Test Ch. 27 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes
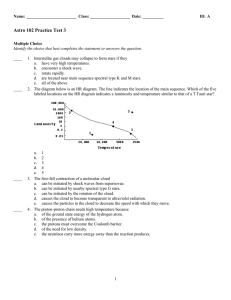
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
Astro 102 Practice Test 3
... d. the material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion. e. c and d ____ 27. As material leaves an expanding star and begins to fall into a white dwarf a. an accretion disk will form around the white dwarf. b. the material will cool off because it begins to move at h ...
... d. the material will increase in temperature and eventually undergo thermonuclear fusion. e. c and d ____ 27. As material leaves an expanding star and begins to fall into a white dwarf a. an accretion disk will form around the white dwarf. b. the material will cool off because it begins to move at h ...
Starry Night Companion - Starry Night Education
... and sixth the dimmest that most people can see without a telescope. It is counter-intuitive for the brighter stars to have a smaller magnitude number, but the scheme has been used for so long that astronomers have gotten used to it. Modern astronomers have recalibrated Hipparchus’ scheme to put it o ...
... and sixth the dimmest that most people can see without a telescope. It is counter-intuitive for the brighter stars to have a smaller magnitude number, but the scheme has been used for so long that astronomers have gotten used to it. Modern astronomers have recalibrated Hipparchus’ scheme to put it o ...
M sin i
... Planets orbit around the center of mass of the Solar system. This is located close to the center of the Sun because it is by far the most massive body. But the Sun also orbits around this barycenter. – Note that Jupiter has contains more than double the mass of all the other planets together. Jupite ...
... Planets orbit around the center of mass of the Solar system. This is located close to the center of the Sun because it is by far the most massive body. But the Sun also orbits around this barycenter. – Note that Jupiter has contains more than double the mass of all the other planets together. Jupite ...
Process of Science: PreMainSequence Stellar Life Tracks on the HR
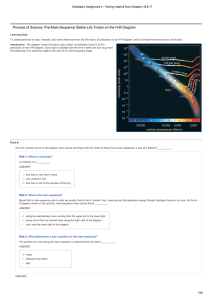
... Hint 4. How do you determine the energy source of a protostar, from the diagram in Hint 1? The following figure is the same as the figure in Hint 1; it shows the progression of a onesolarmass star from the beginning of its formation until it reaches the main sequence. During Stage 2 on the figure, ...
... Hint 4. How do you determine the energy source of a protostar, from the diagram in Hint 1? The following figure is the same as the figure in Hint 1; it shows the progression of a onesolarmass star from the beginning of its formation until it reaches the main sequence. During Stage 2 on the figure, ...
Chap2-RadialVelocity
... Spectrum of a star obtained using the HARPS instrument on the ESO 3.6-metre telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile. The lines are the light from the star spread out through various orders. The dark gaps in the lines are absorption features from different elements in the star. The regularly s ...
... Spectrum of a star obtained using the HARPS instrument on the ESO 3.6-metre telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile. The lines are the light from the star spread out through various orders. The dark gaps in the lines are absorption features from different elements in the star. The regularly s ...
Chapter 5 Theory of Stellar Evolution
... layers can no longer remain in stable equilibrium, and the star will begin to shed its mass. Very few stars with masses above 100M⊙ are known to exist, and those that do show instabilities in their outer layers. At the other end of the mass scale, a mass of about 0.1M⊙ is required to produce core te ...
... layers can no longer remain in stable equilibrium, and the star will begin to shed its mass. Very few stars with masses above 100M⊙ are known to exist, and those that do show instabilities in their outer layers. At the other end of the mass scale, a mass of about 0.1M⊙ is required to produce core te ...
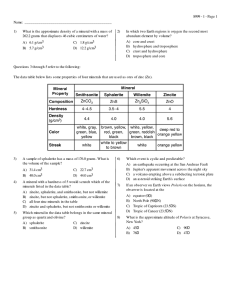
438 Old Regents Questions - Marlboro Central School District
... The map below shows coral reef distribution and diversity (number of different coral types) around the world. Isolines on the map represent the number of different types of coral. Coral reefs are found mostly in shallow tropical waters and do not grow when ocean temperatures fall below 18°C. The 18° ...
