Distances of Planets, in Feet, from Sun 2000 Feet Radius Solar
... Overall, Mars appears to be geologically stable and volcanically inactive. Early in its history, it most likely had active volcanos and a thicker, warmer atmosphere supporting liquid surface water that flowed, and carved some of its terrain. Today’s surface appears to have changed little in the past ...
... Overall, Mars appears to be geologically stable and volcanically inactive. Early in its history, it most likely had active volcanos and a thicker, warmer atmosphere supporting liquid surface water that flowed, and carved some of its terrain. Today’s surface appears to have changed little in the past ...
Week 2
... consists of water ice, like the poles here on Earth. In the winter, as temperatures fall to around -153 Celsius (-243 F), carbon dioxide freezes, forming a few-meter-deep layer of dry ice. When the winter ends and sunlight strikes the dry ice, it sublimates into gas, creating massive winds that trav ...
... consists of water ice, like the poles here on Earth. In the winter, as temperatures fall to around -153 Celsius (-243 F), carbon dioxide freezes, forming a few-meter-deep layer of dry ice. When the winter ends and sunlight strikes the dry ice, it sublimates into gas, creating massive winds that trav ...
calculated using stefan`s law
... center of the star to its surface. - In a star energy generated at the core. - Energy spread in the form of photons - While moving towards the surface it faces a large number of frequent collision - Energy and direction of travel of the photon changes. • In case of sun T=30,000 years ...
... center of the star to its surface. - In a star energy generated at the core. - Energy spread in the form of photons - While moving towards the surface it faces a large number of frequent collision - Energy and direction of travel of the photon changes. • In case of sun T=30,000 years ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF STARS
... The brightness of a star depends on both its size and its temperature. How bright a star looks from Earth depends on both its distance and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in 2 different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent br ...
... The brightness of a star depends on both its size and its temperature. How bright a star looks from Earth depends on both its distance and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in 2 different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent br ...
Homework #2
... 6) a) Star A and Star B both have the same luminosity. If Star A has a higher surface temperature than Star B, how do the radii of both stars compare to each other? No numbers are needed, but justify your answer using a relation/equation from class. b) The star Rigel has a luminosity approximately e ...
... 6) a) Star A and Star B both have the same luminosity. If Star A has a higher surface temperature than Star B, how do the radii of both stars compare to each other? No numbers are needed, but justify your answer using a relation/equation from class. b) The star Rigel has a luminosity approximately e ...
A Triple Conjunction
... millennium BC, however, no less than 7 triple conjunctions also took place – one every 140 years, on average – although the interval varied from 40 years (as between 861 and 821 BC and again between 563 and 523 BC) to 377 years (as between 523 BC and 146 BC). Over the millennium there were 43 “norma ...
... millennium BC, however, no less than 7 triple conjunctions also took place – one every 140 years, on average – although the interval varied from 40 years (as between 861 and 821 BC and again between 563 and 523 BC) to 377 years (as between 523 BC and 146 BC). Over the millennium there were 43 “norma ...
Sun and Other Stars Notes
... -luminosity class considers density of __________________________ which determines between a bright giant and a supergiant -What are binary-star systems? -two stars that are part of the same solar system we can see them __________________ -Why are eclipsing binaries helpful in studying star features ...
... -luminosity class considers density of __________________________ which determines between a bright giant and a supergiant -What are binary-star systems? -two stars that are part of the same solar system we can see them __________________ -Why are eclipsing binaries helpful in studying star features ...
Astronomy Jeopardy Astronomy jeopardy
... What is they are small, dense, rocky surfaces? Or What is they all have a crust, mantel and iron core? ...
... What is they are small, dense, rocky surfaces? Or What is they all have a crust, mantel and iron core? ...
Naked Eye, Binocular, or Small Backyard Telescope Night Sky
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
Historical Overview of the Universe
... catalogued, and the spectroscopic decomposition of light was learned as the first astrophysical method. In the twentieth century, stellar spectroscopy was developed as a way of determining stellar parameters, in particular the abundances of the chemical elements. Computer simulations of the evolutio ...
... catalogued, and the spectroscopic decomposition of light was learned as the first astrophysical method. In the twentieth century, stellar spectroscopy was developed as a way of determining stellar parameters, in particular the abundances of the chemical elements. Computer simulations of the evolutio ...
ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... c) The image to the left shows a configuration in which the Sun is never to the zenith. Are there locations on Earth at which the Sun reaches the Zenith? If so, at what latitudes are they? At which time of the year do they reach the zenith? [hint: remember the tilt angle of the spin axis of the Eart ...
... c) The image to the left shows a configuration in which the Sun is never to the zenith. Are there locations on Earth at which the Sun reaches the Zenith? If so, at what latitudes are they? At which time of the year do they reach the zenith? [hint: remember the tilt angle of the spin axis of the Eart ...
What would the sky look like from the North Pole
... • Easy for us to explain: occurs when we “lap” another planet (or when Mercury or Venus laps us) • But very difficult to explain if you think that Earth is the center of the universe! • In fact, ancients considered but rejected the correct explanation ...
... • Easy for us to explain: occurs when we “lap” another planet (or when Mercury or Venus laps us) • But very difficult to explain if you think that Earth is the center of the universe! • In fact, ancients considered but rejected the correct explanation ...
