Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... (ii) Lines caused by a stellar atmosphere will have a different Doppler shift than those caused by the interstellar gas. (iii) Interstellar gas will generally be much cooler than the gas of the stellar atmosphere. (c) In 1951, Purcell and Ewen used a specially built radio telescope to detect the 21- ...
... (ii) Lines caused by a stellar atmosphere will have a different Doppler shift than those caused by the interstellar gas. (iii) Interstellar gas will generally be much cooler than the gas of the stellar atmosphere. (c) In 1951, Purcell and Ewen used a specially built radio telescope to detect the 21- ...
Here - SDSU Astronomy Department and Mount Laguna Observatory
... use. Digital cameras are more efficient at detecting light than photographic film. Photographic film detects about 5% of the incoming light, whereas digital cameras can detect well over 90% of the incoming light. ...
... use. Digital cameras are more efficient at detecting light than photographic film. Photographic film detects about 5% of the incoming light, whereas digital cameras can detect well over 90% of the incoming light. ...
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
... What could this “dark matter” be? It is dark at all wavelengths, not just the visible. • Stellar-mass black holes? Probably no way enough could have been created • Brown dwarfs, faint white dwarfs, and red dwarfs? Currently the best star-like option ...
... What could this “dark matter” be? It is dark at all wavelengths, not just the visible. • Stellar-mass black holes? Probably no way enough could have been created • Brown dwarfs, faint white dwarfs, and red dwarfs? Currently the best star-like option ...
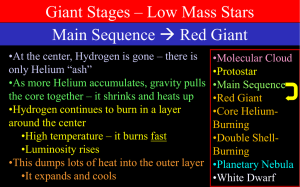
Giant Stars
... Red Giant Core Helium Burning •At 100 million K, the helium core in a red giant star ignites •Suddenly for light stars (< 3 MSun) •Gradually for heavy stars (> 3 MSun) •New heat source in core •It expands and cools •Hydrogen, still burning in a shell, burns more slowly now •Less heat going into h ...
... Red Giant Core Helium Burning •At 100 million K, the helium core in a red giant star ignites •Suddenly for light stars (< 3 MSun) •Gradually for heavy stars (> 3 MSun) •New heat source in core •It expands and cools •Hydrogen, still burning in a shell, burns more slowly now •Less heat going into h ...
The Bigger Picture - Astronomy and Astrophysics
... atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of the H atoms are in the ground state (2) Few oppor ...
... atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of the H atoms are in the ground state (2) Few oppor ...
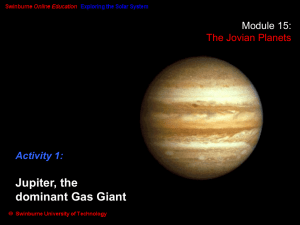
Jupiter, the dominant Gas Giant Planet
... a 60km resolution. Taken on 29 December 2000 during closest approach (at a distance of ~10 million km). ...
... a 60km resolution. Taken on 29 December 2000 during closest approach (at a distance of ~10 million km). ...
129 DYNAMICAL STREAMS IN THE SOLAR NEIGHBOURHOOD B
... • The radial displacements have to be taken into account if one wants to describe the past evolution of the Galaxy, and this is very hard to do because the signature of these events vanishes rapidly (the observed peculiar motions are recent – about 100 Myrs). This warning may apply to most stars in ...
... • The radial displacements have to be taken into account if one wants to describe the past evolution of the Galaxy, and this is very hard to do because the signature of these events vanishes rapidly (the observed peculiar motions are recent – about 100 Myrs). This warning may apply to most stars in ...
Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe
... • It shines mostly by reflected light from its parent star. ! Page 4 ...
... • It shines mostly by reflected light from its parent star. ! Page 4 ...
Lecture2.2014_v4 - UCO/Lick Observatory
... • It shines mostly by reflected light from its parent star. Page 4 ...
... • It shines mostly by reflected light from its parent star. Page 4 ...
Our Galaxy, The Milky Way
... Acceleration of the star moving in a circular orbit must be provided by a net inward gravitational force: ...
... Acceleration of the star moving in a circular orbit must be provided by a net inward gravitational force: ...
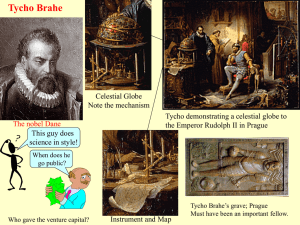
Brahe, Kepler
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
... ``Consecrated to the all-good, great God and Posterity. Tycho Brahe, Son of Otto, who realized that Astronomy, the oldest and most distinguished of all sciences, had indeed been studied for a long time and to a great extent, but still had not obtained sufficient firmness or had been purified of erro ...
