Chapter 1
... Revolution – to go around in the orbit. Rotation – to spin around an axis. The Moon revolves once in about 29 days. The Moon rotates once in exactly the same time. We see only one side of the Moon. The side we don’t see is called the “dark side”. ...
... Revolution – to go around in the orbit. Rotation – to spin around an axis. The Moon revolves once in about 29 days. The Moon rotates once in exactly the same time. We see only one side of the Moon. The side we don’t see is called the “dark side”. ...
Celestial Motions
... • Stars near the north celestial pole are circumpolar and never set. • We cannot see stars near the south celestial pole. • All other stars (and Sun, Moon, planets) rise in east and set in west. ...
... • Stars near the north celestial pole are circumpolar and never set. • We cannot see stars near the south celestial pole. • All other stars (and Sun, Moon, planets) rise in east and set in west. ...
Hifz schooling scienc summer vacation task 5th
... 6. The Earth is not a star but a _____________________________. 7. A planet is ____________________ object that revolves around ______________________. 8. Each planet moves along a certain path known as its _______________________. 9. Different planets take different times to complete one __________ ...
... 6. The Earth is not a star but a _____________________________. 7. A planet is ____________________ object that revolves around ______________________. 8. Each planet moves along a certain path known as its _______________________. 9. Different planets take different times to complete one __________ ...
How long would the Sun shine? Fuel = Gravitational Energy? Fuel
... • Radiative zone (0.25-0.70 Rsolar): 2 to 8 million K – Energy is carried by radiation (photons) up to near the surface of the Sun – Photons frequently scattered by electrons (random walk) ...
... • Radiative zone (0.25-0.70 Rsolar): 2 to 8 million K – Energy is carried by radiation (photons) up to near the surface of the Sun – Photons frequently scattered by electrons (random walk) ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
... Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but make few UV ...
An extrasolar planetary system with three
... Over the past two years, the search for low-mass extrasolar planets has led to the detection of seven so-called ‘hot Neptunes’ or ‘super-Earths’ around Sun-like stars. These planets have masses 5–20 times larger than the Earth and are mainly found on close-in orbits with periods of 2–15 days. Here w ...
... Over the past two years, the search for low-mass extrasolar planets has led to the detection of seven so-called ‘hot Neptunes’ or ‘super-Earths’ around Sun-like stars. These planets have masses 5–20 times larger than the Earth and are mainly found on close-in orbits with periods of 2–15 days. Here w ...
Elements from Stardust
... the nuclei of slightly heavier elements. • First two Helium nucleus can join wit the berylium nucleus, forming a carbon nucleus. • A Helium nucleus can join with a carbon nucleus ...
... the nuclei of slightly heavier elements. • First two Helium nucleus can join wit the berylium nucleus, forming a carbon nucleus. • A Helium nucleus can join with a carbon nucleus ...
Our Place in Universe
... We should probably be able to tell how far away something is based upon a known geometry. 1,000 kilometers 1,000,000 kilometers 1,000,000,000 kilometers This would be inconvenient, so we will be using scientific notation in many cases. Just move the decimal point to the right (or left) to make the n ...
... We should probably be able to tell how far away something is based upon a known geometry. 1,000 kilometers 1,000,000 kilometers 1,000,000,000 kilometers This would be inconvenient, so we will be using scientific notation in many cases. Just move the decimal point to the right (or left) to make the n ...
Zoom Astronomy - visit our webpage
... 39 known moons, and a dark, barely-visible ring. Its most prominent features are bands across its latitudes and a great red spot (which is a storm). Jupiter is composed mostly of gas. This enormous planet radiates twice as much heat as it absorbs from the Sun. It also has an extremely strong magneti ...
... 39 known moons, and a dark, barely-visible ring. Its most prominent features are bands across its latitudes and a great red spot (which is a storm). Jupiter is composed mostly of gas. This enormous planet radiates twice as much heat as it absorbs from the Sun. It also has an extremely strong magneti ...
a ComparativePlanetology 27
... B. a collision of two larger objects that pulverized the protoplanets leaving behind debris out of which the Earth and moon coalesced. Preferred explanation is A. (The object is called Theia after the mother of Selene, the Greek goddess of the moon. This explains lack of volatiles and iron, while p ...
... B. a collision of two larger objects that pulverized the protoplanets leaving behind debris out of which the Earth and moon coalesced. Preferred explanation is A. (The object is called Theia after the mother of Selene, the Greek goddess of the moon. This explains lack of volatiles and iron, while p ...
Outline - March 16, 2010 Interstellar Medium (ISM) Why should you
... The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
... The energy is gravitational. Half the gravitational energy goes into heating the collapsing clout, the other half escapes as light. The central object is called a “protostar”, and they are very bright! (Because they have very large radii.) ...
