History of Astronomy
... Jupiter has four objects orbiting it The objects are moons and they are not circling Earth Milky Way is populated by uncountable number of stars Earth-centered universe is too simple Venus undergoes full phase cycle Venus must circle Sun ...
... Jupiter has four objects orbiting it The objects are moons and they are not circling Earth Milky Way is populated by uncountable number of stars Earth-centered universe is too simple Venus undergoes full phase cycle Venus must circle Sun ...
Sol_157a_midterm_2016
... Of these five minerals, only limestone has absorption features in both bands 1 and 3. Hence, we can identify limestone by these two features. Next, we notice that kaolinite has features in both bands 2 and 4. But so does montmorillonite. However, kaolinite has a much larger transmission in band 3 th ...
... Of these five minerals, only limestone has absorption features in both bands 1 and 3. Hence, we can identify limestone by these two features. Next, we notice that kaolinite has features in both bands 2 and 4. But so does montmorillonite. However, kaolinite has a much larger transmission in band 3 th ...
STANDARD SET 4. Earth Sciences
... The Sun is a star located on the rim of a typical spiral galaxy called the Milky Way and orbits the galactic center. In similar spiral galaxies this galactic center appears as a bulge of stars in the heart of the disk. The bright band of stars cutting across the night sky is the edge of the Milky Wa ...
... The Sun is a star located on the rim of a typical spiral galaxy called the Milky Way and orbits the galactic center. In similar spiral galaxies this galactic center appears as a bulge of stars in the heart of the disk. The bright band of stars cutting across the night sky is the edge of the Milky Wa ...
Astronomical Constants
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
... 27) Circle the seven planets of the ancient world from the alphabetic list presented below. Earth Jupiter Mars ...
Review: Quiz 1 Concepts Celestial sphere
... The precession of the poles was discovered by Hipparchus, but not the pattern." The daily motion of the sun is neither prograde nor retrograde. It is direct." The tropical year is 20 minutes longer than the orbital (sidereal) year." "No two orbits are exactly in the same plane, that's why conjunctio ...
... The precession of the poles was discovered by Hipparchus, but not the pattern." The daily motion of the sun is neither prograde nor retrograde. It is direct." The tropical year is 20 minutes longer than the orbital (sidereal) year." "No two orbits are exactly in the same plane, that's why conjunctio ...
Basic Astronomy Note - Mr. Dewey – Grade 7/8
... would take about 80,000 years to get there (our closest neighbouring solar system). ...
... would take about 80,000 years to get there (our closest neighbouring solar system). ...
The Universe
... When looking up at the sky during a cloudless night you can see little spots of light. These tiny specks of light can be planets, moons, comets, stars, but also complete star systems (galaxies). Our Solar system is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth ...
... When looking up at the sky during a cloudless night you can see little spots of light. These tiny specks of light can be planets, moons, comets, stars, but also complete star systems (galaxies). Our Solar system is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth ...
Inquiry Plan, Year 5/6 - Owairoa Primary School
... centre of our solar system and that it has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (Pluto as a ‘dwarf planet’). They should understand that a moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet (Earth has one moon; Jupiter has four large moons and numerous smaller o ...
... centre of our solar system and that it has eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (Pluto as a ‘dwarf planet’). They should understand that a moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet (Earth has one moon; Jupiter has four large moons and numerous smaller o ...
New Worlds on the Horizon: Earth-Sized Planets Close to Other
... Habitability Our prospects for finding Earth-sized planets close to their host stars and even learning something about them seem promising. ...
... Habitability Our prospects for finding Earth-sized planets close to their host stars and even learning something about them seem promising. ...
Introduction to the Universe
... Students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than the stars are. Students know the Sun is a typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion of hydrogen to form helium. Students know the solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-sha ...
... Students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than the stars are. Students know the Sun is a typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion of hydrogen to form helium. Students know the solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-sha ...
write the scientific term
... Because , it is a dark body revolves around the sun in fixed orbit. Because, the earth rotates around itself once every 24 hours. Because, the earth revolves around the sun once every 1 year. Because, carbon dioxide gas produced during blowing in the lime water changes it into turbid (milky). 8. Bec ...
... Because , it is a dark body revolves around the sun in fixed orbit. Because, the earth rotates around itself once every 24 hours. Because, the earth revolves around the sun once every 1 year. Because, carbon dioxide gas produced during blowing in the lime water changes it into turbid (milky). 8. Bec ...
Episode 14: Planetary paths-2
... the year, he found they had lots of errors. Tycho’s observed positions of Jupiter and Saturn did not match with the positions given in the almanacs; they were off by several days. This was a turning point in Tycho’s life; he decided to take upon himself the task of making accurate observations of t ...
... the year, he found they had lots of errors. Tycho’s observed positions of Jupiter and Saturn did not match with the positions given in the almanacs; they were off by several days. This was a turning point in Tycho’s life; he decided to take upon himself the task of making accurate observations of t ...
Scaling the Solar System
... has a diameter of 9500 km and is located 300,000,000 km from the sun. To find the model diameter, divide the actual diameter by the scaling factor. Likewise, to find the model distance from the sun divide the actual distance by the scaling factor. Be sure to use proper units in your example calculat ...
