Unit 11: Stellar Evolution
... • Chemical nature: mostly hydrogen, most of the rest is helium, and some heavier elements. • Physical nature: mostly gas, some solid particles. ...
... • Chemical nature: mostly hydrogen, most of the rest is helium, and some heavier elements. • Physical nature: mostly gas, some solid particles. ...
Rotation
... and the Eddington Sweet time scale is about 1012 years, i.e., it is unimportant. It can become more important near the surface though as the density decreases (Kippenhahn 42.36) For a 20 M e star , the Kelvin Helmholtz time scale relative to the nuclear lifetime is about three times greater . More i ...
... and the Eddington Sweet time scale is about 1012 years, i.e., it is unimportant. It can become more important near the surface though as the density decreases (Kippenhahn 42.36) For a 20 M e star , the Kelvin Helmholtz time scale relative to the nuclear lifetime is about three times greater . More i ...
Earth Science Spring Break Packet 2016
... A. Gravity is the same wherever you are. B. There is less gravity on the Moon. C. There is more gravity on the Moon. D. Gravity depends on each person. 24. Why does the Moon orbit Earth instead of the Sun? A. Gravity depends on distance and the Moon is closer to Earth. B. Only large objects orbit ar ...
... A. Gravity is the same wherever you are. B. There is less gravity on the Moon. C. There is more gravity on the Moon. D. Gravity depends on each person. 24. Why does the Moon orbit Earth instead of the Sun? A. Gravity depends on distance and the Moon is closer to Earth. B. Only large objects orbit ar ...
The Early Evolution of Protostars
... Consequences of Episodicity The connection between Classes and Stages becomes tenuous The luminosity is not an indicator of stellar mass until nuclear burning dominates (Lacc ~ M*dMacc/dt) Stellar ages from tracks may be way off (Baraffe et al. 2009) The initial conditions for planet format ...
... Consequences of Episodicity The connection between Classes and Stages becomes tenuous The luminosity is not an indicator of stellar mass until nuclear burning dominates (Lacc ~ M*dMacc/dt) Stellar ages from tracks may be way off (Baraffe et al. 2009) The initial conditions for planet format ...
RTF - Digitalis Education
... A) Inform students that the sky is currently set for 2 pm on January 7, 1610. Does anyone know why we're using this date? [It's the date of Galileo's earliest known written recordings of the positions of the Galilean moons.] Obviously Galileo was not able to observe Jupiter and the Galilean moons in ...
... A) Inform students that the sky is currently set for 2 pm on January 7, 1610. Does anyone know why we're using this date? [It's the date of Galileo's earliest known written recordings of the positions of the Galilean moons.] Obviously Galileo was not able to observe Jupiter and the Galilean moons in ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
... There are high-velocity winds in the upper atmosphere, but the atmosphere below the cloud deck appears to be relatively stagnant, with only very weak winds blowing at the surface. Convection driven by differential solar heating should give rise to winds of only a few meters per second, so the high v ...
Paper - Astrophysics - University of Oxford
... 2.1. Formation of stars across the Universe When did stars form? To answer this basic question we can make use of the fact that every star must eventually die. Indeed the more massive stars die in spectacular supernova explosions that can outshine a whole galaxy. With an ELT these explosions can be ...
... 2.1. Formation of stars across the Universe When did stars form? To answer this basic question we can make use of the fact that every star must eventually die. Indeed the more massive stars die in spectacular supernova explosions that can outshine a whole galaxy. With an ELT these explosions can be ...
Solar System Unit
... - The students can then create their planets on the large piece of white paper with the name of their planet clearly showing and their name on the back. (K) - When the students are finished they should show the teacher - The students will then write 3-5 sentences about how this activity went. Specif ...
... - The students can then create their planets on the large piece of white paper with the name of their planet clearly showing and their name on the back. (K) - When the students are finished they should show the teacher - The students will then write 3-5 sentences about how this activity went. Specif ...
Shining Light on the Stars: The Hertzsprung-Russell
... sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are too faint to be seen without a telescope? We immediately see that these two groups of stars lie in completely different parts of the HR diagram. The local group of stars within 25 light ...
... sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are too faint to be seen without a telescope? We immediately see that these two groups of stars lie in completely different parts of the HR diagram. The local group of stars within 25 light ...
CONTINUING GALACTIC FORMATION
... galactic nucleus, and not solely by its own mass. Since the visible galaxy is about 45 million years old, it must regenerate one 45 millionth of this each year. If the Galaxy contains 10 to the tenth stars then it is producing about 200 stars per year or at a rate of approximately one per day. By th ...
