Document
... amino acids, diacids) and bacterial DNA damages (ELISA protocols) at 4 depths (5, 80, 200, and 1000 m) 3-Irradiation experiments of freshly collected seawater: sunlight exposure of DOM (photoproduction of sugars, amino acids, diacids) and bacteria (photoproduction of bacterial DNA damages) followed ...
... amino acids, diacids) and bacterial DNA damages (ELISA protocols) at 4 depths (5, 80, 200, and 1000 m) 3-Irradiation experiments of freshly collected seawater: sunlight exposure of DOM (photoproduction of sugars, amino acids, diacids) and bacteria (photoproduction of bacterial DNA damages) followed ...
22 CHEMISTRY OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Aims of the course
... Teaching methods: Lectures, tutoring and laboratory exercises and practices. Contents of the course: Interpretation of the fundamental properties of the major classes of organic compounds, a subject divided in the following chapters: Alcohols and thiols Ethers, epoxides and sulfides Introduction to ...
... Teaching methods: Lectures, tutoring and laboratory exercises and practices. Contents of the course: Interpretation of the fundamental properties of the major classes of organic compounds, a subject divided in the following chapters: Alcohols and thiols Ethers, epoxides and sulfides Introduction to ...
103 Lecture Ch21b
... • When product concentration is low, it dissociates from E1 and production is resumed • Feedback control allows products to be formed only when needed ...
... • When product concentration is low, it dissociates from E1 and production is resumed • Feedback control allows products to be formed only when needed ...
0 - Microbiology
... Since the discovery of transamination reactions by Braunstein & Kritzmann (1937) opinion concerning the range and importance of such reactions in biological systems has undergone a cyclic change. The early studies by these two workers indicated that many amino acids were capable of transferring thei ...
... Since the discovery of transamination reactions by Braunstein & Kritzmann (1937) opinion concerning the range and importance of such reactions in biological systems has undergone a cyclic change. The early studies by these two workers indicated that many amino acids were capable of transferring thei ...
4:6 Fermentation
... 4.6 Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis ...
... 4.6 Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis ...
The role of sphingolipid metabolism in cutaneous
... containing ULC-FAs (≥C26) including ω-OH-ULC-FAs (Fig. 2) [12]. Its genetically engineered deficiency in model mice results in a complete loss of all ceramides with ULC-FAs and a lack of extracellular lipid matrix. Mutant mice die shortly after birth from transepidermal water loss and are prone to in ...
... containing ULC-FAs (≥C26) including ω-OH-ULC-FAs (Fig. 2) [12]. Its genetically engineered deficiency in model mice results in a complete loss of all ceramides with ULC-FAs and a lack of extracellular lipid matrix. Mutant mice die shortly after birth from transepidermal water loss and are prone to in ...
No Slide Title
... without notes. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... without notes. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... essentially inactive within 5 minutes in 10 mm H2O2. Inactivation appears to be turnover-dependent (similar TONs are reached from reactions in 1 mm, 5 mm, and 10 mm H2O2), and the ratio of peroxygenase turnovers to heme-degrading turnovers increased with each generation of evolution (halflives in a ...
II. The Steps of Translation
... Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotide ...
... Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotide ...
Intracellular Free Amino Acid Patterns in
... aspartate in the intestinal tissue differ most from that of muscle or plasma. These two compounds make up about 50% of all free AA in the mucosa compared with 13% and 1.8% in skeletal muscle and plasma, respectively. Similar to the pattern for liver (5), we found almost equimolar concentrations of a ...
... aspartate in the intestinal tissue differ most from that of muscle or plasma. These two compounds make up about 50% of all free AA in the mucosa compared with 13% and 1.8% in skeletal muscle and plasma, respectively. Similar to the pattern for liver (5), we found almost equimolar concentrations of a ...
Calvin Cycle
... Plants designated C4 have one cell type in which phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is carboxylated via the enzyme PEP Carboxylase, to yield the 4-C oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is converted to other 4-C intermediates that are transported to cells active in photosynthesis, where CO2 is released by decarboxyl ...
... Plants designated C4 have one cell type in which phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is carboxylated via the enzyme PEP Carboxylase, to yield the 4-C oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is converted to other 4-C intermediates that are transported to cells active in photosynthesis, where CO2 is released by decarboxyl ...
bile acids - The Vespiary
... GC. Also, since bile contains only 1}2% of cholesterol, it is much easier to obtain pure bile acids free from cholesterol. Urinary bile acids are also present mainly in conjugated form, and only a few milligrams per day are excreted. However, in hepatobiliary diseases like primary biliary cirrhosis, ...
... GC. Also, since bile contains only 1}2% of cholesterol, it is much easier to obtain pure bile acids free from cholesterol. Urinary bile acids are also present mainly in conjugated form, and only a few milligrams per day are excreted. However, in hepatobiliary diseases like primary biliary cirrhosis, ...
Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading Key Concepts
... What role does NADH and FADH2 have in connecting the citrate cycle to ATP synthesis? Why is the citrate cycle considered the hub of metabolism? Biochemical Applications of the Citrate Cycle: Fluoroacetate is found in poisonous plants and it is the active ingredient in "compound 1080" which is used b ...