... The map below shows coral reef distribution and diversity (number of different coral types) around the world. Isolines on the map represent the number of different types of coral. Coral reefs are found mostly in shallow tropical waters and do not grow when ocean temperatures fall below 18°C. The 18° ...
Chapter 17--Star Stuff
... itself. The clouds that form stars tend to be quite cold, typically only 10–30 K. (Recall that 0 K is absolute zero, and temperatures on Earth are around 300 K.) They also tend to be quite dense compared to the rest of the gas between the stars, although they would qualify as a superb vacuum by eart ...
... itself. The clouds that form stars tend to be quite cold, typically only 10–30 K. (Recall that 0 K is absolute zero, and temperatures on Earth are around 300 K.) They also tend to be quite dense compared to the rest of the gas between the stars, although they would qualify as a superb vacuum by eart ...
Information extracted from Britannica 97
... Prior to the Voyager 2 encounter in August 1989, Neptune's only known satellites were Triton and Nereid. Triton is the lone large moon in the solar system to travel backward (in a direction opposite to the planet's rotation) around its primary. Among the largest satellites in the solar system, incli ...
... Prior to the Voyager 2 encounter in August 1989, Neptune's only known satellites were Triton and Nereid. Triton is the lone large moon in the solar system to travel backward (in a direction opposite to the planet's rotation) around its primary. Among the largest satellites in the solar system, incli ...
Formation of the Solar System
... The solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from the collapse of an interstellar gas cloud (the solar nebula). The planets formed by coagulation of smaller particles (planetesimals). Planets all line in the same orbital plane, all orbit in the same direction, and mostly spin in the same dire ...
... The solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from the collapse of an interstellar gas cloud (the solar nebula). The planets formed by coagulation of smaller particles (planetesimals). Planets all line in the same orbital plane, all orbit in the same direction, and mostly spin in the same dire ...
MPhil Thesis - Final - Suzanne Knight
... low mass planets as it ascends the red giant and asymptotic giant branch evolutionary tracks, but larger mass objects and those further out will survive.! A substellar companion detected around a white dwarf would prove that it could survive the final stages of stellar evolution and place constraint ...
... low mass planets as it ascends the red giant and asymptotic giant branch evolutionary tracks, but larger mass objects and those further out will survive.! A substellar companion detected around a white dwarf would prove that it could survive the final stages of stellar evolution and place constraint ...
azu_etd_13224_sip1_m
... What physical processes and sources of material contribute to exoplanet compositions? Specifically, what roles do the protoplanetary disk composition and structure, and host star abundances play in the different stages of planet formation? In this thesis, beginning with a brief literature review in ...
... What physical processes and sources of material contribute to exoplanet compositions? Specifically, what roles do the protoplanetary disk composition and structure, and host star abundances play in the different stages of planet formation? In this thesis, beginning with a brief literature review in ...
J Gravity and space
... • that the gravitational attraction of the Earth on a mass causes weight • about the planets of the Solar System, how they orbit the Sun, and how gravity causes an attractive force between any two objects with mass; gravitational attraction depends on satellites, e.g. moons, orbit them the mass and ...
... • that the gravitational attraction of the Earth on a mass causes weight • about the planets of the Solar System, how they orbit the Sun, and how gravity causes an attractive force between any two objects with mass; gravitational attraction depends on satellites, e.g. moons, orbit them the mass and ...
Page 1 - Sciss
... into the structure we live in now, even the most elementary particles have endured. This show follows the path of one of these “particles,” a proton, as it participates in nature’s astounding events of rebirth and renewal. ...
... into the structure we live in now, even the most elementary particles have endured. This show follows the path of one of these “particles,” a proton, as it participates in nature’s astounding events of rebirth and renewal. ...
17_Testbank
... 33) Consider the star to which the arrow points. How is it currently generating energy? A) by gravitational contraction B) by hydrogen shell burning around an inert helium core C) by core hydrogen fusion D) by core helium fusion combined with hydrogen shell burning E) by both hydrogen and helium sh ...
