* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How much Sugar in Gum
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical clock wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
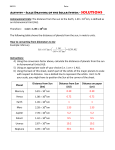
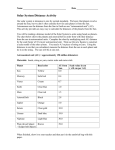
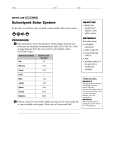
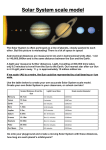
How are astronomical distances measured? Description: Students will create a scale model of the solar system using astronomical units. California State Standard(s): SC.8.4.c. Students know how to use astronomical units and light years as measures of distances between the Sun, stars, and Earth. Student Materials (per group) Strips of paper Planets Scissors Tape or glue Calculator Meter stick Additional Teacher Materials: Background and Misconceptions: Since the distances are vast in the solar system and between stars, astronomers have created various units to represent these large distances. They use them only because they are easier to use and they are agreed upon quantities. The common units are: Astronomical unit (AU) – This is the average distance between the earth and the sun. 1 AU is equal to approximately 93,000,000 miles or 150,000,000 kilometers. Light year (LY) – this is the distance that light travels in 1 year. It is equivalent to about 6 trillion miles or 63,241.1 AU’s. Other units are used by astronomers when necessary or convenient. For example, an additional dimension is the parsec, with is about 3.3 light years. Although a parsec is not significantly different from a light year, its origin resulted from the shifting of stars apparent positions in the night sky during the course of earth’s orbit around the sun. A star that shifts it’s position by 1 arcsecond (which is 1/60th of an arcminute or 1/3600th of a degree.) is said to be 1 parsec from earth with the difference in earth’s position in its orbit is 1 AU. Teacher Guided Questions to Inquiry: Use these questions to get the students started on their own inquiry! 1. How are vast distances in the solar system and galaxy measured? 2. What are astronomical units and light years? 3. How can we scale the solar system and how far away are even the closest stars? Additional Hints: Use adding machine tape for the strips of paper. Students may wish to color the planets prior to gluing or taping onto the paper. TEACHER ANSWER KEY Description: Common units of measurement such as centimeters, meters, and miles are often too small to use when measuring the vast distances between objects in space. Astronomers have created other units to use to measure distances between the sun, planets and the stars. In this activity, you will create a scale model of the solar system using a common unit of measurement in astronomy. Materials: Strips of paper Scissors Planets Calculator Tape or glue Meter stick Procedures: 1. Astronomical units are used to measure to measure large distances within the solar system. An astronomical unit is equal to the average distance between the earth and the sun. This is also equal to 93,000,000 miles. On the table below, determine the distance, in astronomical units (AU) for each of the planets. 2. Create a model of the distances of the planets. Multiply the value in AU’s by 10 (AU x 10 cm). This value will be used to determine where to place the planet on the strip of paper. At one end, glue or tape the planet. 3. On the strip measure the distance from the SURFACE of the sun to the CENTER of the planet. Planet Astronomical Units Distance on tape Mercury Distance from Earth to the Sun (miles) 37,200,000 (1 AU = 93,000,000) 0.4 AU (1 AU = 10 cm) 4 cm Venus 65,100,000 0.7 AU 7 cm Earth 93,000,000 1.00 AU 10 cm Mars 139,000,000 1.5 AU 15 cm Jupiter 483,600,000 5.2 AU 52 cm Saturn 883,500,000 9.5 AU 95 cm Uranus 1,785,600,000 19.2 AU 192 cm Neptune 2,799,300,000 30.1 AU 301 cm Questions: 1. While astronomical units are used to measure the distances within the solar system, it is not easy to use them to measure the distances to the stars. The nearest star is Proxima Centuari. It is 4.3 light years away. A light year is equal to 63,241.1 AU’s. a. How far way is Proxima Centauri in Astronomical Units? 271,937 AU b. How many centimeters down your paper strip would the star be located? 2,719,370 cm, or 27,193.7 kilometers or 16,897 miles! c. Where would this be at the scale of the paper? (Inside the room? School? City?) This would be far outside your city, and in fact would be 2/3rds of the way around the earth! 2. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. If you turned on a flashlight, at the end of 1 year, the beam of light will have traveled about 6 TRILLION miles (6,000,000,000,000). Why do astronomers use units such at light years or astronomical units to measure distances? Since the distances are vast, it is easier to use units that represent larger values. 1 light year is easier to express than 6 trillion miles. Different units are used only because they are easier to use! How are astronomical distances measured? Name _____________________________ Date ____________________ Description: Common units of measurement such as centimeters, meters, and miles are often too small to use when measuring the vast distances between objects in space. Astronomers have created other units to use to measure distances between the sun, planets and the stars. In this activity, you will create a scale model of the solar system using a common unit of measurement in astronomy. Materials: Strips of paper Scissors Planets Calculator Tape or glue Meter stick Procedures: 1. Astronomical units are used to measure to measure large distances within the solar system. An astronomical unit is equal to the average distance between the earth and the sun. This is also equal to 93,000,000 miles. On the table below, determine the distance, in astronomical units (AU) for each of the planets. 2. Create a model of the distances of the planets. Multiply the value in AU’s by 10 (AU x 10 cm). This value will be used to determine where to place the planet on the strip of paper. At one end, glue or tape the planet. 3. On the strip measure the distance from the SURFACE of the sun to the CENTER of the planet. Planet Mercury Distance from Earth to the Sun (miles) 37,200,000 Venus 65,100,000 Earth 93,000,000 Mars 139,000,000 Jupiter 483,600,000 Saturn 883,500,000 Uranus 1,785,600,000 Neptune 2,799,300,000 Astronomical Units Distance on tape (1 AU = 93,000,000) (1 AU = 10 cm) 1.00 AU 10 cm Questions: 1. While astronomical units are used to measure the distances within the solar system, it is not easy to use them to measure the distances to the stars. The nearest star is Proxima Centuari. It is 4.3 light years away. A light year is equal to 63,241.1 AU’s. a. How far way is Proxima Centauri in Astronomical Units? b. How many centimeters down your paper strip would the star be located? c. Where would this be at the scale of the paper? (Inside the room? School? City?) 2. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. If you turned on a flashlight, at the end of 1 year, the beam of light will have traveled about 6 TRILLION miles (6,000,000,000,000). Why do astronomers use units such at light years or astronomical units to measure distances?