... What role does NADH and FADH2 have in connecting the citrate cycle to ATP synthesis? Why is the citrate cycle considered the hub of metabolism? Biochemical Applications of the Citrate Cycle: Fluoroacetate is found in poisonous plants and it is the active ingredient in "compound 1080" which is used b ...
Amino acid contents and biological value of protein in various
... of animal origin in the rations for monogastric animals is the use of amaranth and its processed products, which meet the demands for substitution of meat-and-bone meals (Herzig, 2001). Grain of the current amaranth species is of high nutritional value. Dry matter content ranges from 90 to 94%, N-su ...
... of animal origin in the rations for monogastric animals is the use of amaranth and its processed products, which meet the demands for substitution of meat-and-bone meals (Herzig, 2001). Grain of the current amaranth species is of high nutritional value. Dry matter content ranges from 90 to 94%, N-su ...
Overview on Reactions with Multi
... high affinity towards the enzyme, and it exhibits high activity even with such low substrate concentrations. Otherwise, too much enzyme would be consumed. Additionally, amino acid oxidases are competitively inhibited by a-keto acids,23,24 which would make a continuously operated enzyme membrane reac ...
... high affinity towards the enzyme, and it exhibits high activity even with such low substrate concentrations. Otherwise, too much enzyme would be consumed. Additionally, amino acid oxidases are competitively inhibited by a-keto acids,23,24 which would make a continuously operated enzyme membrane reac ...
06_Lecture_Presentation - Cornerstone Charter Academy
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
... 6.1 Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide energy for life Energy in sunlight is used in photosynthesis to make glucose from CO2 and H2O with release of O2 Other organisms use the O2 and energy in sugar and release CO2 and H2O Together, these two processes are responsible for the maj ...
products of the dioxygenase reaction ... useful intermediates for natural-product syntheses ...
... P450cam that oxidize polychlorinated benzenes with considerably enhanced activity and coupling efficiency [24••]. These same mutants were also found to oxidize monoterpenes, which are of interest in fine chemical synthesis [25]. The ability to make functional cytochrome P450–NADPH reductase fusion p ...
... P450cam that oxidize polychlorinated benzenes with considerably enhanced activity and coupling efficiency [24••]. These same mutants were also found to oxidize monoterpenes, which are of interest in fine chemical synthesis [25]. The ability to make functional cytochrome P450–NADPH reductase fusion p ...
Krebs cycle - Groby Bio Page
... 2 Idea that it is used to link reactions (1); idea that energy is released as a result of the activity of one enzyme and used by another enzyme (1). ...
... 2 Idea that it is used to link reactions (1); idea that energy is released as a result of the activity of one enzyme and used by another enzyme (1). ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 28: Active Transport
... reaction such as ATP hydrolysis is coupled to transport so that the transported substrate is forced to move against the direction of its electrochemical gradient (Lehninger p.415). Simple uniport occurs in the direction of the electrochemical gradient, because if the transporter is randomly flipping ...
... reaction such as ATP hydrolysis is coupled to transport so that the transported substrate is forced to move against the direction of its electrochemical gradient (Lehninger p.415). Simple uniport occurs in the direction of the electrochemical gradient, because if the transporter is randomly flipping ...
Lesson Overview
... low, glycogen is broken down into glucose, which is then released into the blood, -The glycogen stored in your muscles supplies the energy for muscle contraction. ...
... low, glycogen is broken down into glucose, which is then released into the blood, -The glycogen stored in your muscles supplies the energy for muscle contraction. ...
Metabolism of BCAAs
... is the efficiency of the enzyme reaction and is determined by the Kcat (maximum rate at which an enzyme can function) divided by the Km (the rate of substrate-enzyme interaction) [18]. Enzymatic characteristics of BCATc and BCATm: There are many unique features of BCAT enzymes, one of which is a red ...
... is the efficiency of the enzyme reaction and is determined by the Kcat (maximum rate at which an enzyme can function) divided by the Km (the rate of substrate-enzyme interaction) [18]. Enzymatic characteristics of BCATc and BCATm: There are many unique features of BCAT enzymes, one of which is a red ...
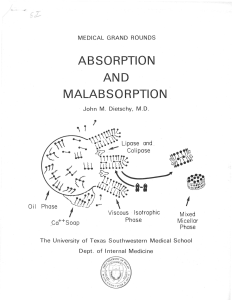
absorption and malabsorption
... The mixed micelles containing the products of lipid digestion (including, probably, the fat soluble vitamins) diffuse up to the region of the intestinal brush border membrane. Here, the free fatty acids, monoglycerides and other components of the mixed micelle diffuse passively through the intestina ...
... The mixed micelles containing the products of lipid digestion (including, probably, the fat soluble vitamins) diffuse up to the region of the intestinal brush border membrane. Here, the free fatty acids, monoglycerides and other components of the mixed micelle diffuse passively through the intestina ...