Our Place In Space
... Our Place In Space Table of Contents Crossword Puzzle and Clues ........................................................................................................ 1 ...
... Our Place In Space Table of Contents Crossword Puzzle and Clues ........................................................................................................ 1 ...
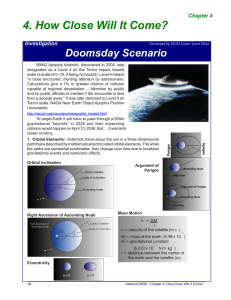
4. How Close Will It Come?
... and by public officials is merited if the encounter is less than a decade away.” It was later demoted to Level 0 on Torino scale. NASA Near Earth Object Apophis Position Uncertainty: http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/apophis/apophis_image3.html ...
... and by public officials is merited if the encounter is less than a decade away.” It was later demoted to Level 0 on Torino scale. NASA Near Earth Object Apophis Position Uncertainty: http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/apophis/apophis_image3.html ...
Oct 2015 - Bays Mountain Park
... measure with the unaided eye from any location on Earth, ranging from 29.38 arc-minutes (0.4897°) to 33.53 arc-minutes (0.5588°) as it orbits our world in an ellipse, that doesn’t tell us its physical size. From its angular size alone, the Moon could just as easily be close and small as it could be ...
... measure with the unaided eye from any location on Earth, ranging from 29.38 arc-minutes (0.4897°) to 33.53 arc-minutes (0.5588°) as it orbits our world in an ellipse, that doesn’t tell us its physical size. From its angular size alone, the Moon could just as easily be close and small as it could be ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... When the hydrogen supply in the core begins to run out, and the star is no longer generating heat by nuclear fusion, the core becomes unstable and contracts. The outer shell of the star, which is still mostly hydrogen, starts to expand. As it expands, it cools and glows red. The star has now reached ...
... When the hydrogen supply in the core begins to run out, and the star is no longer generating heat by nuclear fusion, the core becomes unstable and contracts. The outer shell of the star, which is still mostly hydrogen, starts to expand. As it expands, it cools and glows red. The star has now reached ...
September
... the Dying Grass Moon. Morning Star - Saturn and Mars. Evening Star - Venus, Jupiter and Mercury. ...
... the Dying Grass Moon. Morning Star - Saturn and Mars. Evening Star - Venus, Jupiter and Mercury. ...
Slide 1
... all of the galaxies he had observed were moving back from us, and from each other, at speeds of up to several thousand miles per second. ...
... all of the galaxies he had observed were moving back from us, and from each other, at speeds of up to several thousand miles per second. ...
Ans. - Testlabz.com
... Ans. A football which is placed near us will appear more bigger than a football placed at a distance of 100 m. Q.33. The star Alpha Centauri is at a distance of about 40,000, 000,000,000 km from the Earth. Can you read this distance in kilometers conveniently? Ans. 40,000,000,000,000 = 4 × 1013 km. ...
... Ans. A football which is placed near us will appear more bigger than a football placed at a distance of 100 m. Q.33. The star Alpha Centauri is at a distance of about 40,000, 000,000,000 km from the Earth. Can you read this distance in kilometers conveniently? Ans. 40,000,000,000,000 = 4 × 1013 km. ...
1 - Quia
... A. white dwarf B. main sequence C. giant D. supergiant 4. The color of a star is an indicator of its -. (2 points) A. magnitude B. mass C. size D. surface temperature 5. At what position would Earth be found in the solar system diagram shown? (2 points) A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 ...
... A. white dwarf B. main sequence C. giant D. supergiant 4. The color of a star is an indicator of its -. (2 points) A. magnitude B. mass C. size D. surface temperature 5. At what position would Earth be found in the solar system diagram shown? (2 points) A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 ...
The Sun*s Energy
... Larger its mass, the more atoms it has to keep in equilibrium and therefore the more fuel it burns up. This leads to a shorter life Once the hydrogen supply in the star’s core begins to run out, and the star is no longer generating heat by nuclear fusion, the core becomes unstable and contracts (pul ...
... Larger its mass, the more atoms it has to keep in equilibrium and therefore the more fuel it burns up. This leads to a shorter life Once the hydrogen supply in the star’s core begins to run out, and the star is no longer generating heat by nuclear fusion, the core becomes unstable and contracts (pul ...
Lecture 3 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... Angular separation (distance)--no. of deg., min., sec. between objects or points on sphere. Angular size or diameter--angle an object subtends at observer's ...
... Angular separation (distance)--no. of deg., min., sec. between objects or points on sphere. Angular size or diameter--angle an object subtends at observer's ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.