SUN, MOON, AND PLANETS Overview
... sometimes during the day. In fact, the Moon splits each month evenly between day and night. The Moon’s shape also appears to change with the Moon’s time of arrival and departure in the sky. The changes in shape are known as phases, and one complete pass through the phases, the lunar cycle, takes 4 w ...
... sometimes during the day. In fact, the Moon splits each month evenly between day and night. The Moon’s shape also appears to change with the Moon’s time of arrival and departure in the sky. The changes in shape are known as phases, and one complete pass through the phases, the lunar cycle, takes 4 w ...
Apr/May 2003 - Madison Astronomical Society
... its direction in 2003? The reason for the strange geometry comes from the fact that in both solar eclipses this year, the shadow falls on the earth “beyond the pole,” in or near the midnight sun area when the sun is seen low on the horizon. This causes the ordinary direction of an eclipse to be reve ...
... its direction in 2003? The reason for the strange geometry comes from the fact that in both solar eclipses this year, the shadow falls on the earth “beyond the pole,” in or near the midnight sun area when the sun is seen low on the horizon. This causes the ordinary direction of an eclipse to be reve ...
ON THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STELLAR CLUSTERS
... Richtler 2000 and Larsen 1999). This star-forming activity in which masses similar to the total gas content found in galactic giant molecular clouds (massive elongated structures that extend over 100 pc in length) are turned into stars, all in a very small volume (∼ few pc) much smaller than the typ ...
... Richtler 2000 and Larsen 1999). This star-forming activity in which masses similar to the total gas content found in galactic giant molecular clouds (massive elongated structures that extend over 100 pc in length) are turned into stars, all in a very small volume (∼ few pc) much smaller than the typ ...
Moons and Small Solar System Bodies Sections 17.1-17.6
... rotation at a rate of about 0.002 s per century • Since angular momentum must be conserved, this decrease in Earth’s angular momentum results in an increase in the moon’s angular momentum • The moon’s orbit is increasing about 1.3 cm/y ...
... rotation at a rate of about 0.002 s per century • Since angular momentum must be conserved, this decrease in Earth’s angular momentum results in an increase in the moon’s angular momentum • The moon’s orbit is increasing about 1.3 cm/y ...
Moon, Super-Moon, Planets of the Solar System
... Half of the Moon is always lit by the Sun, although, over time, it’s possible to see as much as 59% of the moon’s surface, due to a slight north-south rocking and east-west wobbling of the Moon known as lunar libration [1,2]. As the Moon orbits the Earth, we see different parts of the lighted area. ...
... Half of the Moon is always lit by the Sun, although, over time, it’s possible to see as much as 59% of the moon’s surface, due to a slight north-south rocking and east-west wobbling of the Moon known as lunar libration [1,2]. As the Moon orbits the Earth, we see different parts of the lighted area. ...
The Human Orrery: a new educational tool for
... Sun at their correct relative speeds. This is achieved by marking each orbit with tiles—we used stainless steel disks—spaced at suitable intervals. If the distance between successive tiles on the ground corresponds to the same fixed timestep for all the planets, then the relative speeds are correct ...
... Sun at their correct relative speeds. This is achieved by marking each orbit with tiles—we used stainless steel disks—spaced at suitable intervals. If the distance between successive tiles on the ground corresponds to the same fixed timestep for all the planets, then the relative speeds are correct ...
Volume 19 Issue 1 – January/February 2017 Edition
... Kepler proposed light spreads out from a point, and that its intensity decreases the farther it travels from its source [4]. An illustra on of this is that Jupiter being about five mes more distant from the Sun than the Earth is, each square meter on Jupiter gets only one twenty-fi h of the Sun ...
... Kepler proposed light spreads out from a point, and that its intensity decreases the farther it travels from its source [4]. An illustra on of this is that Jupiter being about five mes more distant from the Sun than the Earth is, each square meter on Jupiter gets only one twenty-fi h of the Sun ...
FREE Sample Here
... misconceptions. For example, some students might wonder if you could see the galaxy “sticking up” above our own galaxy’s disk—illustrating a misconception about how angular size declines with distance. They might also wonder if a telescope would make a difference, illustrating a misconception about ...
... misconceptions. For example, some students might wonder if you could see the galaxy “sticking up” above our own galaxy’s disk—illustrating a misconception about how angular size declines with distance. They might also wonder if a telescope would make a difference, illustrating a misconception about ...
File - Science Website
... Our star, the Sun, is a medium sized star. If a star is much more massive than the Sun it will eventually swell into a red giant, start to contract, continue to contract and finally explode. ...
... Our star, the Sun, is a medium sized star. If a star is much more massive than the Sun it will eventually swell into a red giant, start to contract, continue to contract and finally explode. ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.