... has a diameter of 9500 km and is located 300,000,000 km from the sun. To find the model diameter, divide the actual diameter by the scaling factor. Likewise, to find the model distance from the sun divide the actual distance by the scaling factor. Be sure to use proper units in your example calculat ...
Related Handout - Orange County Astronomers
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
... Mars is the last of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is 4,116 miles, its mass 11% of Earth’s, and it circles the Sun in 1.88 years at an average distance of 1.5 AU. The planet is cratered, has a thin atmosphere of carbon dioxide, and has two small moons, Deimos and Phobos, beyond the reach of t ...
The sun, the earth, and the moon
... After Sun was formed (from what!?!?) the leftover dust, gases, etc. in nebula continued to spin This created a ___________ around the new star ...
... After Sun was formed (from what!?!?) the leftover dust, gases, etc. in nebula continued to spin This created a ___________ around the new star ...
A new Cosmos – a novel Physics
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
... The ancient view of the cosmos Prior to the Copernican revolution, physics and astronomy were based for more than 1500 years on the writings of the greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BD) and the ancient world’s “house astronomer" Claudius Ptolemy (Ptolemaios, 100180 AD). In Aristotle’s understand ...
Test 2, November 14, 2016 - Physics@Brock
... 36. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) it is redshifted. (b) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (c) it is blueshifted. (d) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. 37. What is the most abundant chemical element in the main sequence stars? (a) Oxygen (O). (b) Car ...
... 36. When a star’s light passes through its cooler atmosphere (a) it is redshifted. (b) new spectral lines appear in the spectrum. (c) it is blueshifted. (d) photons of certain wavelengths are absorbed. 37. What is the most abundant chemical element in the main sequence stars? (a) Oxygen (O). (b) Car ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... Great opposition of Mars (near perihelion) (火星大衝) occurs every 15-16 years. The one in 2003 was the closest in 60,000 years, which the media made a big deal of. However, as shown on the graph, the other great oppositions such as the 1988 one are not much further away. Note: since great opposition oc ...
... Great opposition of Mars (near perihelion) (火星大衝) occurs every 15-16 years. The one in 2003 was the closest in 60,000 years, which the media made a big deal of. However, as shown on the graph, the other great oppositions such as the 1988 one are not much further away. Note: since great opposition oc ...
ph507lecnote07
... is directly related to its median luminosity. This relationship was first discovered from a study of the variables in the Magellanic Clouds, two small nearby companion galaxies to our Galaxy that are visible in the night sky of the southern hemisphere. To a good approximation, you can consider all s ...
... is directly related to its median luminosity. This relationship was first discovered from a study of the variables in the Magellanic Clouds, two small nearby companion galaxies to our Galaxy that are visible in the night sky of the southern hemisphere. To a good approximation, you can consider all s ...
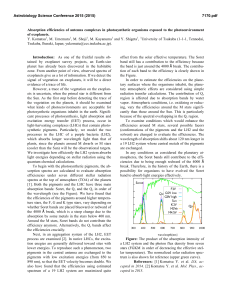
Absorption efficiencies of antenna complexes in photosynthetic
... band still has a contribution to the efficiency because the band is just around the 4000 Å break. The contribution of each band to the efficiency is clearly shown in the Figure. In order to estimate the efficiencies on the planetary surfaces where the organisms inhabit, the planetary atmospheric eff ...
... band still has a contribution to the efficiency because the band is just around the 4000 Å break. The contribution of each band to the efficiency is clearly shown in the Figure. In order to estimate the efficiencies on the planetary surfaces where the organisms inhabit, the planetary atmospheric eff ...
Problem Set #2
... c. What is the temperature, T, in Kelvin of a gas of free electrons whose average electron kinetic energy will be the same as the ionization energy of neutral atomic sodium? 6. A slab of glass 0.5-meters thick absorbs 50% of the light passing through it. Compute how thick of a slab of the identical ...
... c. What is the temperature, T, in Kelvin of a gas of free electrons whose average electron kinetic energy will be the same as the ionization energy of neutral atomic sodium? 6. A slab of glass 0.5-meters thick absorbs 50% of the light passing through it. Compute how thick of a slab of the identical ...
Outer Planets Review Sheet with answers: 1.) Give the order of the
... b.) The object must have enough mass for its gravity to have pulled it into a sphere shape. c.) The Planet must have cleared its orbit. (The objects orbiting the planet must not combine to make up more than half of the actual planet’s size.) 40.) Which of these rules did Pluto fail? (1 Mark) Pluto f ...
... b.) The object must have enough mass for its gravity to have pulled it into a sphere shape. c.) The Planet must have cleared its orbit. (The objects orbiting the planet must not combine to make up more than half of the actual planet’s size.) 40.) Which of these rules did Pluto fail? (1 Mark) Pluto f ...
PPT Format - HubbleSOURCE
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
PT`s IAS Academy
... neutrinos react are put in large pools in mines, and the neutrinos' passage through the pools can be measured by the rare changes they cause in the nuclei in the pools. For example, perchloroethane contains some isotopes of chlorine with 37 particles in the nucleus (17 protons, 2 ...
... neutrinos react are put in large pools in mines, and the neutrinos' passage through the pools can be measured by the rare changes they cause in the nuclei in the pools. For example, perchloroethane contains some isotopes of chlorine with 37 particles in the nucleus (17 protons, 2 ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.