... galactic nucleus, and not solely by its own mass. Since the visible galaxy is about 45 million years old, it must regenerate one 45 millionth of this each year. If the Galaxy contains 10 to the tenth stars then it is producing about 200 stars per year or at a rate of approximately one per day. By th ...
article PDF
... backyard amateur telescopes and orbiting instruments such as Hubble to see what’s going on in the the giant planet to encompass aspects of the origins of life on Earth. When Galileo’s probe dived rest of Jupiter’s atmosphere. “If you add them all together, you have a much into Jupiter, it found that ...
... backyard amateur telescopes and orbiting instruments such as Hubble to see what’s going on in the the giant planet to encompass aspects of the origins of life on Earth. When Galileo’s probe dived rest of Jupiter’s atmosphere. “If you add them all together, you have a much into Jupiter, it found that ...
Saturn - Kansas City Public Schools
... itself from Cassini and parachuted to the surface of Titan. At last, the surface of this primitive world was open for direct study. Landing in what’s been described as “Titanian ice gravel,” Huygens photographed chunks of water ice up to six inches across and found evidence of erosion at the bases o ...
... itself from Cassini and parachuted to the surface of Titan. At last, the surface of this primitive world was open for direct study. Landing in what’s been described as “Titanian ice gravel,” Huygens photographed chunks of water ice up to six inches across and found evidence of erosion at the bases o ...
r - UMD Physics
... collision? (b) Show that the new orbit of Earth around the Sun is an ellipse with Rmax = R and Rmin = R/7. (c) What is the new orbital period of Earth? 9-May-2 ...
... collision? (b) Show that the new orbit of Earth around the Sun is an ellipse with Rmax = R and Rmin = R/7. (c) What is the new orbital period of Earth? 9-May-2 ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 1 to Chapter 9
... light from the next nearest star, Alpha Centauri, takes well over 4 years. The farther away an object is from us in space, the longer it takes for the light from that source to reach us. Our current telescopes can pick up light from objects that we believe to be about 10 billion light years away fro ...
... light from the next nearest star, Alpha Centauri, takes well over 4 years. The farther away an object is from us in space, the longer it takes for the light from that source to reach us. Our current telescopes can pick up light from objects that we believe to be about 10 billion light years away fro ...
Basics – II. Time, Magnitudes and Spectral types
... (along the celestial equator) we see a varying rate due to the projection of the ecliptic on to the celestial equator. This introduces a variation from uniform motion which is a wave of period half a year. The combination of these two effects leads to the Equation of Time (see figures). In effect, w ...
... (along the celestial equator) we see a varying rate due to the projection of the ecliptic on to the celestial equator. This introduces a variation from uniform motion which is a wave of period half a year. The combination of these two effects leads to the Equation of Time (see figures). In effect, w ...
the PDF - Vassar`s Special Collections
... the stars, and already begin to have a new enjoyment.” She thought that the colors had to do with different chemical compositions.) Astronomical research in Maria’s period largely involved studying astronomical orbits such as stars in binary systems, comets and asteroids in the Solar System, and moo ...
... the stars, and already begin to have a new enjoyment.” She thought that the colors had to do with different chemical compositions.) Astronomical research in Maria’s period largely involved studying astronomical orbits such as stars in binary systems, comets and asteroids in the Solar System, and moo ...
Adrian Zielonka`s Space and Astro notes for May `17
... If you manage to see a very thin crescent Moon on the ENE horizon on the 24th (close to 4:50am) look 2½ degrees above it and you will see Mercury. At 4:00am few days either side of the 26th the asteroid Pallas will be just a few degrees to the lower right of Venus. At 10.1 magnitude, a strong pai ...
... If you manage to see a very thin crescent Moon on the ENE horizon on the 24th (close to 4:50am) look 2½ degrees above it and you will see Mercury. At 4:00am few days either side of the 26th the asteroid Pallas will be just a few degrees to the lower right of Venus. At 10.1 magnitude, a strong pai ...
Potential Meteorite Impact - Albert
... through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are termed meteorites. ...
... through the Earth's atmosphere are termed meteors, and these chunks that are hurtling through space are called meteoroids. Large pieces that do not vaporize completely and reach the surface of the Earth are termed meteorites. ...
Declination
... the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and south of the celestial equator. Points n ...
... the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and south of the celestial equator. Points n ...
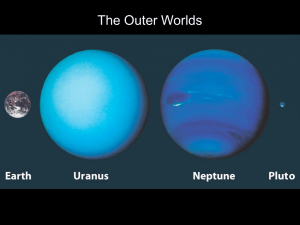
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.