The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... how to proceed. The classical methods for orbit determination assume that at least three positions on the sky at different times have been observed of the body whose orbit is sought. Modern observations of natural and artificial celestial bodies also include distance and radial velocity measurements ...
... how to proceed. The classical methods for orbit determination assume that at least three positions on the sky at different times have been observed of the body whose orbit is sought. Modern observations of natural and artificial celestial bodies also include distance and radial velocity measurements ...
Pre SS1 Models of the Solar System - Bolinas
... Ptolemy also took a stab at estimating the size of the universe. Hipparchus and others before him had set the Earth-moon distance at about 50 Earth radii, and Ptolemy worked from that figure. He assumed that the celestial spheres were all nested tightly together, and made allowances for the room nee ...
... Ptolemy also took a stab at estimating the size of the universe. Hipparchus and others before him had set the Earth-moon distance at about 50 Earth radii, and Ptolemy worked from that figure. He assumed that the celestial spheres were all nested tightly together, and made allowances for the room nee ...
The Habitability of Our Earth and Other Earths: Astrophysical
... Chlorophyll maps of the ocean (McClain et al. 2006) show regions where, despite ample water, photons, and nitrates, there are low concentrations of chlorophyll. Iron fertilization experiments in these enigmatic high-nitrate-low-chlorophyll regions found that the biomass was iron limited, rather than ...
... Chlorophyll maps of the ocean (McClain et al. 2006) show regions where, despite ample water, photons, and nitrates, there are low concentrations of chlorophyll. Iron fertilization experiments in these enigmatic high-nitrate-low-chlorophyll regions found that the biomass was iron limited, rather than ...
Characteristics of Stars
... f. shines brightly in the center of a distant galaxy because of the friction of material spiraling around it ...
... f. shines brightly in the center of a distant galaxy because of the friction of material spiraling around it ...
tremaine_lecture_1
... Unknowns include: • smaller asteroids and Kuiper belt beyond Neptune • mass loss from Sun • drag of solar wind on planetary magnetospheres • tidal forces from the Milky Way • passing stars (highly unlikely) • errors in planetary masses or initial conditions ...
... Unknowns include: • smaller asteroids and Kuiper belt beyond Neptune • mass loss from Sun • drag of solar wind on planetary magnetospheres • tidal forces from the Milky Way • passing stars (highly unlikely) • errors in planetary masses or initial conditions ...
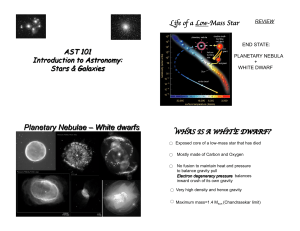
Planetary Nebulae – White dwarfs
... Intermediate-Mass Stars • May burn up to carbon but do not have enough mass to get temperatures high enough to go any higher up the periodic table • Degeneracy pressure stops the core from collapsing and heating enough: particles are squashed together as much as possible • End their lives with pl ...
... Intermediate-Mass Stars • May burn up to carbon but do not have enough mass to get temperatures high enough to go any higher up the periodic table • Degeneracy pressure stops the core from collapsing and heating enough: particles are squashed together as much as possible • End their lives with pl ...
A new Cosmos – a novel Physics
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
Setting the Stage for Habitable Planets
... still “planet-like”, even though they are not technically planets. Second, the word “habitable” can take on a number of meanings. As employed in the present review, habitability refers to the capability of starting life and sustaining it. A habitable planet could include an environment capable of su ...
... still “planet-like”, even though they are not technically planets. Second, the word “habitable” can take on a number of meanings. As employed in the present review, habitability refers to the capability of starting life and sustaining it. A habitable planet could include an environment capable of su ...
Properties of Stars
... • Hydrogen burning migrates outward. The star’s outer envelope expands. • Its surface cools and becomes red. • The core collapses as helium is converted to carbon. Eventually all nuclear fuel is used and gravity squeezes the star. ...
... • Hydrogen burning migrates outward. The star’s outer envelope expands. • Its surface cools and becomes red. • The core collapses as helium is converted to carbon. Eventually all nuclear fuel is used and gravity squeezes the star. ...
The sun - E
... heat. By passing the white light through a prism, we see a rainbow. We call this rainbow a ‘spectrum’ and the colours in a spectrum always follow the same order of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. The sun has an interior and an atmosphere. It does not have a solid surface. The su ...
... heat. By passing the white light through a prism, we see a rainbow. We call this rainbow a ‘spectrum’ and the colours in a spectrum always follow the same order of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. The sun has an interior and an atmosphere. It does not have a solid surface. The su ...
Lecture 4 January 31 - Center for Astrophysics and Space
... As T in core of Sun increases so does energy production ...
... As T in core of Sun increases so does energy production ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E2
... Light emitted from the star will have to pass through the outer layers of the star. Atoms in these layers may absorb light of certain wavelengths if these wavelengths correspond to energy differences in the atomic energy levels. The absorbed photons will therefore not make it through the outer layer ...
