Document
... orbit • Has no moon • Almost no atmosphere—high daytime temperatures, low nighttime temperature ...
... orbit • Has no moon • Almost no atmosphere—high daytime temperatures, low nighttime temperature ...
solar system - Teaching Children
... +the closer to the sun the smallest +has the most tenuous atmosphere +you do not have moons ...
... +the closer to the sun the smallest +has the most tenuous atmosphere +you do not have moons ...
Our Solar Neighbourhood
... • Surface of the Sun is about 5500 C, core is about 15 000 000 C • Solar wind is release charged particles that flow from the sun at about 400 km/s (we are protected by it on Earth due to our magnetic field) ...
... • Surface of the Sun is about 5500 C, core is about 15 000 000 C • Solar wind is release charged particles that flow from the sun at about 400 km/s (we are protected by it on Earth due to our magnetic field) ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun and Stars
... 2. Earth’s rotation on its axis takes about_________. It’s revolution around the sun takes _______________. 3. What 2 forces combine to keep the planets in orbit? a) keeps planets from spiraling into space ______________ b) keeps planets revolving around the sun ______________ 4. Is a light-year a u ...
... 2. Earth’s rotation on its axis takes about_________. It’s revolution around the sun takes _______________. 3. What 2 forces combine to keep the planets in orbit? a) keeps planets from spiraling into space ______________ b) keeps planets revolving around the sun ______________ 4. Is a light-year a u ...
We live in a solar system that consists of a star we call the Sun and
... Galaxy A catherine wheel made up from billions of stars which the Sun is one. Meteorite Pieces of rock or metal which strike Earth’s atmosphere. Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Earth blocks the sunlight to the Moon (Lunar Eclipse). Atmosphere A mixt ...
... Galaxy A catherine wheel made up from billions of stars which the Sun is one. Meteorite Pieces of rock or metal which strike Earth’s atmosphere. Eclipse When the Moon blocks the sunlight to the Earth (Solar Eclipse) or when the Earth blocks the sunlight to the Moon (Lunar Eclipse). Atmosphere A mixt ...
Our Sun is a Star:
... Tracing the Magnetic Sun: What section of the sun is this picture showing us? ...
... Tracing the Magnetic Sun: What section of the sun is this picture showing us? ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE Objectives
... Name & describe the three layers of the sun’s interior? (inner to outer) Name & describe the three layers of the sun’s atmosphere? (inner to outer layers) Name and define the four features found on the sun. Name the inner planets, What do the inner planets have in common? Name the outer planets, Wha ...
... Name & describe the three layers of the sun’s interior? (inner to outer) Name & describe the three layers of the sun’s atmosphere? (inner to outer layers) Name and define the four features found on the sun. Name the inner planets, What do the inner planets have in common? Name the outer planets, Wha ...
Topic 2 Booster PP - AstronomyGCSE.co.uk
... All stars are so far that they are just points of light. Many have planets in orbit. How do we know they exist? Astometry – very accurate measurements of the wobble of stars Light curves as they transit their star Doppler shifts due to wobble ...
... All stars are so far that they are just points of light. Many have planets in orbit. How do we know they exist? Astometry – very accurate measurements of the wobble of stars Light curves as they transit their star Doppler shifts due to wobble ...
Document
... planets. Also our solar system has a dwarf planet. All of our planets revolve around our central star, or in other words, a sun. ...
... planets. Also our solar system has a dwarf planet. All of our planets revolve around our central star, or in other words, a sun. ...
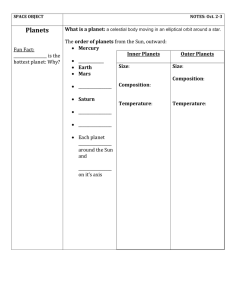
What is a planet
... How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Planets with the LEAST moons: _____________________________ and ______________________________ (0 moons) ...
... How long does it takes our Moon to revolve: ______________ How long does it takes our Moon to rotate: _____________________ Planet with the MOST moons: ________________________(63) Planets with the LEAST moons: _____________________________ and ______________________________ (0 moons) ...
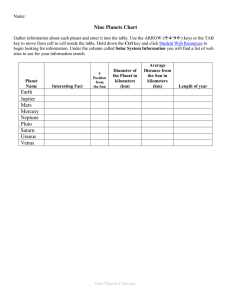
planets - Red Hook Central Schools
... miles would have been vaporized in a 1 mile high wall of fire A 1000ft. high tidal wave would have swept around the world ...
