4.6 billion years old. It still has 5 billion years of life left. • When yellow stars (medium sized) die, they swell up becoming very large. We then call these stars giant stars. • Giant star- When sun sized ...
starevolution - Global Change Program
... weight of about 4). To make one He atom, we therefore need four H atoms and some modifications. Assuming we are able to overcome the repelling force of the protons, the combined mass of 4 H atoms equals 6.696E-24gram, which exceeds the mass of He. The excess mass is released as energy following Albe ...
... weight of about 4). To make one He atom, we therefore need four H atoms and some modifications. Assuming we are able to overcome the repelling force of the protons, the combined mass of 4 H atoms equals 6.696E-24gram, which exceeds the mass of He. The excess mass is released as energy following Albe ...
grade v and vi - Sacred Heart CMI Public School
... around it. Apart from the Sun, the largest members of the Solar System are the eight major planets. Nearest the Sun there are four fairly small, rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Beyond Mars is the asteroid belt – a region populated by millions of rocky objects. These are left-over’s fro ...
... around it. Apart from the Sun, the largest members of the Solar System are the eight major planets. Nearest the Sun there are four fairly small, rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Beyond Mars is the asteroid belt – a region populated by millions of rocky objects. These are left-over’s fro ...
userfiles/602xxh/files/2013%e5%b1%8a%e9%ab%98%e4%b8%89
... most certain about are large—up to 25 times the size of Earth. According to Christophe Lovis, one of the scientists behind the finding, these five planets are similar to Neptune(海王星). “They’re made mainly of rocks and ice,” he said. “They’re probably not suitable for people to live in.” ...
... most certain about are large—up to 25 times the size of Earth. According to Christophe Lovis, one of the scientists behind the finding, these five planets are similar to Neptune(海王星). “They’re made mainly of rocks and ice,” he said. “They’re probably not suitable for people to live in.” ...
How much Sugar in Gum
... 2. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. If you turned on a flashlight, at the end of 1 year, the beam of light will have traveled about 6 TRILLION miles (6,000,000,000,000). Why do astronomers use units such at light years or astronomical units to measure distances? Since the ...
... 2. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. If you turned on a flashlight, at the end of 1 year, the beam of light will have traveled about 6 TRILLION miles (6,000,000,000,000). Why do astronomers use units such at light years or astronomical units to measure distances? Since the ...
Exoanatomy - Jothi's World
... Variability leads to mutations which are variably adapted to their environment. This variability is caused by random variations in the building plans of the organism (the genes). The genetic codes’ structure is meta-stable in a particular way – it preserves its overall structure: dogs don’t give bir ...
... Variability leads to mutations which are variably adapted to their environment. This variability is caused by random variations in the building plans of the organism (the genes). The genetic codes’ structure is meta-stable in a particular way – it preserves its overall structure: dogs don’t give bir ...
Meteors and Comets
... Scientists try to predict when comets will come too close to Earth Sometimes comets collide with planets and their moons Haley’s Comet is the most famous comet, it passes by Earth every 76 years – the last time it passed by Earth was in 1986 When Earth crosses the path of a comet, leftover dust and ...
... Scientists try to predict when comets will come too close to Earth Sometimes comets collide with planets and their moons Haley’s Comet is the most famous comet, it passes by Earth every 76 years – the last time it passed by Earth was in 1986 When Earth crosses the path of a comet, leftover dust and ...
Meteors and Comets
... Scientists try to predict when comets will come too close to Earth Sometimes comets collide with planets and their moons Haley’s Comet is the most famous comet, it passes by Earth every 76 years – the last time it passed by Earth was in 1986 When Earth crosses the path of a comet, leftover dust and ...
... Scientists try to predict when comets will come too close to Earth Sometimes comets collide with planets and their moons Haley’s Comet is the most famous comet, it passes by Earth every 76 years – the last time it passed by Earth was in 1986 When Earth crosses the path of a comet, leftover dust and ...
Astronomy 103 – Midterm 2 – October 29, 2014
... 2 Fusion of helium to carbon in the core 3 Contraction of the entire star 4 Fusion of hydrogen to helium in the core A The energy source for a star just after the helium flash. B The energy source of a star in its first red-giant stage. C The energy source of a main sequence star. D The energy sourc ...
... 2 Fusion of helium to carbon in the core 3 Contraction of the entire star 4 Fusion of hydrogen to helium in the core A The energy source for a star just after the helium flash. B The energy source of a star in its first red-giant stage. C The energy source of a main sequence star. D The energy sourc ...
Significance of the 27 August 2016 Venus Jupiter Conjunction A
... As revealed in the Christmas Star, when the August 3 BC star appeared over Israel, the wise men were more than likely in Persia, about 750 miles east of Jerusalem. This means that the conjunction may not have appeared as a single star when they saw it before it merged. While it is clear that whatev ...
... As revealed in the Christmas Star, when the August 3 BC star appeared over Israel, the wise men were more than likely in Persia, about 750 miles east of Jerusalem. This means that the conjunction may not have appeared as a single star when they saw it before it merged. While it is clear that whatev ...
BENNETT, Constraints on the Orbital Motion of OGLE-2006
... – Slight dependence on distance to the source star when converting to physical from Einstein Radii units ...
... – Slight dependence on distance to the source star when converting to physical from Einstein Radii units ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.