... 33) Consider the star to which the arrow points. How is it currently generating energy? A) by gravitational contraction B) by hydrogen shell burning around an inert helium core C) by core hydrogen fusion D) by core helium fusion combined with hydrogen shell burning E) by both hydrogen and helium sh ...
Full Program with Abstracts - CIERA
... This year, we mark twenty years of exploring the diversity of planets and planetary systems orbiting main sequence stars. Exoplanet discoveries spill into the thousands, and the sensitivity boundaries continue to expand. NASA's Kepler Mission unveiled a galaxy replete with small planets and revealed ...
... This year, we mark twenty years of exploring the diversity of planets and planetary systems orbiting main sequence stars. Exoplanet discoveries spill into the thousands, and the sensitivity boundaries continue to expand. NASA's Kepler Mission unveiled a galaxy replete with small planets and revealed ...
Multiple scattering polarization
... Polarization of substellar mass objects not sustain hydrogen fusion at their core. Therefore, these objects do not have an internal source of energy and the thermal radiation from brown dwarfs arises from the release of gravitational potential energy during their formation and governed by the inter ...
... Polarization of substellar mass objects not sustain hydrogen fusion at their core. Therefore, these objects do not have an internal source of energy and the thermal radiation from brown dwarfs arises from the release of gravitational potential energy during their formation and governed by the inter ...
our planet the earth byalko - ArvindGuptaToys Books Gallery
... The drawing is closed while in fact the Zodiac constellations are cyclic: Pisces are followed again by Aries. This great circle of the celestial sphere is called ecliptic. The ecliptic is the path of the Sun among the stars during a year as observed from the Earth. Stars cannot be distinguished a t ...
... The drawing is closed while in fact the Zodiac constellations are cyclic: Pisces are followed again by Aries. This great circle of the celestial sphere is called ecliptic. The ecliptic is the path of the Sun among the stars during a year as observed from the Earth. Stars cannot be distinguished a t ...
The Human Orrery - Armagh Observatory
... curriculum, familiarising children and their teachers with the structure of the solar system and the near Universe, of which the Earth is a part. 4. It helps people to appreciate the fully three-dimensional nature of the celestial ‘sphere’, overcoming the geocentric illusion. ...
... curriculum, familiarising children and their teachers with the structure of the solar system and the near Universe, of which the Earth is a part. 4. It helps people to appreciate the fully three-dimensional nature of the celestial ‘sphere’, overcoming the geocentric illusion. ...
The evolution of organic matter in space
... cool efficiently enough. Although atomic cooling can ensure temperatures down to 10 000 K, molecular cooling is necessary to reach lower temperatures. The dominant cooling molecule at these stages is believed to be molecular hydrogen, H2 , formed through H + e− → H− and H− + H → H2 + e− [4]. First st ...
... cool efficiently enough. Although atomic cooling can ensure temperatures down to 10 000 K, molecular cooling is necessary to reach lower temperatures. The dominant cooling molecule at these stages is believed to be molecular hydrogen, H2 , formed through H + e− → H− and H− + H → H2 + e− [4]. First st ...
Oxygen and Neon Abundances of B-Type Stars in Comparison with
... by which uncertainties in the gf values (an important source of systematic errors) can be canceled. We here point out based on this standpoint that, among the several candidate oxygen lines observable in both B stars as well as in the Sun, O I triplet lines at the orange region of 6156–8 Å are most ...
... by which uncertainties in the gf values (an important source of systematic errors) can be canceled. We here point out based on this standpoint that, among the several candidate oxygen lines observable in both B stars as well as in the Sun, O I triplet lines at the orange region of 6156–8 Å are most ...
S STR RO ONO OM MY - Supercharged Science
... Clean up Messes: Your lab area should be neat, organized, and spotless before you start, during your experiment, and when you leave. Scientists waste more time hunting for lost papers, pieces of an experiment, and trying to reposition sensitive equipment … all of which could have easily been avoid ...
... Clean up Messes: Your lab area should be neat, organized, and spotless before you start, during your experiment, and when you leave. Scientists waste more time hunting for lost papers, pieces of an experiment, and trying to reposition sensitive equipment … all of which could have easily been avoid ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.