... miles would have been vaporized in a 1 mile high wall of fire A 1000ft. high tidal wave would have swept around the world ...
chapter 13 review
... lunar eclipse visible from Canada every year. Almost an entire hemisphere sees a total eclipse when the Moon enters Earth’s shadow, but only those lucky few in the much smaller Moon’s shadow witness a total solar eclipse. 10. By representing Jupiter’s Great Red Spot as a rectangle, the area would be ...
... lunar eclipse visible from Canada every year. Almost an entire hemisphere sees a total eclipse when the Moon enters Earth’s shadow, but only those lucky few in the much smaller Moon’s shadow witness a total solar eclipse. 10. By representing Jupiter’s Great Red Spot as a rectangle, the area would be ...
the Moon? The Moon has no wind or water to erode the craters
... 9. Why do most of the asteroids in the asteroid belt stay in the asteroid belt? Jupiter’s gravity ...
... 9. Why do most of the asteroids in the asteroid belt stay in the asteroid belt? Jupiter’s gravity ...
AnwerkeyChaper1516
... 12. The orbit of the planets are not perfect circles because they are slight variations in velocity vector created during the formation of the solar system Page# 329 Section 15.2: 1. Mercury 2. Venus 3. A. Earth’s moon ...
... 12. The orbit of the planets are not perfect circles because they are slight variations in velocity vector created during the formation of the solar system Page# 329 Section 15.2: 1. Mercury 2. Venus 3. A. Earth’s moon ...
AIM: What is the Solar System?
... Tail always points away from the sun. Most eccentric orbits. •Asteroids and Meteoroids: found in an orbit between Mars and Jupiter, these rocks can be as big as 1000 Km and as small as a grain of sand. ...
... Tail always points away from the sun. Most eccentric orbits. •Asteroids and Meteoroids: found in an orbit between Mars and Jupiter, these rocks can be as big as 1000 Km and as small as a grain of sand. ...
The Solar System
... The Solar System Contains: • One star (the sun). • Nine planets (well now there’s eight planets and 3 dwarf planets). • 157 moons (at last count) orbiting the planets. • Eight large asteroids. • More than 100 Kuiper belt objects larger than 300 km in diameter. • Tens of thousands of smaller asteroi ...
... The Solar System Contains: • One star (the sun). • Nine planets (well now there’s eight planets and 3 dwarf planets). • 157 moons (at last count) orbiting the planets. • Eight large asteroids. • More than 100 Kuiper belt objects larger than 300 km in diameter. • Tens of thousands of smaller asteroi ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered Earth’s twin due to its size? _____________________________Besides its diameter, what else does it have in common with Earth? _______________________________________ 20. What is the difference ...
... At what location in our galaxy is our solar system?________________________ 19. Which planet is considered Earth’s twin due to its size? _____________________________Besides its diameter, what else does it have in common with Earth? _______________________________________ 20. What is the difference ...
Lecture - Faculty
... The Chaotic Early Solar System • Recent computer models are challenging earlier views that planets formed in an orderly way at their current locations • These models suggest that the jovian planets changed their orbits substantially, and that Uranus and Neptune could have changed places • These cha ...
... The Chaotic Early Solar System • Recent computer models are challenging earlier views that planets formed in an orderly way at their current locations • These models suggest that the jovian planets changed their orbits substantially, and that Uranus and Neptune could have changed places • These cha ...
How the Universe Works: Extreme Planets Name State whether the
... 16. The larger the gas giants got the more _________________ they have. 17. Jupiter and Saturn have over _______ moons each. They formed from the massive amounts of gas and dust that the planets were able to collect because of their gravity. 18. All gas giants have rings. True or false? 19. What is ...
... 16. The larger the gas giants got the more _________________ they have. 17. Jupiter and Saturn have over _______ moons each. They formed from the massive amounts of gas and dust that the planets were able to collect because of their gravity. 18. All gas giants have rings. True or false? 19. What is ...
space facts sheet
... Valles Marineris, is as wide as the United States. Might have had running water at one time. Has ice caps Largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons Jupiter The largest planet has an atmosphere of cold hydrogen gas. It has many moons, so far 17 have been found. It has a giant red spot that is ...
... Valles Marineris, is as wide as the United States. Might have had running water at one time. Has ice caps Largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons Jupiter The largest planet has an atmosphere of cold hydrogen gas. It has many moons, so far 17 have been found. It has a giant red spot that is ...
Grade 9 Academic Science – Space
... measure of the amount of light produced and emitted must be ________________________. In space terminology, the measure _________________________ means the total amount of energy emitted by a star in joules per second (i.e., watts). ...
... measure of the amount of light produced and emitted must be ________________________. In space terminology, the measure _________________________ means the total amount of energy emitted by a star in joules per second (i.e., watts). ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.