The Solar System
... Solar system: a group of objects in space that move around a central star The SUN ...
... Solar system: a group of objects in space that move around a central star The SUN ...
Chapter 1
... gradation (erosion) • The solar system is believed to have formed from a contracting cloud of gas and dust (a nebula) that flattened into a disc. This protoplanetary disc stage was theoretical until the 1990s, when highresolution images from the Hubble Space Telescope began to reveal such discs in n ...
... gradation (erosion) • The solar system is believed to have formed from a contracting cloud of gas and dust (a nebula) that flattened into a disc. This protoplanetary disc stage was theoretical until the 1990s, when highresolution images from the Hubble Space Telescope began to reveal such discs in n ...
Intro to the Solar System Note 15 Solar System Components: * Sun
... * a planet’s orbit lies in a flat plane (like a sheet of paper) * orbital planes of planets are tilted slightly (most are within 3° of Sun’s equator) ...
... * a planet’s orbit lies in a flat plane (like a sheet of paper) * orbital planes of planets are tilted slightly (most are within 3° of Sun’s equator) ...
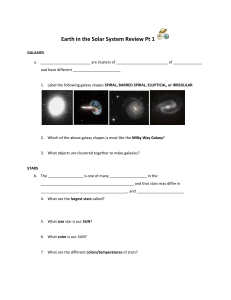
Earth in the Solar System - San Diego Unified School District
... 13. Circle the object(s) above that produce their own light 14. Explain how an eclipse of the Moon proves that the Moon does not produce its own light. ...
... 13. Circle the object(s) above that produce their own light 14. Explain how an eclipse of the Moon proves that the Moon does not produce its own light. ...
Solar System - U
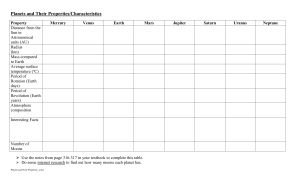
... mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface features, such as rift valleys and volcanoes. The four outer planets, or ...
... mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface features, such as rift valleys and volcanoes. The four outer planets, or ...
Panel 3 Ingles ALTA
... These are mainly made up of hydrogen and helium, like stars. There are four in our solar system: Jupiter and Saturn, which are gassy bodies; and Uranus and Neptune, which are largely made up of ice. All of them have many satellites, as well as ring systems made up of rocks, dust and frozen water. ...
... These are mainly made up of hydrogen and helium, like stars. There are four in our solar system: Jupiter and Saturn, which are gassy bodies; and Uranus and Neptune, which are largely made up of ice. All of them have many satellites, as well as ring systems made up of rocks, dust and frozen water. ...
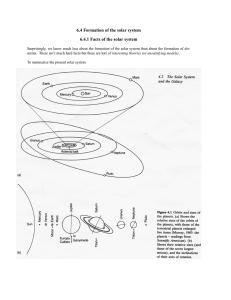
Formation of the solar system
... motion is in one plane and has a common axis. B. Planetary orbits are nearly circular. This plus A. suggest that the solar system has a common origin rather than a random collection of objects captured by the sun. C. The inner (terrestrial) and outer (major) planets are two distinct groups based on ...
... motion is in one plane and has a common axis. B. Planetary orbits are nearly circular. This plus A. suggest that the solar system has a common origin rather than a random collection of objects captured by the sun. C. The inner (terrestrial) and outer (major) planets are two distinct groups based on ...
Quiz # 5
... 3. The most probable process for the formation or acquisition of the planets of the Sun is A) capture of planets from outer space by gravity. B) relatively slow growth of smaller objects by collisions and mutual gravitational attraction. C) the freezing of immense gas clouds by the cold temperature ...
... 3. The most probable process for the formation or acquisition of the planets of the Sun is A) capture of planets from outer space by gravity. B) relatively slow growth of smaller objects by collisions and mutual gravitational attraction. C) the freezing of immense gas clouds by the cold temperature ...
Solar System Study Guide Answer Key
... The ____sun______ is the center of the Solar System. The air surrounding Earth is our __________atmosphere_____. Meteors are objects that ___burn_ up as they enter the Earth’s atmosphere. 5. The ______sun__ is the only ___star______ close enough for us to study. 6. Natural satellites that orbit bodi ...
... The ____sun______ is the center of the Solar System. The air surrounding Earth is our __________atmosphere_____. Meteors are objects that ___burn_ up as they enter the Earth’s atmosphere. 5. The ______sun__ is the only ___star______ close enough for us to study. 6. Natural satellites that orbit bodi ...
NOTES April 21, 2008 Earth Science – 6th Grade Mrs. Elliott
... radiation that may briefly outshine an entire galaxy before fading from view over several weeks or months. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun could emit over its life span.[1] The explosion expels much or all of a star's material[2] at a velocity of up to a ...
... radiation that may briefly outshine an entire galaxy before fading from view over several weeks or months. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun could emit over its life span.[1] The explosion expels much or all of a star's material[2] at a velocity of up to a ...
A Solar System is Born 4/29/11
... • Solar System – composed of the sun (a star) and the planets and other bodies that travel around the sun. ...
... • Solar System – composed of the sun (a star) and the planets and other bodies that travel around the sun. ...
FORMATION OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... get larger by their gravitational pull attracting more matter creating PLANETS accreation ...
... get larger by their gravitational pull attracting more matter creating PLANETS accreation ...
Earth, Sun, and Moon Picture Vocabulary
... that supplies heat and light to Earth; its enormous gravity keeps the solar system in orbit. ...
... that supplies heat and light to Earth; its enormous gravity keeps the solar system in orbit. ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.