Planet Formation Gas Giants
... • Before H-burning, the Sun had an unstable (T Tauri) phase – high luminosity and intense solar wind. • Sun lost ~10 % of mass. Nebula dispersed halting gas-giant growth. • Occurred at ~107 years – after Jupiter/Saturn runaway but before that of Uranus/Neptune. • May be why MJ, MS > MU, MN ...
... • Before H-burning, the Sun had an unstable (T Tauri) phase – high luminosity and intense solar wind. • Sun lost ~10 % of mass. Nebula dispersed halting gas-giant growth. • Occurred at ~107 years – after Jupiter/Saturn runaway but before that of Uranus/Neptune. • May be why MJ, MS > MU, MN ...
Part I: Moons, Asteroids, and Comets
... 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is an asteroid? _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Where are most asteroids located? __________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Do all planets have moons? _________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is an asteroid? _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Where are most asteroids located? __________________________________________________________ ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 5 - 9th Edition 2. Pluto is most
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
Space Jeopardy
... The sun appears to be the brightest star in the sky because it is the _________ to the earth. ...
... The sun appears to be the brightest star in the sky because it is the _________ to the earth. ...
Fun Facts: Sunshine
... Without the sun, there would be no heat or light on earth. This means there would be no life either. It takes 8 minutes for light to travel from the sun to the earth. ...
... Without the sun, there would be no heat or light on earth. This means there would be no life either. It takes 8 minutes for light to travel from the sun to the earth. ...
Solar System Basics 1 - Usk Astronomical Society
... The Sun is huge. If it were hollow, over a million and a quarter Earth's would fit inside it. The Sun is also massive and contains about 99% of the matter in the solar system and so its gravity dominates the planets; holding them in orbit. Such a mass as the Sun has a nuclear core releasing energy o ...
... The Sun is huge. If it were hollow, over a million and a quarter Earth's would fit inside it. The Sun is also massive and contains about 99% of the matter in the solar system and so its gravity dominates the planets; holding them in orbit. Such a mass as the Sun has a nuclear core releasing energy o ...
Bodies of our Solar System
... • Has 16 moons • Composed mostly of hydrogen and helium gas • Scientist speculate that if it were 10 times bigger, it may have formed into a star ...
... • Has 16 moons • Composed mostly of hydrogen and helium gas • Scientist speculate that if it were 10 times bigger, it may have formed into a star ...
Chapter 9 Lesson 2
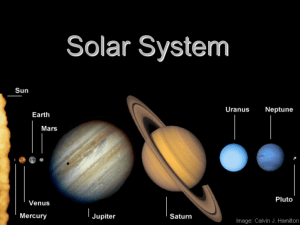
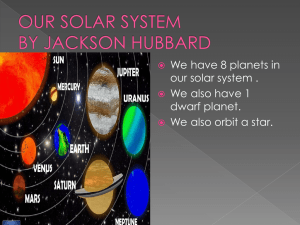
... In our solar system, there are EIGHT (8) planets. Pluto is now considered a dwarf planet, so there are no longer 9 planets . Often scientists group them as the inner planets (closer to the sun) and the outer planets (farther from the sun). The groups are separated by a ring of asteroids. ...
... In our solar system, there are EIGHT (8) planets. Pluto is now considered a dwarf planet, so there are no longer 9 planets . Often scientists group them as the inner planets (closer to the sun) and the outer planets (farther from the sun). The groups are separated by a ring of asteroids. ...
14.2 The Solar System Solar System: made of 9 planets and
... o Largest planet, Great Red Spot is a huge red whirlwind rotating slowly around middle of planet, 28 moons, Io moon has more active volcanoes than anywhere else in solar system Asteroid Belt o Between Jupiter and Mars o Asteroids are pieces of rock made of minerals similar to planet materials o The ...
... o Largest planet, Great Red Spot is a huge red whirlwind rotating slowly around middle of planet, 28 moons, Io moon has more active volcanoes than anywhere else in solar system Asteroid Belt o Between Jupiter and Mars o Asteroids are pieces of rock made of minerals similar to planet materials o The ...
a planet rotates on its own axis and revolves around
... balance each other out to prevent nebula from collapsing or falling apart ...
... balance each other out to prevent nebula from collapsing or falling apart ...
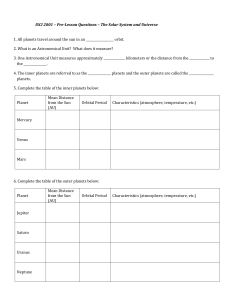
The Solar System Planets, Moons and Other Bodies Mercury Venus
... • Orbital period ~ 3 months • Rotational period ~ 59 days • Visible shortly after sunset or before sunrise • Highly cratered; no atmosphere ...
... • Orbital period ~ 3 months • Rotational period ~ 59 days • Visible shortly after sunset or before sunrise • Highly cratered; no atmosphere ...
Formation of the Solar System Target 1 Notes
... Our solar system formed around __________________ years ago. Scientists believe that a molecular cloud (something called a stellar nursery), consisting of hydrogen collapsed on itself. The collapsing of the cloud resulted in the collision of hydrogen atoms, a process known as __________________. The ...
... Our solar system formed around __________________ years ago. Scientists believe that a molecular cloud (something called a stellar nursery), consisting of hydrogen collapsed on itself. The collapsing of the cloud resulted in the collision of hydrogen atoms, a process known as __________________. The ...
Planets Worksheet
... Use the section on the planets to answer the following questions. 1. From Earth, when can we see Mercury?_________________ ...
... Use the section on the planets to answer the following questions. 1. From Earth, when can we see Mercury?_________________ ...
Describing the Solar System File
... The Kinetic energy of the dust and gas was converted into heat energy. The cloud started to flatten out into a disc with a hot, dense Protostar at the centre. Dense material in the disc, such as dust, was pulled in closer than the lighter gas. Several small, whirlpool like eddies formed in t ...
... The Kinetic energy of the dust and gas was converted into heat energy. The cloud started to flatten out into a disc with a hot, dense Protostar at the centre. Dense material in the disc, such as dust, was pulled in closer than the lighter gas. Several small, whirlpool like eddies formed in t ...
Document
... Mars , Earth , Venus , and Mercury. Those are the inner planets that are surrounded by the asteroid belt ...
... Mars , Earth , Venus , and Mercury. Those are the inner planets that are surrounded by the asteroid belt ...
Cornell Notes Page
... The four parts of the Earth’s Structure are: o ___inner core___________________ ...
... The four parts of the Earth’s Structure are: o ___inner core___________________ ...
solar system study guide
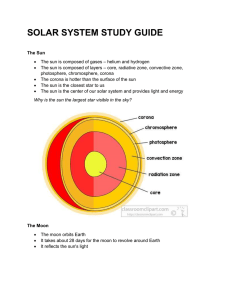
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
Instructor Notes
... The inner solar system consisted of 4 terrestrial (Earth‐like) planets; the outer solar system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
... The inner solar system consisted of 4 terrestrial (Earth‐like) planets; the outer solar system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.