... Light emitted from the star will have to pass through the outer layers of the star. Atoms in these layers may absorb light of certain wavelengths if these wavelengths correspond to energy differences in the atomic energy levels. The absorbed photons will therefore not make it through the outer layer ...
A new Cosmos – a novel Physics
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
Exam 2 Physics 102 - Colorado Mesa University
... B) the region around a star where liquid water can exist on planetary surfaces C) the region around a star where its ultraviolet radiation is too weak to destroy biological organisms on a planetary surface D) the region around a star outside of its hot, tenuous corona E) the region around a star whe ...
... B) the region around a star where liquid water can exist on planetary surfaces C) the region around a star where its ultraviolet radiation is too weak to destroy biological organisms on a planetary surface D) the region around a star outside of its hot, tenuous corona E) the region around a star whe ...
The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... how to proceed. The classical methods for orbit determination assume that at least three positions on the sky at different times have been observed of the body whose orbit is sought. Modern observations of natural and artificial celestial bodies also include distance and radial velocity measurements ...
... how to proceed. The classical methods for orbit determination assume that at least three positions on the sky at different times have been observed of the body whose orbit is sought. Modern observations of natural and artificial celestial bodies also include distance and radial velocity measurements ...
Introduction to the Planets and other solar
... Planetismals – these are the planetary building blocks that were common in the early solar system. There are no specific guidelines for the sizes of these things, so they can be anywhere from microscopic to about 1000 km in size. Over time many of these became incorporated into the planets or satell ...
... Planetismals – these are the planetary building blocks that were common in the early solar system. There are no specific guidelines for the sizes of these things, so they can be anywhere from microscopic to about 1000 km in size. Over time many of these became incorporated into the planets or satell ...
Astronomy Club of Asheville May 2016 Sky Events
... So good telescopic views of Saturn will be a late night affair this month. Saturn reaches opposition – closest position to Earth for the year on June 3rd. Venus, Uranus and Neptune are all too close to the Sun in the sky to observe easily this month. You will have only one chance to see Mercury ...
... So good telescopic views of Saturn will be a late night affair this month. Saturn reaches opposition – closest position to Earth for the year on June 3rd. Venus, Uranus and Neptune are all too close to the Sun in the sky to observe easily this month. You will have only one chance to see Mercury ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E5
... It would be hard to believe, as the stars being O stars would have enormous luminosity and so would very quickly leave the main sequence since they consume energy too fast. The age of 100 million years is too long for these stars. ...
... It would be hard to believe, as the stars being O stars would have enormous luminosity and so would very quickly leave the main sequence since they consume energy too fast. The age of 100 million years is too long for these stars. ...
Oct 2015 - Bays Mountain Park
... off of him before they reached Olympus. Pegasus continued on and Zeus took control of him and used him to carry his thunder and lighting. Later Zeus put him in up in the constellations, according to Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the astronomer Ptolemy. I am sure every ...
... off of him before they reached Olympus. Pegasus continued on and Zeus took control of him and used him to carry his thunder and lighting. Later Zeus put him in up in the constellations, according to Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the astronomer Ptolemy. I am sure every ...
6 March 2013 Exoplanets and Where to Find Them Professor
... parts of the disc are inclined at about 5° relative to the outer regions. When first discovered, the disturbances (particularly the clear dust-free gap) were attributed to the presence of one or more exoplanets in the system, and in 2008 infrared images finally detected a point source in this clear ...
... parts of the disc are inclined at about 5° relative to the outer regions. When first discovered, the disturbances (particularly the clear dust-free gap) were attributed to the presence of one or more exoplanets in the system, and in 2008 infrared images finally detected a point source in this clear ...
PTYS/ASTR 206 – Section 2 - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
... large craters, mare, and mountain ranges, but cannot make out any fine detail such as rimae, rille (lava channels), or small craters. At 30 arcminutes, you can easily see Jupiter as a planet (and not just a dot) and the 4 Galilean satellites. You may also be able to see two large bands of gas clouds ...
... large craters, mare, and mountain ranges, but cannot make out any fine detail such as rimae, rille (lava channels), or small craters. At 30 arcminutes, you can easily see Jupiter as a planet (and not just a dot) and the 4 Galilean satellites. You may also be able to see two large bands of gas clouds ...
Astronomy 100—Exam 1
... A. A force that larger objects exert on smaller ones. B. The pressure of the atmosphere on us. C. An attraction force that exists only among astronomical objects D. A force that keeps electrons on their orbits in atoms. E. The attraction force between any two objects with mass. ...
... A. A force that larger objects exert on smaller ones. B. The pressure of the atmosphere on us. C. An attraction force that exists only among astronomical objects D. A force that keeps electrons on their orbits in atoms. E. The attraction force between any two objects with mass. ...
Stellar Parallax Problems
... 6. A. The European Space Agency sent an exact copy of the Gaia mission to orbit Saturn and take parallax measurements, what would be the largest distance to a star that the Gaia spacecraft could measure from that orbit? ...
... 6. A. The European Space Agency sent an exact copy of the Gaia mission to orbit Saturn and take parallax measurements, what would be the largest distance to a star that the Gaia spacecraft could measure from that orbit? ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.