LAB: Star Classification
... ScienceDaily (Dec. 12, 2008) — Astronomy & Astrophysics is publishing observations of the white dwarf KPD 0005+5106. The team who present these observations show that this white dwarf is among the hottest stars known so far, with a temperature of 200,000º K at its surface. Stars of intermediate mass ...
... ScienceDaily (Dec. 12, 2008) — Astronomy & Astrophysics is publishing observations of the white dwarf KPD 0005+5106. The team who present these observations show that this white dwarf is among the hottest stars known so far, with a temperature of 200,000º K at its surface. Stars of intermediate mass ...
Chapter 2: The Science of Life in the Universe
... Test Bank for Life in the Universe, Third Edition Chapter 2: The Science of Life in the Universe ...
... Test Bank for Life in the Universe, Third Edition Chapter 2: The Science of Life in the Universe ...
Introduction
... simultaneous thorium-argon lamp observation (see, e.g., Konacki et al. 2003c) and an Iodine absorption cell (see, e.g., Cumming, Marcy, & Butler 1999 and references therein). While the Iodine cell is placed into the path of the star signal, before entering the spectrograph (and thus reducing the sig ...
... simultaneous thorium-argon lamp observation (see, e.g., Konacki et al. 2003c) and an Iodine absorption cell (see, e.g., Cumming, Marcy, & Butler 1999 and references therein). While the Iodine cell is placed into the path of the star signal, before entering the spectrograph (and thus reducing the sig ...
Part 2 - Hewlett
... Large & gaseous 6. What are the characteristics of these planets? _________________________________________ Venus 7. Which planet is most similar in size to Earth? __________________________________________ Venus 8. Which planet has a longer day than year? ___________________________________________ ...
... Large & gaseous 6. What are the characteristics of these planets? _________________________________________ Venus 7. Which planet is most similar in size to Earth? __________________________________________ Venus 8. Which planet has a longer day than year? ___________________________________________ ...
Greek Astronomy
... context of this theory. Viewing the universe in any other way requires a complete shift in thinking. ...
... context of this theory. Viewing the universe in any other way requires a complete shift in thinking. ...
Monday, April 15
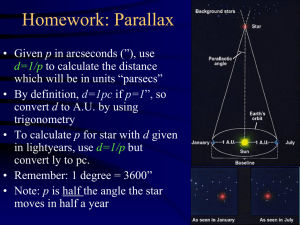
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
TRANSIT
... The software, called NEOimpactor, has been specifically developed for measuring the impact of 'small' asteroids under one kilometre in diameter, and early results indicate that the ten countries most at risk are China, Indonesia, India, Japan, the United States, the Philippines, Italy, the United Ki ...
... The software, called NEOimpactor, has been specifically developed for measuring the impact of 'small' asteroids under one kilometre in diameter, and early results indicate that the ten countries most at risk are China, Indonesia, India, Japan, the United States, the Philippines, Italy, the United Ki ...
Earth Science 24.3B The Sun`s Interior
... to have formed from an enormous compressed cloud of dust and gases, mostly hydrogen. ...
... to have formed from an enormous compressed cloud of dust and gases, mostly hydrogen. ...
The Solar System and its Place in the Galaxy
... The local density of stars in the solar neighborhood is about 0.11 pc^-3, though many of the stars are in binary or multiple star systems. The local density of binary and multiple star systems is 0.086 pc^-3. Most of these are low-mass stars, less massive and less luminous than the Sun. The nearest ...
... The local density of stars in the solar neighborhood is about 0.11 pc^-3, though many of the stars are in binary or multiple star systems. The local density of binary and multiple star systems is 0.086 pc^-3. Most of these are low-mass stars, less massive and less luminous than the Sun. The nearest ...
Orbits - davis.k12.ut.us
... supposed to be 116 days. That number is actually an average synodic period that takes into account the average speed of the Earth and Mercury. Now that you understand Kepler's second law you will also understand that these kinds of calculations are trickier than we first assumed. Mercury's synodic p ...
... supposed to be 116 days. That number is actually an average synodic period that takes into account the average speed of the Earth and Mercury. Now that you understand Kepler's second law you will also understand that these kinds of calculations are trickier than we first assumed. Mercury's synodic p ...
1 Sun Stars Planets. Problem Sheet I
... (a) Find a general equation for the temperature T of a planet’s surface given the luminosity of the star it is orbiting is L and the radius of the orbit is d, ignoring the effect of any planetary atmosphere that might be present, and assuming the planet’s orbit is circular. (b) A planetary system i ...
... (a) Find a general equation for the temperature T of a planet’s surface given the luminosity of the star it is orbiting is L and the radius of the orbit is d, ignoring the effect of any planetary atmosphere that might be present, and assuming the planet’s orbit is circular. (b) A planetary system i ...
Lecture #33: Solar System Origin I The Main Point What is a
... – Previous generations of stars lived and died before our solar system was formed. The violent death of a previous star or stars contributed material to the present solar system ("cosmic recycling"). ...
... – Previous generations of stars lived and died before our solar system was formed. The violent death of a previous star or stars contributed material to the present solar system ("cosmic recycling"). ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.