Powerpoint Notes on Meteors, Asteroids and Comets
... our atomosphere and burns up, producing a streak of light time lapse photo of meteor shower Meteorite – a meteor so large it does not completely burn up and strikes the surface. ...
... our atomosphere and burns up, producing a streak of light time lapse photo of meteor shower Meteorite – a meteor so large it does not completely burn up and strikes the surface. ...
Our Sun is a Star:
... What are the dark spots on this picture? (Hint: they are not sunspots.) ___ Coronal Holes ___ Plumes ___ Active Regions ...
... What are the dark spots on this picture? (Hint: they are not sunspots.) ___ Coronal Holes ___ Plumes ___ Active Regions ...
Our Solar System
... over from the beginning of the solar system billions of years ago 100,000 asteroids lie in belt between Mars and Jupiter Largest asteroids have been given names ...
... over from the beginning of the solar system billions of years ago 100,000 asteroids lie in belt between Mars and Jupiter Largest asteroids have been given names ...
document
... planetesimals in its vicinity. The asteroid belt objects have their orbits “pumped up” into more and more eccentric orbits. Some were absorbed by Jupiter, and some got ejected from the Solar System. This process reduced the “feeding zone” of Mars. Perturbations also lead to higher velocity collision ...
... planetesimals in its vicinity. The asteroid belt objects have their orbits “pumped up” into more and more eccentric orbits. Some were absorbed by Jupiter, and some got ejected from the Solar System. This process reduced the “feeding zone” of Mars. Perturbations also lead to higher velocity collision ...
11.2-11.3 PPT
... Our solar system was formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. As the Sun burst into existence, the leftover material combined to form eight planets and numerous other planetary bodies: moons, asteroids, and comets. Closest to the Sun are the inner planets (terrestrial planets) and further away are th ...
... Our solar system was formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. As the Sun burst into existence, the leftover material combined to form eight planets and numerous other planetary bodies: moons, asteroids, and comets. Closest to the Sun are the inner planets (terrestrial planets) and further away are th ...
Gravity in the Solar System Quiz
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
Earth Science Chapter One: How Do Earth and Its Moons Create
... 1. What do we know about the shape of the orbit of each planet in our solar system? 2. What causes Earth to have different seasons? 3. What happens in the Southern Hemisphere as the March equinox approaches? 4. What do we know about the temperature and position of the sun in the Northern Hemisphere ...
... 1. What do we know about the shape of the orbit of each planet in our solar system? 2. What causes Earth to have different seasons? 3. What happens in the Southern Hemisphere as the March equinox approaches? 4. What do we know about the temperature and position of the sun in the Northern Hemisphere ...
THE SOLAR SYSTEM - Mercer Island School District
... THE SOLAR SYSTEM • The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that is orbiting around it. • 8 Planets • Dwarf Planets • Moons • Comets • Meteoroids • Asteroids Images and information used in this presentation were taken from Microsoft Encarta Reference Suite. ...
... THE SOLAR SYSTEM • The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that is orbiting around it. • 8 Planets • Dwarf Planets • Moons • Comets • Meteoroids • Asteroids Images and information used in this presentation were taken from Microsoft Encarta Reference Suite. ...
Astronomy Name ______KEY Solar System Objects Quiz Study
... 4. Meteorite rock/metal found on Earth that came from space 5. Asteroid large piece of rock/metal floating in space 6. Comet dirty snowball (ice and dust) orbiting Sun in very elliptical orbit; can be seen for weeks or months 3. Solar System Facts to know: 1. Order of planets from Sun. Mercury, Venu ...
... 4. Meteorite rock/metal found on Earth that came from space 5. Asteroid large piece of rock/metal floating in space 6. Comet dirty snowball (ice and dust) orbiting Sun in very elliptical orbit; can be seen for weeks or months 3. Solar System Facts to know: 1. Order of planets from Sun. Mercury, Venu ...
Astronomy Study Guide axis - A real or imaginary line through the
... debris - Bits and pieces of leftover dust and rocks galaxy - A large collection of stars, dust, and gas, held together by a powerful force and separated from other star systems by an extensive amount of space light-years, n. Distance traveled by light over a period of years; a measure of length used ...
... debris - Bits and pieces of leftover dust and rocks galaxy - A large collection of stars, dust, and gas, held together by a powerful force and separated from other star systems by an extensive amount of space light-years, n. Distance traveled by light over a period of years; a measure of length used ...
Order of the Planets Review WS 1. List the
... 1. List the planets in order from the closest to the farthest from the sun. ...
... 1. List the planets in order from the closest to the farthest from the sun. ...
Astronomy Unit Notes - sciencepowerpoint.com
... Craters can be found on earth, but most craters are eroded away by wind and water. Most meteorites also burn up in our atmosphere. Phases of the Moon ...
... Craters can be found on earth, but most craters are eroded away by wind and water. Most meteorites also burn up in our atmosphere. Phases of the Moon ...
Objects Beyond Neptune
... Neptune and that contains dwarf planets and other small bodies made mostly of ice • Looks like a doughnut-shaped ring just beyond the orbit of Neptune • Short period comets originate in the Kuiper Belt • There may be hundreds of thousands of icy bodies larger than 100 km (62 miles) and an estimated ...
... Neptune and that contains dwarf planets and other small bodies made mostly of ice • Looks like a doughnut-shaped ring just beyond the orbit of Neptune • Short period comets originate in the Kuiper Belt • There may be hundreds of thousands of icy bodies larger than 100 km (62 miles) and an estimated ...
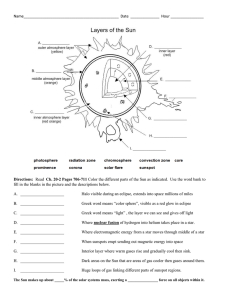
Ch. 20-2 Sun Study Gd. Revised
... 9. The region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is known as the _________________. 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edges surrounding the solar system is the _______ ...
... 9. The region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter is known as the _________________. 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edges surrounding the solar system is the _______ ...
mary - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Small Solar System bodies that orbit the Sun Balls of rock and ice Known as “dirty snowballs” Grow tails or leave trails as they approach the Sun, which becomes illuminated and glows ...
... Small Solar System bodies that orbit the Sun Balls of rock and ice Known as “dirty snowballs” Grow tails or leave trails as they approach the Sun, which becomes illuminated and glows ...
Our Solar System Formation
... with no activity. Scientist believe that in order for the cloud to start becoming active a near by super nova might have exploded and sent a shock wave through the cloud, which triggered it to start collapsing on itself. Large masses in space have a natural spin. As a result of the cloud collapsing ...
... with no activity. Scientist believe that in order for the cloud to start becoming active a near by super nova might have exploded and sent a shock wave through the cloud, which triggered it to start collapsing on itself. Large masses in space have a natural spin. As a result of the cloud collapsing ...
Astronomy Review Name: Date: Name the planets in order from the
... 34. In terms of stars, explain the meaning of E = mc2. When hydrogen is fused into helium, some of the mass within the atoms is lost. This mass is transformed into huge amounts of energy, which the star emits as light, heat and other radiation. 35. What is meant by axial tilt? The angle at which the ...
... 34. In terms of stars, explain the meaning of E = mc2. When hydrogen is fused into helium, some of the mass within the atoms is lost. This mass is transformed into huge amounts of energy, which the star emits as light, heat and other radiation. 35. What is meant by axial tilt? The angle at which the ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.